Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this review was to search systematically for disease-generic factors associated with either work retention (WR) or return to work (RTW) in people of working age with a chronic disease.
Methods
An extensive search was performed in PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO and CINAHL for English-, Dutch- and German-language studies searching on synonyms of the terms chronic disease, WR and RTW. Studies were selected if they described factors related to WR or RTW and included participants with a chronic disease of working age (15–67 years old).
Results
From 2597 hits in the electronic databases, we identified six studies reporting 23 factors associated with work participation. Categorized according to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health, health-related factors (comorbidity, duration of symptoms and less dysfunction), environmental factors (work environment and duration of absence) and personal factors (age, gender, education and own prediction of RTW) were identified.
Conclusions
Various disease-generic factors are associated with work participation, of which most of the reported factors are independent of diagnosis. Evidence of the retrieved factors is restricted due to the limited availability of studies focusing on disease-generic factors and overall low quality of the retrieved studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Chronic diseases, defined by the World Health Organization as “diseases with long duration and generally slow progression” (WHO 2014), are the leading cause of morbidity worldwide (WHO 2008). In 2011, approximately 29 % of the male population and 34 % of the female population aged 16 years or over in the European Union reported having a chronic illness. In the working population, the prevalence of having one or more chronic diseases ranges from 10 % (16–24 years) to 55 % (55–64 years; Eurostat 2014). Due to enhanced treatment, which improved the survival rates of patients with various diagnoses (Baan and Schoemaker 2009), and an increase in incidence of diseases due to unhealthy lifestyles (WHO 2002), increasing numbers of people in the working population are affected by one or more chronic diseases.
Having work is beneficial for health status, since it improves functional outcomes, social integration and satisfaction with life status and financial status (Kirsh et al. 2009). Previous studies showed that having a chronic disease affects work participation negatively; people with a chronic disease are less often employed (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2009; Maurits et al. 2013) and, when they are employed, work on average fewer hours (Koppes et al. 2012) than the general population does. In addition, employees with a chronic disease report having difficulties meeting work demands (Koppes et al. 2012; Koolhaas et al. 2013). If, however, factors that hinder or promote work retention (WR) and return to work (RTW) could be identified, these factors could be considered in interventions whose aim is to improve work participation.
WR focuses on preventing work loss in workers with a chronic disease. This is important because employees experience RTW as being difficult once absent from work (Noordik et al. 2011; Kuijer et al. 2006). However, sometimes sickness absence is inevitable which is, if possible, followed by re-entry in the same job or a different one after a period of sickness absence. Encouragement and early intervention in targeted subgroups of workers are important factors, since the longer the sickness absence lasts, the less likely people are to RTW (Peters et al. 2007).
Previous research has shown that some people manage to stay at work or return to work, where others with the same disease and prognosis do not (Van Muijen et al. 2013; De Vries et al. 2012; Achterberg et al. 2009). This indicates that besides disease-related factors, other factors could influence work participation of patients with various diagnoses, i.e., disease-generic factors. This is reflected in the ICF that describes mutual interactions between six different dimensions, showing that participation is not only affected by disease-related factors but also affected by personal and environmental factors, which are independent of diagnoses (WHO 2001). A previous review did address these disease-generic factors in relation to work disability, in which it was found that perceived complaints, limitation in physical activities, heavy manual work and female gender were associated with work disability (Detaille et al. 2009).
In this systematic review, we want to broaden the applicability of disease-generic factors by placing no limit on the chronic diseases to be included. Instead, we searched for studies that examined study populations with a variety of chronic diseases. Moreover, to our knowledge, no systematic review has been previously conducted in order to search for disease-generic factors associated with WR or RTW specifically. The purpose of this systematic review is therefore to answer the following question: Which disease-generic factors are associated with WR or RTW of people of working age with a chronic disease?
Materials and methods
During the development of this review, we strived to address all items reported in the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement (Moher et al. 2009).
Search strategy
The literature search aimed to identify all published papers that studied factors associated with WR or RTW in people of working age with a chronic disease. The first author (MV) and an experienced clinical librarian (JD) performed an extensive search in March 2014 in PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO and CINAHL, using MeSH terms, subheadings and free text words. Since our aim was to retrieve studies, which included a study sample with various diagnoses, we searched on synonyms of the term “chronic disease,” in combination with terms related to the outcome variables. A full description of the literature search is presented in Appendix 1. The strategy was formulated in PubMed (MEDLINE) and was adapted for the use in EMBASE (OvidSP), PsycINFO (OvidSP) and CINAHL (EBSCOhost). The search was limited to articles with a publication date ranging from January 2004 to March 2014. The references of all included studies were screened for additional relevant publications, which were checked according to the original search terms in order to retrieve studies with a study sample of various diagnoses.
