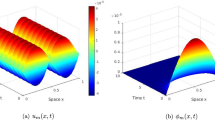
Abstract
This paper presents a numerical algorithm based on a perturbation technique named asymptotic numerical method (ANM) to solve nonlinear problems with hyperelastic constitutive behaviors. The main advantages of this technique compared to Newton–Raphson are: (a) a large reduction of the number of tangent matrix decompositions; (b) in presence of instabilities or limit points no special treatment such as arc-length algorithms is necessary. The ANM uses high order series approximation with auto-adaptive step length and without need of any iteration. Introduction of this expansion into the set of nonlinear equations results into a sequence of linear problems with the same linear operator. The present work aims at providing algorithms for applying the ANM to the special case of compressible and incompressible hyperelastic materials. The efficiency and accuracy of the method are examined by comparing this algorithm with Newton–Raphson method for problems involving hyperelastic structures with large strains and instabilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABAQUS TM (2008) Version 6.8, Hibbit, Karlsson and Sorensen Inc
Abichou H, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M (2002) Asymptotic numerical method for problems coupling several nonlinearities. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191: 5795–5810
Aggoune W, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M (2004) High-order prediction–correction algorithms for unilateral contact problems. J Comput Appl Math 168: 1–9
Aggoune W, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M (2006) Asymptotic numerical method for unilateral contact. Int J Numer Method Eng 68: 605–631
Assidi M, Zahrouni H, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (2009) Regularization and perturbation technique to solve plasticity problems. Int J Mater Form 2: 1–14
Azrar L, Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1993) An asymptotic numerical method to compute the post-buckling behaviour of elastic plates and shells. Int J Numer Method Eng 36: 1251–1277
Baker G, Graves-Morris P (1981) Padé Approximants, vol. 13. In: Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications
Balzani D, Neff P, Schröder J, Holzapfel G (2006) A polyconvex framework for soft biological tissues: adjustment to experimental data. Int J Solids Struct 43: 6052–6070
Boutyour E, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M, Boudi M (2004) Asymptotic numerical method for buckling analysis of shell structures with large rotations. J Comput Appl Math 168: 77–85
Boutyour E, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M, Boudi M (2004) Bifurcation points and bifurcated branches by an asymptotic numerical method and Padé approximants. Int J Numer Methods Eng 60: 1987–2012
Charpentier I, Potier-Ferry M (2008) Automatic differentiation of the asymptotic numerical method: the diamant approach. C R Méca 336: 336–340
Cochelin B (1994) A path following technique via an asymptotic numerical method. Comput Struct 53: 1181–1192
Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1994) The asymptotic-numerical method: an efficient perturbation technique for non-linear structural mechanics. Rev Eur Eléments Finis 3: 281–297
Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1994) Asymptotic numerical methods and Padé approximants for non linear elastic structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37: 1187–1213
Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (2007) Méthode asymptotique numérique. Hermès Science Publications, Paris
Criscione J, Sacks M, Hunter W (2003) Experimentally tractable, pseudo-elastic constitutive caw for biomembranes: I. Theory. J Biomech Eng 125: 94–99
Crisfield M (1991) Non-linear finite element analysis of solids and structures. Wiley, Chichester
Elhage-Hussein A, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1998) An asymptotic numerical algorithm for frictionless contact problems. Rev Eur Eléments Finis 7: 119–130
Elhage-Hussein A, Potier-Ferry M, Damil N (2000) A numerical continuation method based on Padé approximants. Int J Solids Struct 37: 6981–7001
Eriksson A (1991) Derivatives of tangential stiffness matrices for equilibrium path descriptions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 32: 1093–1113
Frakley P, Payne A (1978) Theory and practice of enginnering with rubber. Applied Science Publishers, London
Galliet I (2000) Une version parallele des méthodes asymptotiques numériques: application a des structures complexes base d’lastomres. Ph.D. thesis, Universit de Marseille II, Marseille, France
Gent A (1974) Rubber and rubber elasticity; a review. J Polym Sci Polym Symp 48: 1–17
Gent A (1996) A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 69: 59–61
Holzapfel G (2000) Nonlinear solid mechanics : a continuum approach for engineering. Wiley, London
Holzapfel G, Gasser T (2000) A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J Elast 61: 1–48
Humphrey J (2002) Cardiovascular solid mechanics: cells, tissues and organs. Springer, New York
Kouhia R (1999) Techniques for the analysis of non-linear systems with applications to solids and structural mechanics. Ph.D. thesis, In the series ’Acta Polytechnica Scandinavia’, Espoo, Finland
