Abstract
Background
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a known complication after intracranial surgery. Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis has been associated with cognitive dysfunction in animal models.
Methods
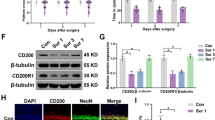
In order to assess hippocampal changes after brain surgery, a frontal lobe corticectomy was performed in ten adult Wistar rats (group 4). Three different control groups (n = 10 each) included no treatment (G1), general anesthesia alone (G2), and craniectomy without dural opening (G3). Twenty-four hours after surgery, half of the animals were killed, and the mRNA levels for IL-6, TNF-α, and brain-derived growth factor (BDNF) in the contralateral hippocampus were assessed by qPCR. Seven days later, the remaining animals underwent anxiety and memory testing. Afterwards, the number of immature neurons in the hippocampal cortex was measured by doublecortin (DCX) staining.
Results
Twenty-four hours after surgery, mRNA levels of IL-6 and TNF-α increased and BDNF decreased in both surgical groups G3 and G4 (p = 0.012). Cognitive tests demonstrated an increase in anxiety levels and memory impairment in surgical groups compared with non-surgical animals. These changes correlated with an inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis evidenced by a decreased number of new neurons (mean ± SD for G1-4: 66.4 ± 24; 57.6 ± 22.2; 21.3 ± 3.78; 5.7 ± 1.05, p < 0.001, non-parametric ANOVA).
Conclusions
Intracranial surgery was demonstrated to induce an inflammatory reaction within the hippocampus that compromised neurogenesis and impaired normal cognitive processing. Corticectomy had a greater effect than craniotomy alone, indicating a central trigger for hippocampal inflammatory changes. POCD after craniotomy may originate from a central inflammatory response resulting from surgical trauma to the brain parenchyma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abildstrom H, Rasmussen LS, Rentowl P, Hanning CD, Rasmussen H, Kristensen PA, Moller JT (2000) Cognitive dysfunction 1–2 years after non-cardiac surgery in the elderly. ISPOCD group. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 44(10):1246–1251
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Medina JH (2014) BDNF and memory processing. Neuropharmacology 76:677–683
Biedler A, Juckenhöfel S, Larsen R, Radtke F, Stotz A, Warmann J, Braune E, Dyttkowitz A, Henning F, Strickmann B, Lauven PM (1999) Postoperative cognition disorders in elderly patients. the results of the “International Study of Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction” ISPOCD 1). Anaesthesist 48(12):884–895
Binder DK, Scharfman HE (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors 22(3):123–131
Bramham CR (2007) Control of synaptic consolidation in the dentate gyrus: mechanisms, functions, and therapeutic implications. Prog Brain Res 163:453–471
Canet J, Raeder J, Rasmussen LS, Enlund M, Kuipers HM, Hanning CD, Jolles J, Korttila K, Siersma VD, Dodds C, Abildstrom H, Sneyd JR, Vila P, Johnson T, Munoz Corsini L, Silverstein JH, Nielsen IK, Moller JT (2003) Cognitive dysfunction after minor surgery in the elderly. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 47(10):1204–1210
Cao X-Z, Ma H, Wang J-K, Liu F, Wu B-Y, Tian A-Y, Wang L-L, Tan W-F (2010) Postoperative cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation in the hippocampus triggered by surgical trauma are exacerbated in aged rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34(8):1426–1432
Caza N, Taha R, Qi Y, Blaise G (2008) The effects of surgery and anesthesia on memory and cognition. Prog Brain Res 169:409–422
Chen K, Wei P, Zheng Q, Zhou J, Li J (2015) Neuroprotective effects of intravenous lidocaine on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients following spine surgery. Med Sci Monit 21:1402–1407
Chida K, Ogasawara K, Suga Y, Saito H, Kobayashi M, Yoshida K, Otawara Y, Ogawa A (2009) Postoperative cortical neural loss associated with cerebral hyperperfusion and cognitive impairment after carotid endarterectomy 123I-iomazenil SPECT study. Stroke. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.515775
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D, Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS, Maze M (2010) Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Ann Neurol 68(3):360–368
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):339–350
DiPatri AJ, Pham M, Muro K (2009) Late effects of neurosurgery. Cancer Treat. Res, 7–22
Failla MD, Juengst SB, Arenth PM, Wagner AK (2015) Preliminary associations between brain-derived neurotrophic factor, memory impairment, functional cognition, and depressive symptoms following severe TBI. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. doi:10.1177/1545968315600525
Griesbach GS, Hovda DA, Molteni R, Gomez-Pinilla F (2002) Alterations in BDNF and synapsin I within the occipital cortex and hippocampus after mild traumatic brain injury in the developing rat: reflections of injury-induced neuroplasticity. J Neurotrauma 19(7):803–814
Hillis AE, Anderson N, Sampath P, Rigamonti D (2000) Cognitive impairments after surgical repair of ruptured and unruptured aneurysms. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(5):608–615
Hong JH, Chiang CS, Campbell IL, Sun JR, Withers HR, McBride WH (1995) Induction of acute phase gene expression by brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 33(3):619–626
Ji R-R, Xu Z-Z, Gao Y-J (2014) Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(7):533–548
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Peel A, Mao XO, Batteur S, Greenberg DA (2003) Directed migration of neuronal precursors into the ischemic cerebral cortex and striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 24(1):171–189
Leal G, Afonso PM, Salazar IL, Duarte CB (2014) Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by BDNF. Brain Res. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.019