Selection of studies
Citations and abstracts of all studies were retrieved, and duplicates were removed. Selection of the studies was performed in two rounds; the first round consisted of the title and abstract screening in which the first author (MV) screened all the retrieved records. Four authors (ML, JH, HW and MF) each screened a quarter of the records independently regarding whether the records reported a chronic disease, used an adequate study design and used WR or RTW as an outcome. If the title and abstract failed to meet one or more selection criteria, the publication was excluded. When there was no sufficient information in the title and abstract to judge eligibility, the full-text article was retrieved. In the second round, full-text articles were ordered and studies were selected based on all defined criteria by the first author (MV) and second author (ML). We included reviews, cohort studies (both prospective and retrospective), cross-sectional studies and case–control studies, which searched for factors associated with the outcomes WR or RTW. We defined WR as preventing work loss or staying employed. RTW was defined as re-entering employment in the same job or a different one after a period of sickness absence. We included studies in which the participants were of working age (15–67 years) and had a chronic disease for more than 3 months, following the definition of chronic disease according to the National Centre for Health Statistics (2010). Only papers written in English, Dutch or German to which we had access to both abstract and full-text article were considered for inclusion in this review. The original studies of the reviews which were included in full-text selection were retrieved and screened on title and abstract and, if the selection criteria were met, on full text. Disagreements during the process of selecting were resolved by obtaining consensus during a weekly meeting with the reviewers. For practical considerations, papers were not blinded for authors, institutions, journal, results or conclusions.
Quality assessment
Two reviewers (MV and JH) independently scored the quality of the included studies using an adapted version of the Methodological Evaluation of Observational Research checklist (Shamliyan et al. 2011), derived from Robroek et al. (2013) and Ijaz et al. (2013). Criteria addressed were study design, loss of follow-up or non-response, standardized or valid measurement of both outcomes and factors, measurement of confounding factors and methods to reduce bias. When the criterion was sufficiently met, it was scored as 1. When the criterion was not sufficiently met or not reported, it was scored as 0. It was decided that the study had to meet four of the six criteria in order to obtain the label “of sufficient quality.” Disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved through consensus. If agreement was not reached, the fifth author (HW) made the final decision.
Data extraction
The first reviewer (MV) performed the data extraction using a standardized form that included items on demographic characteristics of the study population (age, gender and chronic disease), study design, sample size, outcome measures concerning WR and RTW, factors associated with outcome and estimated effect size. Data extraction was checked by four reviewers (ML, JH, HW and MF). When performing the data extraction, we reported the associations observed in the multivariate model. When a prediction model was used, the univariate associations were reported in order to retrieve the independent associations. When multiple models were estimated for different outcomes, we used the model that matched our outcome as closely as possible. Data were extracted for all factors, including the factors that were specifically aimed at one specific disease (e.g., “primary type of dialyses”). However, it was decided not to include this data in the further description of the results. The data extraction can be found in Appendix 2.
Results
Selection of studies
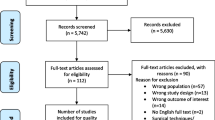
The search yielded 4,281 unique records: 1,463 from PubMed, 1,932 from EMBASE, 302 from PsycINFO and 584 from CINAHL. After duplicates had been removed, 2,597 articles were identified. Based on title and abstract, 2,477 articles were excluded, mostly because their outcomes did not match WR or RTW. From the 120 remaining articles, five studies and seven reviews were selected. Checking the original studies of the included seven reviews did not yield any additional studies. Reference checking of the five included studies revealed one new article. This resulted in a total of six studies that met the inclusion criteria and were included in this review, five studies with WR as their focus and one study whose topic was RTW. The results of the literature search are presented in Fig. 1. The summary of the methodological ranking for each study is presented in Table 1. As can been seen from Table 1, of the six studies, two studies were rated as sufficiently meeting the quality criteria.
Data analyses and outcomes
Regardless of the analyzing methods used, all studies reported one or more factors statistically significantly associated with the outcomes WR and RTW. As data analyses varied considerably, direct comparisons between studies presenting absolute point estimates and studies presenting regression parameters are less informative. We considered the pooling of the results as not being useful, due to the heterogeneity in study quality and studied factors between the studies. For this reason, we evaluated the results of the study in a qualitative way and described the factors according to the ICF model.
Work retention
Five studies were retrieved regarding WR, of which one study was of sufficient quality. Factors associated with WR are listed in Table 2.Footnote 1 Regarding the ICF dimension of personal factors, two studies found that female gender (p < 0.01a, neg.; OR 0.78, 95 % CI 0.74–0.81) and older age were negatively associated with WR. Age reduced the chance of WR when being over 55 years old (55–59 years old, OR 0.87, 95 % CI 0.82–0.93 and 60–64 years old, OR 0.89, 95 % CI 0.82–0.97) and being 20–24 years of age (OR 0.85, 95 % CI 0.75–0.97). On the other hand, being 25–44 years old was positively associated with WR (p < 0.01a). Also, a lower educational level, race, substance use, use of medication and nocturnal toilet use were found to be negatively associated with WR. Having a higher socioeconomic status (SES) index was positively associated with WR. Other factors associated with WR, using the ICF model, were comorbidity and experiencing motor control problems (body function/structure dimension). Also, inability to ambulate (activity dimension), living in an urban area, workplace environment and financial considerations (environmental dimension) were reported to be associated with WR.
