Abstract
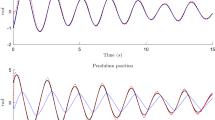
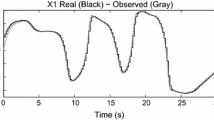
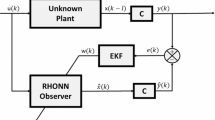
This paper deals with the problem of state observation by means of a continuous-time recurrent neural network for a broad class of MIMO unknown nonlinear systems subject to unknown but bounded disturbances and with an unknown deadzone at each input. With respect to previous works, the main contribution of this study is twofold. On the one hand, the need of a matrix Riccati equation is conveniently avoided; in this way, the design process is considerably simplified. On the other hand, a faster convergence is carried out. Specifically, the exponential convergence of Euclidean norm of the observation error to a bounded zone is guaranteed. Likewise, the weights are shown to be bounded. The main tool to prove these results is Lyapunov-like analysis. A numerical example confirms the feasibility of our proposal.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thau FE (1973) Observing the state of nonlinear dynamical systems. Int J Control 17:471–479
Raghavan S, Hedrick JK (1994) Observer design for a class of nonlinear systems. Int J Control 59:515–528
Rajamani R (1998) Observers for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 43:397–401
Rajamani R, Cho YM (1998) Existence and design of observers for nonlinear systems: relation to distance of unobservability. Int J Control 69:717–731
Pertew A, Marquez HJ, and Zhao Q (2005) Dynamic observer for nonlinear Lipschitz systems. In: The proceedings of the 16th IFAC World Congress
Marino R, Santosuosso GL, Tomei P (2001) Robust adaptive observers for nonlinear systems with bounded disturbances. IEEE Trans Autom Control 46:967–972
Choi YU, Shim H, Son YI, Seo JH (2003) Design of an adaptive observer for a class of nonlinear systems. Int J Control Autom Syst 1:28–34
Kim YH, Lewis F, Abdallah CT (1997) A dynamic recurrent neural network based adaptive observer for a class of nonlinear systems. Automatica 33:1539–1543
Poznyak Alexander S, Wen Yu (2000) Robust asymptotic neuro observer with time delay. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 10:535–560
Norgaard M, Ravn O, Poulsen NK, Hansen LK (2000) Neural networks for modelling and control of dynamic systems. Springer, Berlin
Haykin S (2009) Neural networks and learning machines, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Poznyak AS, Sanchez EN, Yu W (2001) Dynamic neural networks for nonlinear control: identification, state estimation and trajectory tracking. World Scientific, Singapore
Chairez I, García-Peña I, Cabrera A (2009) Dynamic numerical reconstruction of a fungal biofiltration system using differential neural network. J Process Control 19:1103–1110
Chairez I, Poznyak A, Poznyak T, (2004) Model free sliding mode neural observer for ozonation reaction. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on variable structure systems, Villanova i la Geltru′, Spain
Chairez I, Poznyak A, Poznyak T (2006) New sliding mode learning law for dynamic neural network observer. Trans IEEE Circ Syst II 53:1338–1342
Chairez I, Poznyak A, Poznyak T (2009) Stable weights dynamics for a class of differential neural network observer. IET Control Theory Appl 3:1437–1447
Magyar B, Hős C, Stépán G (2010) Influence of control valve delay and dead zone on the stability of a simple hydraulic positioning system. Math Probl Eng 2010:15, Article ID 349489
Yuan X, Yang Y, Wang H, Wang Y (2013) Genetic algorithm-based adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for electronic throttle valve. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1327-1
Bessa WM, Dutra MS, Kreuzer E (2010) Sliding mode control with adaptive fuzzy dead-zone compensation of an electro-hydraulic servo-system. J Intell Rob Syst 58:3–16
Valdiero AC, Ritter CS, Rios CF, Rafikov M (2011) Nonlinear mathematical modeling in pneumatic servo position applications. Math Probl Eng 2011:16, Article ID 472903
Liu L, Liu Y-J, Chen CLP (2013) Adaptive neural network control for a DC motor system with dead-zone. Nonlinear Dyn 72:141–147
Tao G, Kokotovic PV (1996) Adaptive control of systems with actuator and sensor nonlinearities. Wiley, New York
Liu L, Liu Y-J, Li D-J (2012) Intelligence computation based on adaptive tracking design for a class of non-linear discrete-time systems. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1080-5
Li D-J, Tang L (2013) Adaptive control for a class of chemical reactor systems in discrete-time form. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-013-1420-0
Chang C-Y, Chiang T-C (2009) Overhead cranes fuzzy control design with deadzone compensation. Neural Comput Appl 18:749–757
Lewis FL, Campos J, Selmic R (2002) Neuro-fuzzy control of industrial systems with actuator nonlinearities, Siam, Philadelphia
Wang XS, Su CY, Hong H (2004) Robust adaptive control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown dead zone. Automatica 40:407–413
Zhou J, Shen XZ (2007) Robust adaptive control of nonlinear uncertain plants with unknown dead-zone. IET Control Theory Appl 1:25–32
Wang ZH, Zhang Y, Fang H (2008) Neural adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems with unknown dead zone. Neural Comput Appl 17:339–345
Liu YJ, Zhou N (2010) Observer-based adaptive fuzzy-neural control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown dead-zone input. ISA Trans 49:462–469
Poznyak T, Chairez I, Poznyak A (2005) Application of a neural observer to phenols ozonation in water: simulation and kinetic parameters identification. Water Res 39:2611–2620
Chairez I, Poznyak A, Poznyak T (2007) Reconstruction of dynamics of aqueous phenols and their products formation in ozonation using differential neural network observer. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:5855–5866
Poznyak T, García A, Chairez I, Gómez M, Poznyak A (2007) Application of the differential neural network observer to the kinetic parameters identification of the anthracene degradation in contaminated model soil. J Hazard Mater 146:661–667
Chairez I, Fuentes R, Poznyak T, Franco M, Poznyak A (2010) Numerical modeling of the benzene reaction with ozone in gas phase using differential neural networks. Catal Today 151:159–165
Acknowledgments
First author would like to thank the financial support through a postdoctoral fellowship from Mexican National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) under Grant 194775-IPN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Cruz, J.H., Rubio, J.J., Pacheco, J. et al. State estimation in MIMO nonlinear systems subject to unknown deadzones using recurrent neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 25, 693–701 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1533-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1533-5