Lee WH, Sonntag WE, Mitschelen M, Yan H, Lee YW (2010) Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain. Int J Radiat Biol 86(2):132–144
Lin G-X, Wang T, Chen M-H, Hu Z-H, Ouyang W (2014) Serum high-mobility group box 1 protein correlates with cognitive decline after gastrointestinal surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 58(6):668–674
Lin S-Y, Yin Z-L, Gao J, Zhou L-J, Chen X (2014) Effect of acupuncture-anesthetic composite anesthesia on the incidence of POCD and TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 in elderly patients. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 34(7):795–799
Lunn S, Crawley F, Harrison MJG, Brown MM, Newman SP (1999) Impact of carotid endarterectomy upon cognitive functioning. Cerebrovasc Dis 9(2):74–81
Ma Y, Cheng Q, Wang E, Li L, Zhang X (2015) Inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-α signaling attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats. Mol Med Rep 12(2):3095–3100
Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, Rabbitt P, Jolles J, Larsen K, Hanning CD, Langeron O, Johnson T, Lauven PM, Kristensen PA, Biedler A, Van Beem H, Fraidakis O, Silverstein JH, Beneken JEW, Gravenstein JS (1998) Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly: ISPOCD1 study. Lancet 351(9106):857–861
Mumby DG, Gaskin S, Glenn MJ, Schramek TE, Lehmann H (2002) Hippocampal damage and exploratory preferences in rats: memory for objects, places, and contexts. Learn Mem 9(2):49–57
Oomen CA, Bekinschtein P, Kent BA, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2014) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its role in cognition. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci 5(5):573–587
Otawara Y, Ogasawara K, Ogawa A, Yamadate K (2005) Cognitive function before and after surgery in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysm. Stroke 36(1):142–143
Parihar VK, Acharya MM, Roa DE, Bosch O, Christie L-A, Limoli CL (2014) Defining functional changes in the brain caused by targeted stereotaxic radiosurgery. Transl Cancer Res 3(2):124–137
Peng L, Xu L, Ouyang W (2013) Role of peripheral inflammatory markers in postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD): a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(11):e79624
Radtke FM, Franck M, Herbig TS, Papkalla N, Kleinwaechter R, Kork F, Brockhaus WR, Wernecke K-D, Spies CD (2012) Incidence and risk factors for cognitive dysfunction in patients with severe systemic disease. J Int Med Res 40(2):612–620
Rasmussen LS, Johnson T, Kuipers HM, Kristensen D, Siersma VD, Vila P, Jolles J, Papaioannou A, Abildstrom H, Silverstein JH, Bonal JA, Raeder J, Nielsen IK, Korttila K, Munoz L, Dodds C, Hanning CD, Moller JT (2003) Does anaesthesia cause postoperative cognitive dysfunction? A randomised study of regional versus general anaesthesia in 438 elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 47(3):260–266
Riazi K, Galic MA, Kentner AC, Reid AY, Sharkey KA, Pittman QJ (2015) Microglia-dependent alteration of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus during peripheral inflammation. J Neurosci 35(12):4942–4952
Richardson JTE (1991) Cognitive performance following rupture and repair of intracranial aneurysm. Acta Neurol Scand 83(2):110–122
Schober ME, Block B, Requena DF, Hale MA, Lane RH (2012) Developmental traumatic brain injury decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression late after injury. Metab Brain Dis 27(2):167–173
Seo JS, Park SW, Lee YS, Chung C, Kim YB (2014) Risk factors for delirium after spine surgery in elderly patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 56(1):28–33
Shi C, Yang C, Gao R, Yuan W (2015) Risk factors for delirium after spinal surgery: a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.05.057
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse N, Rasmussen LS (2009) Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 110(3):548–555
Strøm C, Rasmussen LS (2014) Challenges in anaesthesia for elderly. Singapore Dent J 35C:23–29
Vacas S, Degos V, Feng X, Maze M (2013) The neuroinflammatory response of postoperative cognitive decline. Br Med Bull 106:161–178
Vezzani A, Viviani B (2015) Neuromodulatory properties of inflammatory cytokines and their impact on neuronal excitability. Neuropharmacology 96(Pt A):70–82
Walf AA, Frye CA (2007) The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat Protoc 2(2):322–328
Walker AK, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ, Dantzer R (2014) Neuroinflammation and comorbidity of pain and depression. Pharmacol Rev 66(1):80–101
Wang F (2014) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: current developments in mechanism and prevention. Med Sci Monit 20:1908–1912
Wang L, Chang X, She L, Xu D, Huang W, Poo M (2015) Autocrine action of BDNF on dendrite development of adult-born hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 35(22):8384–8393
Weber CF, Friedl H, Hueppe M, Hintereder G, Schmitz-Rixen T, Zwissler B, Meininger D (2009) Impact of general versus local anesthesia on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction following carotid endarterectomy: GALA Study Subgroup Analysis. World J Surg 33(7):1526–1532
Zheng XU, Ma Z, Gu X (2015) Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-α in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients serve as a predictor for the incidence of early postoperative cognitive dysfunction following orthopedic surgery. Exp Ther Med 9(4):1443–1447
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Pablo Argibay, a true master for all of us. This work was supported by a grant from “Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from “Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hem, S., Albite, R., Loresi, M. et al. Pathological changes of the hippocampus and cognitive dysfunction following frontal lobe surgery in a rat model. Acta Neurochir 158, 2163–2171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2938-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2938-6