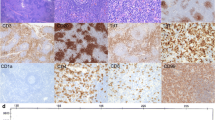
Abstract
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) is a relatively rare peripheral T cell lymphoma derived from follicular T helper cells. AITL has a varied presentation, both clinically and morphologically. AITL can pose a diagnostic challenge as it may be difficult to identify and characterize the neoplastic cells among the polymorphous infiltrates composed of polyclonal B immunoblasts and plasma cells. In AITL, the reactive B cell and plasma cell proliferation is secondary to dysregulated secretion of cytokines such as interleukin-6 by the neoplastic follicular T helper cells. SPBIP is a condition of unknown etiopathogenesis characterized by systemic involvement by polyclonal B immunoblasts and plasma cells. We report two cases of AITL, which are presented with atypical findings making it difficult to diagnose. The cases had features similar to SPBIP. Our cases highlight the importance of screening cases of polyclonal plasmacytosis and SPBIP like cases for underlying AITL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attygalle AD, Al Jehani R, Diss TC et al (2002) Neoplastic T-cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma express CD10. Blood 99:627–633
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (2008) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC press, Lyon
Dunleavy K, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES (2007) Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: pathobiological insights and clinical implications. Curr Opin Hematol 14:348–353
Lachenal F, Berger F, Ghesquieres H et al (2007) Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Clinical and laboratory features at diagnosis in 77 patients. Medicine 86:282–292
Frizzera G, Moran EM, Rappaport H (1974) Angio-immunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinaemia. Lancet 1(7866):1070–1073
Dogan A, Attygalle AD, Kyriakou C (2003) Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Br J Hematol 121:681–691
Warnke RA, Jones D, Hsi ED (2007) Morphologic and immunophenotypic variants of nodal T-cell lymphomas and T-cell lymphoma mimics. Am J Clin Pathol 127:511–527
Attygalle AD, Chuang SS, Diss TC et al (2007) Distinguishing angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma from peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified, using morphology, immunophenotype and molecular genetics. Histopathology 50:498–508
Gaulard P, de Leval L (2011) Follicular helper T cells: implications in neoplastic hematopathology. Semin Diagn Pathol 28:202–213
O’Connor NT, Crick JA, Wainscoat JS et al (1986) Evidence for monoclonal T-lymphocyte proliferation in angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy. J Clin Pathol 39:1229–1232
Lipford EH, Smith HR, Pittaluga S et al (1987) Clonality of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy and implications for its evolution to malignant lymphoma. J Clin Invest 79:637–642
Feller AC, Griesser H, Schilling CV et al (1988) Clonal gene rearrangement patterns correlate with immunophenotype and clinical parameters in patients with angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy. Am J Pathol 133:549–556
Baker AM, Davis DW, Berg KK (2001) Polyclonal systemic immunoblast proliferation: an unusual hematologic entity presenting as a medical examiner case. J Forensic Sci 46(1):156–159
Peterson LC, Kueck B, Arthur DC et al (1988) Systemic polyclonal immunoblastic proliferations. Cancer 61:1350–1358
Poje EJ, Soori GS, Weisenburger DD (1992) Systemic polyclonal B-immunoblastic proliferation with marked peripheral blood and bone marrow plasmacytosis. Am J Clin Pathol 98:222–226
Peterson L, Marcerelli A, Arthur D et al (1998) Systemic polyclonal immunoblastic proliferation: a distinct atypical lymphoproliferative disorder. Mod Pathol 11:138A
McGrath MS (1991) EBV negative polyclonal lymphoma: identification of a new HIV-associated disease process. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 4(4):408–415
Chang KL, Chen YY, Shibata D et al (1992) Description of an in situ hybridization methodology for detection of Epstein–Barr virus RNA in paraffin-embedded tissues with a survey of normal and neoplastic tissues. Diagn Mol Pathol 1:246–255
Van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M et al (2003) Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 17(12):2257–2317
Chen W, Kesler MV, Karandikar NJ et al (2006) Flow cytometric features of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 70B:142–148
Cook J, Craig F, Swerdlow S (2003) Benign CD10-positive T cells in reactive lymphoid proliferations and B-cell lymphomas. Mod Pathol 16(9):879–885
Yu H, Shahsafaei A, Dorfman D (2009) Germinal-center T-helper cell markers PD-1 and CXCL13 are both expressed by neoplastic cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 131:33–41
Grogg K, Attygale A, Macon W et al (2006) Expression of CXCL13, a chemokine highly upregulated in germinal center T-helper cells, distinguishes angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma from peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Mod Pathol 19:1101–1107
Grogg K, Morice WG, Macon WR (2007) Spectrum of bone marrow findings in patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Br J Hematol 137(5):416–422
Koduri PR, Naides SJ (1996) Transient blood plasmacytosis in parvovirus B19 infection: a report of two cases. Ann Hematol 72:49–51
Barnett EV, Stone G, Swisher SN et al (1963) Serum sickness and plasmacytosis: a clinical, immunologic and hematologic analysis. Am J Med 35:113–122
Komiya I, Kuriya S (1991) Perpheral blood plasmacytosis in a patient with infectious mononucleosis-like illness. Eur J Hematol 46:61–62
Kothol RC, Hamilton HE (1981) Azathioprine-induced plasmacytosis. JAMA 246:2193
Gorden L, Smith C, Graber SE (1991) Case report: marked plasmacytosis and immunoglobulin abnormalities following infusion of streptokinase. Am J Med Sci 301:186–189
Moake JL, Ladry PR, Oren ME et al (1974) Transient peripheral plasmacytosis. Am J Clin Pathol 62:8–15
Barker BE, Farnes P, LaMarche PH (1966) Peripheral blood plasmacytosis following systemic exposure to Phytolacca americana (pokeweed). Pediatrics 38:490–493
Gawoski J, Ooi W (2003) Dengue fever mimicking plasma cell leukemia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:1026–1027
Kojimaa M, Murayamab K, Igarashib T et al (2007) Bone marrow plasmacytosis in idiopathic plasmacytic lymphadenopathy with polyclonal hyperimmunoglobulinemia: a report of four cases. Pathol Res Pract 203(11):789–794
Kass L, Votaw ML (1975) Eosinophilia and plasmacytosis of the bone marrow in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol 64(2):248–250
Lee J, Chang J, Cho Y et al (2005) A case of reactive plasmacytosis mimicking multiple myeloma in a patient with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J Korean Med Sci 20:506–508
Ohno H, Tanaka H, Sakai H et al (2005) Polyclonal proliferation of plasma cells associated with marked hypergammaglobulinemia in an elderly patient. Int J Hematol 81:62–65
Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1993) Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol 54:1–78
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papadi, B., Polski, J.M., Clarkson, D.R. et al. Atypical angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas masquerading as systemic polyclonal B-immunoblastic proliferation. Virchows Arch 461, 323–331 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1280-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-012-1280-5