Abstract
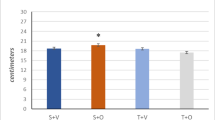
We have previously shown in the rat slow-twitch soleus muscle that adrenaline greatly potentiates insulin-stimulated protein kinase B (PKB) phosphorylation without having an effect alone. However, insulin signalling capacity through the PKB pathway is higher in soleus than in fast-twitch muscles, whereas adrenaline activates phosphorylase more strongly in epitrochlearis. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the interaction between adrenaline and insulin signalling in the fast-twitch epitrochlearis muscle. Insulin increased insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase activity threefold, and adrenaline did not influence basal or insulin-stimulated PI 3-kinase activity. Insulin but not adrenaline increased PKB activity and phosphorylation of Ser473 and Thr308. It is interesting to note that adrenaline potentiated insulin-stimulated PKB activity and PKB Ser473 and Thr308 phosphorylation. These effects were mimicked by dibutyryl-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (db-cAMP). Adrenaline and db-cAMP increased glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β Ser9 phosphorylation independently of PKB activation and enhanced insulin-stimulated GSK-3β Ser9 phosphorylation. Although adrenaline increased GSK-3 phosphorylation (inhibiting activity), phosphorylation of its target sites on glycogen synthase was increased, and adrenaline blocked insulin-stimulated glycogen synthase dephosphorylation of Ser641 and Ser645,649,653,657, glycogen synthase activation and glycogen synthesis. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport was not influenced by adrenaline despite the increased PKB activation. In conclusion, as in the slow-twitch soleus muscle, adrenaline potentiates insulin-stimulated PKB activation in the fast-twitch glycolytic epitrochlearis muscle without increasing IRS-1-associated PI 3-kinase activity. Furthermore, adrenaline induces phosphorylation of a pool of GSK-3 that is not involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism. These results indicate that the combination of adrenaline and insulin may activate novel signalling molecules rather than just summing up their effects on linear pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi DR, Cohen P (1998) Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8:55–62
Aslesen R, Jensen J (1998) Effects of epinephrine on glucose metabolism in contracting rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 275:E448–E456
Brennesvik EO, Ktori C, Ruzzin J, Jebens E, Shepherd PR, Jensen J (2005) Adrenaline potentiates insulin-stimulated PKB activation via cAMP and Epac: implications for cross talk between insulin and adrenaline. Cell Signal 17:1551–1559
Clausen T, Flatman JA (1987) Effects of insulin and epinephrine on Na+–K+ and glucose transport in soleus muscle. Am J Physiol 252:E492–E499
Cleasby ME, Reinten TA, Cooney GJ, James DE, Kraegen EW (2007) Functional studies of Akt isoform specificity in skeletal muscle in vivo; maintained insulin sensitivity despite reduced insulin receptor substrate-1 expression. Mol Endocrinol 21:215–228
Cohen P (2002) The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 4:E127–E130
Daugaard JR, Richter EA (2001) Relationship between muscle fibre composition, glucose transporter protein 4 and exercise training: possible consequences in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Physiol Scand 171:267–276
Fang X, Yu SX, Lu Y, Bast RC, Woodgett JR, Mills GB (2000) Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11960–11965
Filippa N, Sable CL, Filloux C, Hemmings B, Van Obberghen E (1999) Mechanism of protein kinase B activation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol 19:4989–5000
Franch J, Aslesen R, Jensen J (1999) Regulation of glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle after glycogen depleting contractile activity: effects of adrenaline on glycogen synthesis and activation of glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase. Biochem J 344:231–235
Han XX, Bonen A (1998) Epinephrine translocates GLUT-4 but inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat muscle. Am J Physiol 274:E700–E707
Henriksen EJ, Bourey RE, Rodnick KJ, Koranyi L, Permutt MA, Holloszy JO (1990) Glucose transporter protein content and glucose transport capacity in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 259:E593–E598
Hoover F, Mathiesen I, Skalhegg BS, Lømo T, Tasken K (2001) Differential expression and regulation of the PKA signalling pathway in fast and slow skeletal muscle. Anat Embryol (Berl) 203:193–201
Hunt DG, Ivy JL (2002) Epinephrine inhibits insulin-stimulated muscle glucose transport. J Appl Physiol 93:1638–1643
James DE, Hiken J, Lawrence JC Jr (1989) Isoproterenol stimulates phosphorylation of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter in rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8368–8372
James DE, Jenkins AB, Kraegen EW (1985) Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol 248:E567–E574
Jensen J, Aslesen R, Ivy JL, Brørs O (1997) Role of glycogen concentration and epinephrine on glucose uptake in rat epitrochlearis muscle. Am J Physiol 272:E649–E655
Jensen J, Aslesen R, Jebens E, Skrondal A (1999) Adrenaline-mediated glycogen phosphorylase activation is enhanced in rat soleus muscle with increased glycogen content. Biochim Biophys Acta 1472:215–221
Jensen J, Brennesvik EO, Bergersen LH, Oseland H, Jebens E, Brørs O (2002) Quantifitative determination of cell surface β-adrenoceptors in different rat skeletal muscles. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol 444:213–219
Jensen J, Brennesvik EO, Lai YC, Shepherd PR (2007) GSK-3 regulation in skeletal muscles by adrenaline and insulin: evidence that PKA and PKB regulate different pools of GSK-3. Cell Signal 19:204–210
Jensen J, Brørs O, Dahl HA (1995) Different β-adrenergic receptor density in different rat skeletal muscle fibre types. Pharmacol Toxicol 76:380–385
