Abstract
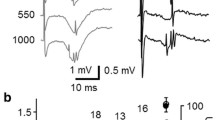
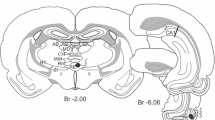
To better understand information transfer along the hippocampal pathways and its plasticity, here we studied the antidromic responses of the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA3 to activation of the mossy fibers and Schaffer collaterals, respectively, in hippocampal slices from naïve and epileptic rats. We applied trains of 600 electrical stimuli at functionally meaningful frequencies (θ, β/γ and γ). The responses of the DG to θ frequency trains underwent rapid potentiation that lasted about 400 stimuli, after which they progressively returned to control value. At β/γ and γ frequencies, however, the initial potentiation was followed by a strong frequency-dependent depression within the first 50 stimuli. In kindled animals, the initial potentiation was stronger than in control preparations and the resonant phase at θ frequency lasted longer. In contrast, CA3 responses were exponentially depressed at all frequencies, but depression was significantly less intense at θ frequency in epileptic preparations. Failure of fibers to fire action potentials could account for some of the aforementioned characteristics, but waveforms of the intracellular action potentials also changed as the field responses did, i.e., half-duration and time-to-peak increased in both structures along the stimulation trains. Noteworthy, block of glutamate and GABA ionotropic receptors prevented resonance and reduced the depression of antidromic responses to β/γ and γ stimulation recorded in the DG, but not in CA3. We show that the different behavior in the information transfer along these pathways depends on the frequency at which action potentials are generated, excitability history and anatomical features, including myelination and tortuosity. In addition, the mossy fibers are endowed with ionotropic receptors and terminal active properties conferring them their sui generis non-passive antidromic responses.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akam T, Kullmann DM (2010) Oscillations and filtering networks support flexible routing of information. Neuron 67:308–320
Akam T, Oren I, Mantoan L, Ferenczi E, Kullmann DM (2012) Oscillatory dynamics in the hippocampus support dentate gyrus-CA3 coupling. Nat Neurosci 15:763–768
Alle H, Roth A, Geiger JR (2009) Energy-efficient action potentials in hippocampal mossy fibers. Science 325:1405–1408
Bähner F, Weiss EK, Birke G, Maier N, Schmitz D, Rudolph U, Frotscher M, Traub RD, Both M, Draguhn A (2011) Cellular correlate of assembly formation in oscillating hippocampal networks in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:607–616
Bean BP (2007) The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:451–465
Berke JD, Hetrick V, Breck J, Greene RW (2008) Transient 23–30 Hz oscillations in mouse hippocampus during exploration of novel environments. Hippocampus 18:519–529
Boulton CL, von Haebler D, Heinemann U (1992) Tracing of axonal connections by rhodamine–dextran-amine in the rat hippocampal–entorhinal cortex slice preparation. Hippocampus 2:99–106
Bower MR, Buckmaster PS (2008) Changes in granule cell firing rates precede locally recorded spontaneous seizures by minutes in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurophysiol 99:2431–2442
Bucher D, Goaillard JM (2011) Beyond faithful conduction: short-term dynamics, neuromodulation, and long-term regulation of spike propagation in the axon. Prog Neurobiol 94:307–346
Bukalo O, Campanac E, Hoffman DA, Fields RD (2013) Synaptic plasticity by antidromic firing during hippocampal network oscillations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5175–5180
Claiborne BJ, Amaral DG, Cowan WM (1986) A light and electron microscopic analysis of the MFs of the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 246:435–458
Dugladze T, Schmitz D, Whittington MA, Vida I, Gloveli T (2012) Segregation of axonal and somatic activity during fast network oscillations. Science 336:1458–1461
Engel D, Jonas P (2005) Presynaptic action potential amplification by voltage-gated Na+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons. Neuron 45:405–417
Geiger JR, Jonas P (2000) Dynamic control of presynaptic Ca(2+) inflow by fast-inactivating K(+) channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons. Neuron 28:927–939
Gutiérrez R (2000) Seizures induce simultaneous GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission in the dentate gyrus—CA3 system. J Neurophysiol 84:3088–3090
Hamzei-Sichani F, Kamasawa N, Janssen WGM, Yasamura T, Davidson KGV, Hof PR, Wearne SL, Stewart MG, Young SR, Whittington MA, Rash JE, Traub RD (2007) Gap junctions on hippocampal mossy fiber axons demonstrated by thin-section electron microscopy and freeze-fracture replica immunogold labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12548–12553
Henze DA, Wittner L, Buzsáki G (2002) Single granule cells reliably discharge targets in the hippocampal CA3 network in vivo. Nat Neurosci 5:790–795