Return to work
In the one study using RTW as an outcome, having a younger age (OR 2.48, 95 % CI 1.43–4.31) and the sick-listed persons’ own prediction of their RTW (≤44 years old, OR 15.99, 95 % CI 6.86–37.25) were reported to be positively associated with RTW. Other factors associated with RTW, in terms of ICF dimensions, are as follows: complaints from not more than one group of symptoms, duration of complaints <5 years, less pain and less impairment (body function/structure dimension), shorter duration of sick leave (participation dimension) and, regarding the environmental dimension, the perception of feeling welcome back at work (see Table 2).
Discussion
The aim of this systematic review was to retrieve disease-generic factors associated with WR or RTW of workers with a chronic disease. We identified several factors associated with WR or RTW across all ICF dimensions. Of these results, factors reported in multiple studies were age and gender. The patient’s own prediction of RTW was found to have a large effect on RTW in one study.
Both older age and female gender, relating to the personal dimension of the ICF, were reported to be negatively associated with work participation, which is consistent with the findings of other systematic reviews (Van Muijen et al. 2013; De Vries et al. 2012), focusing on specific diseases. The systematic review of Detaille et al. (2009), focusing on prognostic factors of work disability common in the five most prevalent chronic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes mellitus and ischemic heart disease), found a negative association of both older age and female gender with work disability. Since our results are in line with these previous studies, despite the different outcome parameters and study populations, this would indicate that the associations of older age and female gender with work participation are independent of diagnosis. This supports our hypothesis that factors other than disease-related factors play a significant role in WR or RTW of the chronically ill.
Age was reported by several studies in this review (Heijbel et al. 2006; Baanders et al. 2002; Muehrer et al. 2011), with the most consistent finding of older age being negatively associated with work participation. Fraser et al. (2009) reported that older workers can experience age discrimination and consider this a barrier for work participation. The negative association of female gender with work participation (Baanders et al. 2002; Muehrer et al. 2011) was explained by Côté and Coutu (2010) by how men and women perceive themselves in relation to their social environment, i.e., social identity. Work-associated self-identity may foster social stereotyping of gender roles, especially that of the man as breadwinner (Ghaill and Haywood 2007), which may influence the higher chance of RTW for men. Given the aging working population, the increasing work participation by women and the trend that people will have to work longer before their retirement in Western countries (Crepaldi et al. 2008), a substantial part of the workers will be at risk for reduced work participation. As these personal factors, age and gender, are not modifiable, more intensive guidance at an early stage targeted at these higher-risk groups could be implemented to enhance future work participation.
With regard to the association of one’s own prediction of RTW and work participation, Heijbel et al. (2006) reported that the predictive value of a person’s own negative prediction regarding RTW was 96 %. This means that only 4 out of 100 people with a negative prediction does in fact RTW after sickness absence. This result is in line with previous research, indicating that the prediction of RTW is an important indicator of RTW (Cole et al. 2002). In addition, the study of Wind et al. (Wind et al. 2013) showed that patients are capable of predicting their own RTW in the context of disability claims. Dunstan et al. (2013), which operationalized the prediction of RTW by the term “Behavioral Intention” (BI), states that BI can be influenced by a change in how one thinks about work, how the social environment thinks about RTW and how one perceives the behavior, RTW, to be under his or her control. With regard to the social environment, Dunstan et al. (2013) reported that the doctor’s opinion carried the greatest weight and therefore influences the patient’s expectation of RTW, meaning that health professionals should bear in mind that their opinion influences the RTW of their patients. In addition, expectation of RTW is subject to change by altering the patient’s attitude about work and the perception of feeling in control of their own behavior of RTW (Dunstan et al. 2013), these being the two other components of BI. By identifying workers with a negative prediction of their RTW at an early stage, and aiming specific interventions at these groups, work participation could be enhanced.
This systematic review revealed that studies including study populations with various diagnoses are limited. Therefore, in addition to the low overall quality of the retrieved studies, evidence of the factors associated with work participation is restricted. The factors retrieved in this review, i.e., age, gender and prediction of RTW, are among the most commonly reported factors associated with work participation. This review shows that these factors are applicable to populations with various diagnoses. These disease-generic factors provide insight for health professionals who are at risk for reduced work participation. One should keep in mind that participation in work could also be affected by factors dependent on the type of diagnosis. For example, treatment-related factors, such as the adverse effects of intensive chemotherapy (Taskila and Lindbohm 2007), can influence work participation in workers with cancer. Both disease-generic and disease-specific factors can be targeted to optimize work participation efforts.
Further research should aim to increase the evidence regarding disease-generic factors associated with work participation in chronically ill workers, additional to those identified in our review. These factors could help professionals involved in work participation programmes to identify workers who are at high risk of not participating in work and to target interventions early in the process in order to enhance work participation.
Conclusion
The objective of this review was to search systematically for disease-generic factors associated with either WR or RTW in people of working age with a chronic disease.
Various disease-generic factors are associated with work participation, of which most of the reported factors are independent of diagnosis. Evidence for the retrieved factors is restricted, due to the limited availability of studies focusing on disease-generic factors and the overall low quality of the studies.