Jensen J, Dahl HA, Opstad PK (1989) Adrenaline-mediated glycogenolysis in different skeletal muscle fibre types in the anaesthetized rat. Acta Physiol Scand 136:229–233
Jensen J, Jebens E, Brennesvik EO, Ruzzin J, Soos MA, Engebretsen EM, O'Rahilly S, Whitehead JP (2006) Muscle glycogen inharmoniously regulates glycogen synthase activity, glucose uptake, and proximal insulin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E154–E162
Jensen J, Ruzzin J, Jebens E, Brennesvik EO, Knardahl S (2005) Improved insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and glycogen synthase activation in rat skeletal muscles after adrenaline infusion: role of glycogen content and PKB phosphorylation. Acta Physiol Scand 184:121–130
Jiang ZY, Zhou QL, Coleman KA, Chouinard M, Boese Q, Czech MP (2003) Insulin signaling through Akt/protein kinase B analyzed by small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7569–7574
Klein J, Fasshauer M, Ito M, Lowell BB, Benito M, Kahn CR (1999) β3-Adrenergic stimulation differently inhibits insulin signaling and decreases insulin-induced glucose uptake in brown adipocytes. J Biol Chem 274:34795–34802
Lai YC, Stuenes JT, Kuo CH, Jensen J (2007) Glycogen content and contraction regulate glycogen synthase phosphorylation and affinity for UDP-glucose in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1622–E1629
Langfort J, Ploug T, Ihlemann J, Baranczuk E, Donsmark M, Gorski J, Galbo H (2003) Additivity of adrenaline and contractions on hormone-sensitive lipase, but not on glycogen phosphorylase, in rat muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 178:51–60
Larance M, Ramm G, James DE (2008) The GLUT4 code. Mol Endocrinol 22:226–233
Lawrence JC Jr, Hiken JF, James DE (1990) Phosphorylation of the glucose transporter in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem 265:2324–2332
Lee AD, Hansen PA, Schluter J, Gulve EA, Gao J, Holloszy JO (1997) Effects of epinephrine on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and GLUT-4 phosphorylation in muscle. Am J Physiol 273:C1082–C1087
Li M, Wang X, Meintzer MK, Laessig T, Birnbaum MJ, Heidenreich KA (2000) Cyclic AMP promotes neuronal survival by phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. Mol Cell Biol 20:9356–9363
McManus EJ, Sakamoto K, Armit LJ, Ronaldson L, Shpiro N, Marquez R, Alessi DR (2005) Role that phosphorylation of GSK3 plays in insulin and Wnt signalling defined by knockin analysis. EMBO J 24:1571–1583
Mei FC, Qiao J, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL, Quilliam LA, Cheng X (2002) Differential signaling of cyclic AMP: opposing effects of exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP and cAMP-dependent protein kinase on protein kinase B activation. J Biol Chem 277:11497–11504
Moule KS, Welsh GI, Edgell NJ, Foulstone EJ, Proud CG, Denton RM (1997) Regulation of protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin and β-adrenergic agonists in rat epididymal fat cells. J Biol Chem 272:7713–7719
Pette D, Staron RS (1990) Cellular and molecular diversities of mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 116:1–76
Ramm G, Larance M, Guilhaus M, James DE (2006) A role for 14-3-3 in insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation through its interaction with the RabGAP AS160. J Biol Chem 281:29174–29180
Richter EA, Garetto LP, Goodman MN, Ruderman NB (1982) Muscle glucose metabolism following exercise in the rat. Increased sensitivity to insulin. J Clin Invest 69:785–793
Shepherd PR (2005) Mechanisms regulating phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in insulin-sensitive tissues. Acta Physiol Scand 183:3–12
Song XM, Ryder JW, Kawano Y, Chibalin AV, Krook A, Zierath JR (1999) Muscle fiber type specificity in insulin signal transduction. Am J Physiol 277:R1690–R1696
Tanji C, Yamamoto H, Yorioka N, Kohno N, Kikuchi K, Kikuchi A (2002) A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to glycogen synthase kinase-3b (GSK-3β) and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3β. J Biol Chem 277:36955–36961
Turinsky J, Damrau-Abney A (1999) Akt kinases and 2-deoxyglucose uptake in rat skeletal muscles in vivo: study with insulin and exercise. Am J Physiol 276:R277–R282
Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR (2000) The PI3K–PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346:561–576
Wallberg-Henriksson H (1987) Glucose transport into skeletal muscle. Influence of contractile activity, insulin, catecholamines and diabetes mellitus. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 564:1–80
Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Aslesen R, O'Rahilly S, Jensen J (2000) Contraction inhibits insulin-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1/2-associated phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity, but not PKB activation or glucose uptake in rat muscle. Biochem J 349:775–781
Zhang J, Hiken J, Davies AE, Lawrence JC Jr (1989) Insulin stimulated dephosphorylation of phosphorylase in rat epitrochlearis muscles. J Biol Chem 264:17513–17523
Zierath JR, Hawley JA (2004) Skeletal muscle fiber type: influence on contractile and metabolic properties. PLoS Biol 2:e348
Acknowledgements
We thank Jorid Thrane Stuenæs, Ada Ingvaldsen and Astrid Bolling for expert technical assistance. The study was supported by The Research Council of Norway, Novo Nordisk Foundation, Aktieselskabet Freia Chocolade Fabriks Medisinske Fond and The European Commission via COST B17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, J., Grønning-Wang, L.M., Jebens, E. et al. Adrenaline potentiates insulin-stimulated PKB activation in the rat fast-twitch epitrochlearis muscle without affecting IRS-1-associated PI 3-kinase activity. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 456, 969–978 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0471-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0471-z