Ishizuka N, Weber J, Amaral DG (1990) Organization of intrahippocampal projections originating from CA3 pyramidal cells in the rat. J Comp Neurol 295:580–623
Jaffe DB, Gutiérrez R (2007) Mossy fiber synaptic transmission: communication from the dentate gyrus to area CA3. Prog Brain Res 163:109–805
Jung MW, McNaughton BL (1993) Spatial selectivity of unit activity in the hippocampal granular layer. Hippocampus 3:165–182
Kim E, Owen B, Holmes WR, Grover LM (2012) Decreased afferent excitability contributes to synaptic depression during high frequency stimulation in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurophysiol 108:1965–1976
Lega BC, Jacobs J, Kahana M (2012) Human hippocampal theta oscillations and the formation of episodic memories. Hippocampus 22:748–761
Liotta A, Rösner J, Huchzermeyer C, Wojtowicz A, Kann O, Schmitz D, Heinemann U, Kovács R (2012) Energy demand of synaptic transmission at the hippocampal Schaffer-collateral synapse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:2076–2083
Manjarrez E, Rojas-Piloni G, Méndez I, Flores A (2003) Stochastic resonance within the somatosensory system: effects of noise on evoked field potentials elicited by tactile stimuli. J Neurosci 23:1997–2001
Meeks JP, Mennerick S (2007) Action potential initiation and propagation in CA3 pyramidal axons. J Neurophysiol 97:3460–3472
Meier S, Bräuer AU, Heimrich B, Nitsch R, Savaskan NE (2004) Myelination in the hippocampus during development and following lesion. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:1082–1094
Neishabouri A, Faisal AA (2014) Axonal noise as a source of synaptic variability. PLoS Comput Biol 10:e1003615
Pietersen AN, Patel N, Jefferys JGR, Vreugdenhil M (2009) Comparison between spontaneous and kainate-induced gamma oscillations in the mouse hippocampus in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 2145–2156
Roopun AK, Middleton SJ, Cunningham MO, LeBeau FE, Bibbig A, Whittington MA, Traub RD (2006) A beta2-frequency (20–30 Hz) oscillation in nonsynaptic networks of somatosensory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15646–15650
Rosenbaum R, Zimnikc A, Zheng F, Turner RS, Alzheimer C, Doiron B, Rubina JE (2014) Axonal and synaptic failure suppress the transfer of firing rate oscillations, synchrony and information during high frequency deep brain stimulation. Neurobiol Dis 62:86–99
Ruiz AJ, Kullmann DM (2013) Ionotropic receptors at hippocampal mossy fibers: roles in axonal excitability, synaptic transmission, and plasticity. Front Neural Circuits 6:112
Sasaki T, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y (2011) Action-potential modulation during axonal conduction. Science 331:599–601
Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J (2008) Action potential initiation and propagation in hippocampal mossy fibre axons. J Physiol 586(7):1849–1857
Schmitz D, Schuchmann S, Fisahn A, Draguhn A, Buhl EH, Petrasch-Parwez RE, Dermietzel R, Heinemann U, Traub RD (2001) Axo-axonal coupling: a novel mechanism for ultrafast neuronal communication. Neuron 31:831–840
Shepherd MG, Raastad M, Andersen P (2002) General and variable features of varicosity spacing along unmyelinated axons in the hippocampus and cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6340–6345
Shimono K, Brucher F, Granger R, Lynch G, Taketani M (2000) Origins and distribution of cholinergically induced β rhythms in hippocampal slices. J Neurosci 20:8462–8473
Stacey WC, Krieger A, Litt B (2011) Network recruitment to coherent oscillations in a hippocampal computer model. J Neurophysiol 105:1464–1481
Stepan J, Dine J, Fenz T, Polta SA, vonWolff G, Wotjak CT, Eder M (2012) Entorhinal theta-frequency input to the dentate gyrus trisynaptically evokes hippocampal CA1 LTP. Front Neural Circuits 6:Art. 64
Traub RD, Schmitz D, Maier N, Whittington MA, Draguhn A (2012) Axonal properties determine somatic firing in a model of in vitro CA1 hippocampal sharp wave/ripples and persistent gamma oscillations. Eur J Neurosci 36:2650–2660
Treviño M, Vivar C, Gutiérrez R (2007) β/γ Oscillatory activity in the CA3 hippocampal area is depressed by aberrant GABAergic transmission from the dentate gyrus after seizures. J Neurosci 27:251–259
Treviño M, Vivar C, Gutiérrez R (2011) Excitation-inhibition balance in the CA3 network—neuronal specificity and activity-dependent plasticity. Eur J Neurosci 33:1771–1785
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT), México (Grant numbers 45754, I0110/193/10 FON.INST.-29-10 to RG). LMF, JQB and JT contributed equally to this work. LMF, JQB and FO received a scholarship for postgraduate training by CONACYT. EM acknowledges support from “Cátedra Marcos Moshinsky” and CONACYT grant #229866. We thank Dr. G. Gómez-Lira for the preparation of the histological material and Dr. Liset Menéndez de la Prida for insightful discussions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, L.M., Beltrán, J.Q., Tapia, J.A. et al. Differential frequency-dependent antidromic resonance of the Schaffer collaterals and mossy fibers. Brain Struct Funct 221, 1793–1807 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1003-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1003-1