Notes
aOR not available for this study
References
Achterberg TJ, Wind H, de Boer AG, Frings-Dresen MH (2009) Factors that promote or hinder young disabled people in work participation: a systematic review. J Occup Rehabil 19:129–141
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (2009) Chronic disease and participation in work. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442459085. Assessed 18 July 2014
Baan CA, Schoemaker CG (2009) Diabetes tot 2025: preventie en zorg in samenhang. Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Zorg. http://medisch-fitness.com/documents/RIVMrapportDiabetes.pdf. Assessed 4 Feb 2015
Baanders AN, Rijken PM, Peters L (2002) Labour participation of the chronically ill: a profile sketch. Eur J Public Health 12:124–130
Botticello AL, Chen Y, Tulsky D (2012) Geographic variation in participation for physically disabled adults: the contribution of area economic factors to employment after spinal cord injury. Soc Sci Med 75:1505–1513
Calsbeek H, Rijken PM, Dekker J, van Berge Henegouwen GP (2006) Disease characteristics as determinants of the labour market position of adolescents and young adults with chronic digestive disorders. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:203–209
Cole DC, Mondloch MV, Hogg-Johnson S, Early Claimant Cohort Prognostic Modelling Group (2002) Listening to injured workers: how recovery expectations predict outcomes—a prospective study. CMAJ 166:749–754
Côté D, Coutu M (2010) A critical review of gender issues in understanding prolonged disability related to musculoskeletal pain: how are they relevant to rehabilitation? Disabil Rehabil 32:87–102
Crepaldi C, Barbera M, Ravelli F (2008) Cancer and in general long term illnesses at the workplace. Policy Department Economic and Scientific Policy. http://www.europarl.europa.eu/document/activities/cont/201107/20110718ATT24299/20110718ATT24299EN.pdf. Assessed at 17 July 2014
De Vries HJ, Reneman MF, Groothoff JW, Geertzen JH, Brouwer S (2012) Factors promoting staying at work in people with chronic nonspecific musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review. Disabil Rehabil 34:443–458
Detaille SI, Heerkens YF, Engels JA, van der Gulden JW, van Dijk FJ (2009) Common prognostic factors of work disability among employees with a chronic somatic disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Scand J Work Environ Health 35:261–281
Dunstan DA, Covic T, Tyson GA (2013) What leads to the expectation to return to work? Insights from a Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) model of future work outcomes. Work 46:25–37
European Commission Eurostat (2014) Health status statistics—statistics explained (2014/2/3). European Commission Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/statistics_explained/index.php/Health_status_statistics. Assessed at 17 July 2014
Fraser L, McKenna K, Turpin M, Allen S, Liddle J (2009) Older workers: an exploration of the benefits, barriers and adaptations for older people in the workforce. Work 3:261–272
Ghaill MMA, Haywood C (2007) Gender, culture and society: contemporary femininities and masculinities. MacMillan, London
Heijbel B, Josephson M, Jensen I, Stark S, Vingård E (2006) Return to work expectation predicts work in chronic musculoskeletal and behavioral health disorders: prospective study with clinical implications. J Occup Rehabil 16:173–184
Ijaz S, Verbeek J, Seidler A, Lindbohm ML, Ojajärvi A, Orsini N et al (2013) Night-shift work and breast cancer—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Work Environ Health 39:431–447
Kirsh B, Stergiou-Kita M, Gewurtz R, Dawson D, Krupa T, Lysaght R et al (2009) From margins to mainstream: what do we know about work integration for persons with brain injury, mental illness and intellectual disability? Work 32:391–405
Koolhaas W, van der Klink JJL, de Boer MR, Groothoff JW, Brouwer S (2013) Chronic health conditions and work ability in the ageing workforce: the impact of work conditions, psychosocial factors and perceived health. Int Arch Occup Health 87:433–443
Koppes LLJ, de Vroome EMM, Mars GMJ, Janssen BJM, van Zwieten MHJ, van den Bossche SNJ (2012) Nationale enquête arbeidsomstandigheden. TNO, Hoofddorp
Kuijer W, Groothoff JW, Brouwer S, Geertzen JH, Dijkstra PU (2006) Prediction of sickness absence in patients with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. J Occup Rehabil 16:439–467
Maurits E, Rijken M, Friele R (2013) Kennissynthese ‘Chronisch ziek en werk’: Arbeidsparticipatie door mensen met een chronische ziekte of lichamelijke beperking. Nivel: Utrecht
Messmer Uccelli M, Specchia C, Battaglia MA, Miller DM (2009) Factors that influence the employment status of people with multiple sclerosis: a multinational study. J Neurol 256:1989–1996
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Muehrer RJ, Schatell D, Witten B, Gangnon R, Becker BN, Hofmann RM (2011) Factors affecting employment at initiation of dialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 6:489–496
National Center for Health Statistics (2011) United States 2010. With special feature on death and dying. US Government Printing Office, Hyattsville, pp 486–487