Lahmam H, Cadou J, Zahrouni H, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (2002) High-order predictor–corrector algorithms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 55: 685–704
Marckmann G, Verron E (2006) Comparison of hyperelastic models for rubber-like materials. Rubber Chem Technol 79: 835–858
Miehe C (2003) Computational micro-to-macro transitions for discretized micro-structures of heterogeneous materials at finite strains based on the minimization of averaged incremental energy. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192: 559–591
Mooney M (1940) A theory of large elastic deformations. J Appl Mech 11: 582–592
Mullins L, Thomas A (1963) The chemistery and physics of rubber-like substances. In: Bateman L (ed) Maclaren and Sons, London
Najah A, Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1998) Effect of thermal residual stress and fiber packing on deformation of metal-matrix composites. Arch Comput Methods Eng 5: 31–50
Nezamabadi S, Yvonnet J, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M (2009) A multilevel computational strategy for microscopic and macroscopic instabilities. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198: 2099–2110
Nezamabadi S, Zahrouni H, Yvonnet J, Potier-Ferry M (2010) A multiscale finite element approach for buckling analysis of elastoplastic long fiber composites. Int J Multiscale Comput Eng 3: 287–301
Nielsen P, Hunter P, Smaill B (1991) Biaxial testing of membrane biomaterials: testing equipment and procedures. J Biomech Eng 113: 295–300
Niroomandi S, Alfaro I, Cueto E, Chinesta F (2009) Model order reduction for hyperelastic materials. Int J Numer Methods Eng 81: 1180–1206
Oden J (1972) Finite elements of non-linear continua. McGraw-Hill, New York
Oden J, Kikuchi N (1982) Finite element methods for constrained problems in elasticity. Int J Numer Methods Eng 18: 701–725
Ogden R (1972) Large deformation isotropic elastic—on the correlation of theory and experiment for incompressible rubberlike solids. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society A, vol 326, pp 565–584
Ogden R (1982) Elastic deformation of rubber-like solids. In: Hopkins HG, Sewell MJ (eds) Mechanics of solids, The Rondey Hill 60th Anniversary Volume. Pergamon, Oxford
Ogden R (1984) Non-linear elastic deformations. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Potier-Ferry M, Damil N, Braikat B, Descamps J, Cadou J, Cao H, Elhage Hussein A (1997) Traitement des fortes non linéarités par la méthode asymptotique numérique. C R Acad Sci Ser IIB 324: 171–177
Riks E (1984) Some computational aspects of the stability analysis of nonlinear structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 47: 219–259
Rivlin R (1948) Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. IV. Further developments of the general theory. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A 241: 379–397
Sacks M (2003) Incorporation of experimentally-derived fiber orientation into a structural constitutive model for planar collagenous tissues. J Biomech Eng 125: 280–287
Schröder J, Neff P, Balzani D (2005) A variational approach for materially stable anisotropic hyperelasticity. Int J Solids Struct 42: 4352–4371
Treloar L (1975) The physics of rubber elasticity, 3rd edn. Oxford university press, Oxford
Valanis K, Landel R (1967) The strain-energy function of a hyperelastic material in terms of the extension ratios. J Appl Phys 38: 2997–3002
Vannucci P, Cochelin B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (1998) An asymptotic-numerical method to compute bifurcated branches. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41: 1365–1389
Yvonnet J, Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M (2007) A model reduction method for the post-buckling analysis of cellular microstructures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 265–280
Zahrouni H, Aggoune W, Brunelot J, Potier-Ferry M (2004) Asymptotic numerical method for strong nonlinearities. Rev Eur Eléments Finis 118: 13–97
Zahrouni H, Braikat B, Damil N, Potier-Ferry M (2005) Solving plasticity problems by a perturbation technique. In: Proceedings in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, vol 5, pp 455–456
Zahrouni H, Cochelin B, Potier-Ferry M (1999) Computing finite rotations of shells by an asymptotic numerical method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 175: 71–85
Zahrouni H, Potier-Ferry M, Elasmar H, Damil N (1998) Asymptotic numerical method for nonlinear constitutive laws. Rev Eur Eléments Finis 7: 841–869
Zienkiewicz O, Taylor R (2000) Finite element method, 5th edn. Volume 1—The Basis. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Zulliger M, Fridez P, Hayashi K, Stergiopulos N (2004) A strain energy function for arteries accounting for wall composition and structure. J Biomech 37: 989–1000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nezamabadi, S., Zahrouni, H. & Yvonnet, J. Solving hyperelastic material problems by asymptotic numerical method. Comput Mech 47, 77–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0531-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-010-0531-z