Abstract
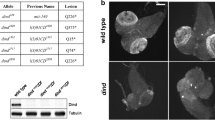
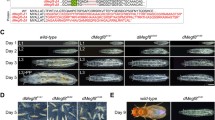
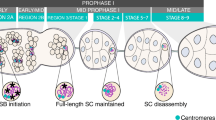
The swallow gene of Drosophila is required for the localization of two messenger RNAs, bicoid and hu-li tai shao, to the anterior pole of oocytes during the later stages of oogenesis. In addition, swallow appears to play a role in early embryogenesis, as swallow mutant embryos have defects in early nuclear cleavage and migration. In an effort to identify regions of the Swallow protein that are essential for function, we have initiated a molecular characterization of seven existing alleles of swallow. All seven alleles have been sequenced, and comparison to wild-type swallow indicates that the seven alleles include single amino acid substitutions that identify critical residues, as well as lesions that result in truncated proteins. Western blots using affinity-purified antibodies agree well with the DNA sequence data, and identify a probable null protein. In order to determine the extent to which each allele affects swallow function, females homozygous or hemizygous for each allele were tested for the range and abundance of (1) RNA localization defects, and (2) embryonic cuticular defects. Swallow alleles can be grouped into two categories: those that retain partial function, and those indistinguishable from the putative null allele. Some swallow mutant alleles partially rescue the dominant female sterility of mutations in the atypical 67C α-tubulin gene, supporting other studies that suggest a link between RNA localization and the microtubule cytoskeleton.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arn EA, Cha BJ, Theurkauf WE, Macdonald PM (2003) Recognition of a bicoid mRNA localization signal by a protein complex containing swallow, Nod, and RNA binding proteins. Dev Cell 4:41–51
Berleth T, Burri M, Thoma G, Bopp D, Richstein S, Frigerio G, Noll M, Nüsslein-Volhard C (1988) The role of localization of bicoid RNA in organizing the anterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J 7:1749–1756
Ding D, Parkhurst SM, Lipshitz HD (1993) Different genetic requirements for anterior RNA localization revealed by the distribution of Adducin-like transcripts during Drosophila oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2512–2516
Frohnhöfer H, Nüsslein-Volhard C (1987) Maternal genes required for the anterior localization of bicoid activity in the embryo of Drosophila. Genes Dev 1:880–890
Gans M, Audit C, Masson M (1975) Isolation and characterization of sex-linked female-sterile mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 81:683–704
Johnstone O, Lasko P (2001) Translational regulation and RNA localization in Drosophila oocytes and embryos. Ann Rev Genet 35:365–406
Matthews KA, Rees D, Kaufman TC (1993) A functionally specialized alpha-tubulin is required for oocyte meiosis and cleavage mitoses in Drosophila. Development 117:977–991
Matthies HJG, Messina LG, Namba R, Greer KJ, Walker MY, Hawley RS (1999) Mutations in the alpha-tubulin 67c gene specifically impair achiasmate segregation in Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol 147:1137–1144
Meng J, Stephenson EC (2002) Oocyte and embryonic cytoskeletal defects caused by mutations in the Drosophila swallow gene. Dev Genes Evol 212:239–247
Mische S, Mooseker M, Morrow J (1987) Erythrocyte adducin: a calmodulin-regulated actin-binding protein that stimulates spectrin-actin binding. J Cell Biol 105:2837–2845
Olmsted JB (1981) Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotised paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem 256:11955–11957
Pokrywka NJ, Stephenson EC (1991) Microtubules mediate the localization of bicoid RNA during Drosophila oogenesis. Development 113:55–66
Pokrywka NJ, Fishbein L, Frederick J (2000) New phenotypes associated with the swallow gene of Drosophila: evidence for a general role in oocyte cytoskeletal organization. Dev Genes Evol 210:426–435
Schnorrer F, Bohmann K, Nusslein-Volhard C (2000) The molecular motor dynein is involved in targeting swallow and bicoid RNA to the anterior pole of Drosophila oocytes. Nat Cell Biol 2:185–190
Schnorrer F, Luschnig S, Koch I, Nusslein-Volhard C (2002) Gamma-tubulin 37C and gamma-tubulin ring complex protein 75 are essential for bicoid RNA localization during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev Cell 3:685–696
Zaccai M, Lipshitz HD (1996) Role of Adducin-like (hu-li tai shao) mRNA and protein localization in regulating cytoskeletal structure and function during Drosophila oogenesis and early embryogenesis. Dev Genet 19:249–257
Acknowledgements
We thank the Iowa State Sequencing Facility for performing DNA sequencing of alleles TG31, TN62, and VA11. This work was supported in part by a National Science Foundation grant (IBN-9630705) to E.S. and by a National Institute of Health grant (R15 GM057608–01) to N.J.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by C. Desplan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pokrywka, N.J., Meng, L., Debiec, K. et al. Identification of hypomorphic and null alleles of swallow via molecular and phenotypic analyses. Dev Genes Evol 214, 185–192 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0394-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0394-4