Noordik E, Nieuwenhuijsen K, Varekamp I, van der Klink JJ, van Dijk F (2011) Exploring the return-to-work process for workers partially returned to work and partially on long-term sick leave due to common mental disorders: a qualitative study. Disabil Rehabil 33:1625–1635
Peters J, Pickvance S, Wilford J, Macdonald E, Blank L (2007) Predictors of delayed return to work or job loss with respiratory ill-health: a systematic review. J Occup Rehabil 17:317–326
Robroek SJW, Reeuwijk KG, Hillier FC, Bambra CL, van Rijn R, Burdorf A (2013) The contribution of overweight, obesity, and lack of physical activity to exit from paid employment: a meta-analysis. Scand J Work Environ Health 39:233–240
Shamliyan TA, Kane RL, Ansari MT, Raman G, Berkman ND, Grant M et al (2011) Development quality criteria to evaluate nontherapeutic studies of incidence, prevalence, or risk factors of chronic diseases: pilot study of new checklists. J Clin Epidemiol 64:637–657
Taskila T, Lindbohm L (2007) Factors affecting cancer survivors’ employment and work ability. Acta Oncol 46:446–451
Van Muijen P, Weevers NL, Snels IA, Duijts SF, Bruinvels DJ, Schellart AJ, van der Beek AJ (2013) Predictors of return to work and employment in cancer survivors: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer Care 22:144–160
Wind H, Samoocha D, van der Beek AJ, Frings-Dresen MHW (2013) Prevention of disability: the opinion of claimants applying for a disability benefit. Work 00:1–7
World Health Organization (2001) ICF: International classification of functioning, disability and health. World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (2002) The World Health Report 2002 - Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. WHO Press. Available from: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/. Assessed at 18 July 2014
World Health Organization (2008) The global burden of disease: 2004 update. WHO Press. http://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004update_full.pdf. Assessed at 17 July 2014
www.who.int [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization [updated 2014 March; cited 2014 Jul 17]. Available from: http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/noncommunicable_diseases/en/
Acknowledgments
This study was granted by the Instituut Gak.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1: Search strategy
PubMed, Date of search February 27, 2014
(“chronic disease”[Mesh] OR chronic disease*[tw] OR chronic disorder*[tw] OR chronic health[tw] OR chronic condition*[tw]) AND (“return to work”[Mesh] OR (return to[tw] AND work[tw]) OR back to work[tw] OR unemployment[Mesh] OR unemployment[tw] OR “Employment”[Mesh:NoExp] OR employment[tw] OR employability[tw] OR work resumption[tw] OR working age[tw] OR “job satisfaction”[Mesh] OR “sick leave”[Mesh] OR absenteeism[Mesh] OR sick leave[tw] OR absenteeism[tw] OR work retention[tw] OR job retention[tw] OR job status[tw] OR work status[tw] OR employment status[tw] OR paid work[tw] OR vocational status[tw] OR occupational status[tw] OR work functioning[tw] OR job functioning[tw] OR work capacity[tw] OR employment capacity[tw] OR work participation[tw] OR employment participation[tw] OR stay at work[tw] OR presenteeism[tw] OR work outcomes[tw] OR work ability[tw]).
Note: no additional limits have been applied.
EMBASE Classic + EMBASE 1947: Present (OvidSP), Date of search March 4, 2014
-
1.
chronic disease/
-
2.
(chronic illness or chronic disease* or chronic disorder* or chronic condition or chronic health). ab, kw, ti.
-
3.
return to work/
-
4.
(return to work or (return to adj3 work) or back to work). ab, kw, ti
-
5.
unemployment/
-
6.
unemployment. ab, kw, ti
-
7.
employment/
-
8.
(employment or employability). ab, kw, ti
-
9.
employment status/
-
10.
(employment status or job status or work status or vocational status or occupational status or paid work). ab, kw, ti
-
11.
work resumption/
-
12.
(work resumption or working age or work retention or job retention or work functioning or job functioning or work participation or employment participation or stay at work or presenteeism or work outcomes). ab, kw, ti
-
13.
work capacity/
-
14.
(work capacity or employment capacity or work ability). ab, kw, ti
-
15.
job satisfaction/
-
16.
job satisfaction. ab, kw, ti
-
17.
absenteeism/
-
18.
(absenteeism or sick leave). ab, kw, ti
-
19.
or/3–18 [RTW or job retention]
-
20.
1 or 2 [chronic diseases]
-
21.
19 and 20
Note: no additional limits have been applied.
PsycINFO 1806 to Present (OvidSP), Date of search March 5, 2014
-
1.
”chronicity (Disorders)”/or “chronic illness”/
-
2.
(chronic disease or chronic disorder? or chronic health or chronic condition or chronic illness). ab, id, ti
-
3.
reemployment/
-
4.
(return to work or (return to adj3 work) or back to work). ab, id, ti
-
5.
unemployment/
-
6.
unemployment. ab, id, ti
-
7.
employment status/
-
8.
(employment status or employment or work resumption or working age or paid work or work functioning or job functioning). ab, id, ti
-
9.
occupational status/
-
10.
(occupational status or job status or work status or vocational status or work participation or employment participation or stay at work or presenteeism or work outcomes or work ability). ab, id, ti
-
11.
employability/
-
12.
(employability or work capacity or employment capacity). ab, id, ti
-
13.
job satisfaction/
-
14.
(job satisfaction or work retention or job retention). ab, id, ti
-
15.
employee absenteeism/
-
16.
(employee absenteeism or sick leave or absenteeism). ab, id, ti
-
17.
1 or 2 [chronic disorders]
-
18.
or/3–16 [RTW or job retention]
-
19.
17 and 18
Note: no additional limits have been applied.
CINAHL Plus with Full Text (EBSCOhost), Date of search 6 March 2014
-
(MH “Chronic Disease”)
-
SU chronic disease OR chronic disorder
-
(MH “Job Re-Entry”)
-
SU job re-entry
-
MH “Unemployment”
-
SU unemployment
-
(MH “Employment+”)
-
SU employment OR employment status OR working age
-
(MH “Job Satisfaction+”)
-
SU job satisfaction
-
(MH “Sick Leave”)
-
SU sick leave
-
(MH “Absenteeism”)
-
SU absenteeism
-
(S1 OR S2)
-
(S3 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 OR S8 OR S9 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14)
-
S15 AND S16
Notes: no additional limits have been applied.
Appendix 2
Data-extraction of the six included studies
First author (year), country of origin | Study design | Participants: a) Sample size b) Gender (F %) c) Range of age (mean, SD) d) Chronic disease e) Employment at baseline (employed %) | Outcome: a) Definition b) Type of measurement | Factor: a) Definition b) Type of measurement | Effect (HR/OR/RR/correlation) | Quality assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Heijbel et al. (2006), Sweden | PC | a) 508 b) 90.9 c) 24–64 (50*, NR) d) Musculoskeletal pain (33.7 %**), mental distress (15.6 %**), respiratory disorders (1.9 %**), cardiovascular disorders (1.5 %**), other (i.e., neurological disorders, factures, diabetes, 12.0 %**), combination of disorders (35.2 %**) e) 100 | a) RTW, defined as work status on the 18th month after baseline. Persons who were returned (part-time) and were working for <15 days during the 18th month were counted as returners b) Human resource departments in 5 municipalities and 4 county councils | a) Univariate logistic regression analyses: 1. Sex, male (r: female) 2. Age ≤44 years (r: 55–65 years) 3. Age 45–54 years (r: 55–65 years) 4. Own prediction of RTW, yes (r: no) 5. Complaints from >1 group of symptoms, no (r: yes) 6. Duration of the complaints ≤5 years (r: >5 years) 7. Duration of sick leave <1 year (r: ≥1 year) 8. Pain, 1st quartile (r: 4th quartile), measured by von Korff’s questionnaire 9. Pain, 2nd quartile (r: 4th quartile) 10. Pain, 3rd quartile (r: 4th quartile) 11. Function, 1st quartile (r: 4th quartile), measured by von Korff’s questionnaire 12. Function, 2nd quartile (r: 4th quartile) 13. Function, 3rd quartile (r: 4th quartile) 14. Physically strenuous work, no (r: yes) 15. Contact with the workplace/workmates, yes (r: no) 16. Perception of being welcome back to work, yes (r: no or do not know) 17. Contact with the Occupational Health Service, yes (r: no) 18. Contact with the Regional Social Insurance officer, yes (r: no) 19. Contact with the Trade Union, yes (r: no) 20. Rehabilitation programme, yes (r: no) b) Postal questionnaire (n = 520), telephone interview (n = 5) | OR [95 % CI]: 1. 1.23 [0.64, 2.39] 2. 2.48 [1.43, 4.31] 3. 2.18 [1.30, 3.67] 4. 15.99 [6.86, 37.25] 5. 2.01 [1.29, 3.13] 6. 1.75 [1.12, 2.72] 7. 2.67 [1.76, 4.05] 8. 3.73 [1.84, 7.55] 9. 5.51 [2.74, 11.07] 10. 2.23 [1.06, 4.70] 11. 2.70 [1.41, 5.16] 12. 2.05 [1.06, 3.97] 13. 1.61 [0.82, 3.16] 14. 1.54 [1.00, 2.38] 15. 1.97 [0.94, 4.14] 16. 1.92 [1.23, 2.99] 17. 1.35 [0.90, 2.02] 18. 0.84 [0.54, 1.31] 19. 1.08 [0.73, 1.61] 20. 1.12 [0.72, 1.75] | Sufficient |
Baanders et al. (2002), the Netherlands | CS | a) 1,266 b) 56.5 c) 15–64 (NR, NR) d) Cardiovascular disease (7.7 %), chronic nonspecific lung diseases (18.6 %), locomotor disease (15.0 %), cancer (5.1 %), diabetes mellitus (10.4 %), neurological disease (9.1 %), digestive disorder (3.5 %), other (30.6 %) e) 45.1 | a) WR, defined as labor market participation is defined as having a paid job for at least twelve hours per week b) Postal questionnaire | a) Not employed versus employed: 1. Gender, female (r: male) 2. Age, 25–44 years (r: 15–24 years) 3. Age, 45–64 years (r: 15–24 years) 4. Education level, primary (r: university) 5. Educational level, lower secondary + vocational (r: university) 6. Educational level, intermediate secondary + vocational (r: university) 7. Educational level, higher vocational (r: university) 8. Experiencing motor control problems, yes (r: no) b) Postal questionnaire. | B-coefficient***: 1. p < 0.01, neg. 2. p < 0.01, pos. 3. Nonsignificant 4. p < 0.01, neg. 5. p < 0.01, neg. 6. Nonsignificant 7. Nonsignificant 8. p < 0.01, neg. | Insufficient |
Botticello et al. (2012), USA | CS | a) 1,013 b) 19.1 c) 17–64 (41.2, NR) d) Spinal cord injury; paraplegia (53.2 %), tetraplegia (46.8 %) e) 63.4 | a) WR, defined as employment status, assessed at least one follow-up using the categories: working, homemaker, job-training program, sheltered workshop, student, retired, unemployed, or other (which includes volunteer work, disability, or medical leave). The variable was dichotomized as ‘paid employment’ ‘yes’ (category: ‘working’) and ‘no’ (remaining categories) b) Telephone interview | a) 1. >SES index (r: < SES index) defined as area-level socioeconomic index, combination of (1) employment rate, (2) percent of population residing within an urban area, (3) measures of household income, housing values, education and portion of residents employed in high status occupations 2. Rural (r: suburban), defined as <60 % of residents lived in an urban area (>50.000 residents) 3. Urban (r: suburban), defined as >90 % of residents lived in an urban area b) National Historical Geographical Information System, 2000 US Census Summary File | OR [95 % CI]: 1. 1.09 [1.04, 1.14] 2. 0.53 [0.13, 2.20] 3. 0.46 [0.23, 0.93] | Sufficient |
Calsbeek et al. (2006), The Netherlands | CS | a) 246 b) 58.2** c) 15–24 (20.1**, NR) d) Inflammatory bowel disease (49.2 %), chronic liver diseases (11.7 %), congenital digestive disorder (17.6 %), food allergy (9.4 %), celiac disease (12.1 %) e) NR | a) WR, defined as labor participation, assessed by the number of hours employed per week which were dichotomized in ‘having a paid job’ (<12 h/w) vs. ‘not having a paid job) b) Postal questionnaire | a) Bivariate logistic regression analyses: 1. Physical complaints, yes (r: no) 2. Anxiety, yes (r: no) 3. Depression, yes (r: no) 4. Disability in endurance, yes (r: no) 5. Hospitalization, yes (r: no) 6. Use of medication, yes (r: no) 7. Need to diet adherence, yes (r: no) 8. Nocturnal toilet use, yes (r: no) b) Postal questionnaire | OR [95 % CI]: 1. 0.99 [0.94, 1.03] 2. 0.94 [0.88, 1.01] 3. 0.98 [0.89, 1.07] 4. 0.93 [0.80, 1.08] 5. 0.91 [0.80, 1.03] 6. 0.78 [0.62, 0.98] 7. 1.04 [0.76, 1.43] 8. 0.70 [0.53, 0.91] | Insufficient |
Messmer Uccelli et al. (2009), 18 European countries | CS | a) 1,141 b) 67 c) 21–67 (41.8, 9.2) d) Multiple sclerosis e) 61 | a) WR, defined as employment status; differentiating between employed or not employed b) Questionnaire | a) Category variables: 1. MS-related symptoms (more difficult, n = 20) 2. MS-related symptoms (easier, n = 7) 3. Workplace environment (more difficult, n = 13) 4. Workplace environment (easier, n = 19) 5. Your attitude toward work (more difficult, n = 6) 6. Your attitude toward work (easier, n = 4) 7. Attitudes of others in the workplace (more difficult, n = 6) 8. Attitudes of others in the workplace (easier, n = 4) 9. Financial considerations (more difficult, n = 5) 10. Financial considerations (easier, n = 4) 11. Personal considerations (more difficult, n = 9) 12. Personal considerations (easier, n = 9) Measured by the employed group, reference group is the unemployed group b) Questionnaire. Participants were asked to indicate to what extent each item made job maintenance easier or more difficult, from one of three options (1) not at all, (2) somewhat, (3) very much | OR [95 %]: 1. 0.96 [0.94, 0.98] 2. 1.10 [1.04, 1.16] 3. 0.97 [0.93, 1.10] 4. 1.04 [1.01, 1.06] 5. 0.97 [0.90, 1.05] 6. 1.08 [0.99, 1.17] 7. 1.00 [0.92, 1.07] 8. 1.02 [0.95, 1.10] 9. 0.95 [0.89, 1.02] 10. 1.15 [1.07, 1.23] 11. 1.00 [0.94, 1.06] 12. 0.98 [0.93, 1.03] | Insufficient |
Muehrer et al. (2011), USA | RC | a) 102,104 b) NR c) 15–64 (NR, NR) d) Chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease (ESRD) e) NR | a) WR, defined as maintaining employment. Person’s inability to maintain employed was identified when, at initiation of treatment, persons changed employment from full- to part-time or to any other status (retired, student, homemaker, etc.) b) United States Renal Data System (USRDS) | a) Univariate logistic regression analyses (model 1999 through 2003): 1. Age, 15–19 years (r: 50–54 years) 2. Age, 20–24 years (r: 50–54 years) 3. Age, 25–29 years (r: 50–54 years) 4. Age, 30–34 years (r: 50–54 years) 5. Age, 35–39 (r: 50–54 years) 6. Age, 40–44 years (r: 50–54 years) 7. Age, 45–49 years (r: 50–54 years) 8. Age, 55–59 (r: 50–54 years) 9. Age, 60–64 (r: 50–54 years) 10. Gender, women (r: men) 11. Race, black (r: white) 12. Race, Asian (r: white) 13. Race, Native American (r: white) 14. Race, other (r: white) 15 Race, Hispanic (r: white) 16. ESDR cause, hypertension (r: diabetes) 17. ESRD cause, glomerulonephritis (r: diabetes) 18. ESRD cause, other (r: diabetes) 19. ESRD cause, cystic kidney (r: diabetes) 20. ESRD cause, other urologic (r: diabetes) 21. Inability to transfer, yes (r: no) 22. Alcohol use, yes (r: no) 23 Coronary vascular disease, yes (r: no) 24. Use of drugs, yes (r: no) 25. Cancer, yes (r: no) 26. Congestive heart failure, yes (r: no) 27. Tobacco use, yes (r: no) 28. Pericarditis, yes (r: no) 29. Arrhythmia, yes (r: no) 30. Inability to ambulate, yes (r: no) 31. Ischemic heart disease, yes (r: no) 32. COPD, yes (r: no) 33. Cardiac arrest, yes (r: no) 34. Diabetes (no insulin), yes (r: no) 35. Peripheral vascular disease, yes (r: no) 36. Anemia, yes (r: no) 37. Hypertension, yes (r: no) 38. Diabetes (insulin), yes (r: no) 39. Myocardial infarction, yes (r: no) 40. Predialysis erythropoietin use, yes (r: no) 41. Dialysis setting, home (r: dialysis facility) 42. Dialysis setting, hospital inpatient (r: dialysis facility) 43. Primary type of dialysis, continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (r: hemodialysis) 44. Primary type of dialysis, continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (r: hemodialysis) 45. Primary type of dialysis, intermittent peritoneal dialysis (r: hemodialysis) 46. Primary type of dialysis, other (r: hemodialysis) 47. Medicaid, yes (r: no) 48. Department of Veterans Affairs, yes (r: no) 49. Medicare, yes (r: no) 50. Insurance by employer, yes (r: no) 51. Other, yes (r: no) 52. No insurance (r: having an insurance) b) United States Renal Data System (USRDS) | OR [95 %]: 1. 0.79 [0.57, 1.12] 2. 0.85 [0.75, 0.97] 3. 0.97 [0.88, 1.07] 4. 1.10 [0.92, 1.09] 5. 1.02 [0.95, 1.11] 6. 0.98 [0.91, 1.05] 7. 1.05 [0.98, 1.12] 8. 0.87 [0.82, 0.93] 9. 0.89 [0.82, 0.97] 10. 0.78 [0.74, 0.81] 11. 0.75 [0.72, 0.78] 12. 0.82 [0.74, 0.90] 13. 0.99 [0.84, 1.17] 14. 0.85 [0.73, 0.98] 15. 0.68 [0.65, 0.71] 16. 1.02 [0.95, 1.10] 17. 1.22 [1.13, 1.32] 18. 0.85 [0.78, 0.92] 19. 1.68 [1.50, 1.87] 20. 1.17 [1.00, 1.38] 21. 0.85 [0.54, 1.34] 22. 0.56 [0.47, 0.67] 23. 0.70 [0.62, 0.79] 24. 0.73 [0.60, 0.89] 25. 0.73 [0.65, 0.81] 26. 0.80 [0.76, 0.85] 27. 0.85 [0.79, 0.93] 28. 0.97 [0.77, 1.21] 29. 0.88 [0.76, 1.02] 30. 0.45 [0.35, 0.58] 31. 0.92 [0.85, 0.99] 32. 0.86 [0.75, 0.98] 33. 0.55 [0.39, 0.76] 34. 1.02 [0.96, 1.08] 35. 0.94 [0.86, 1.02] 36. 1.01 [0.99, 1.02] 37. 1.06 [1.00, 1.11] 38. 0.94 [0.89, 1.00] 39. 0.94 [0.84, 1.05] 40. 1.29 [1.23, 1.35] 41. 1.01 [0.89, 1.15] 42. 1.13 [1.01, 1.26] 43. 1.40 [1.23, 1.59] 44. 1.61 [1.40, 1.87] 45. 1.47 [0.64, 3.37] 46. 0.90 [0.13, 6.10] 47. 0.39 [0.35, 0.43] 48. 0.80 [0.65, 0.99] 49. 0.81 [0.74, 0.88] 50. 1.51 [1.36, 1.67] 51. 1.36 [1.23, 1.50] 52. 0.43 [0.38, 0.48] | Insufficient |
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Vooijs, M., Leensen, M.C.J., Hoving, J.L. et al. Disease-generic factors of work participation of workers with a chronic disease: a systematic review. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 88, 1015–1029 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-015-1025-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-015-1025-2