Abstract
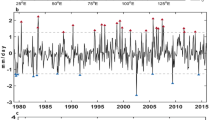
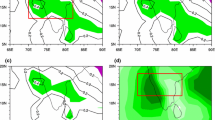
Relationship between the Southern Annular Mode (SAM) and the India summer monsoon rainfall (ISMR) has been examined based on the data period 1949–2013. While the entire data period indicates a significant increasing trend in SAM, recent decades 1983–2013 indicate no trend. The relationship between the two strengthened considerably since 1983. Results reveal that the February–March SAM is significantly related with the subsequent ISMR. A positive (negative) SAM during February–March is favorable (unfavorable) for the ensuing summer monsoon rainfall over the Indian sub-continent. The delayed response is relayed through the central Pacific Ocean. We propose a hypothesis that states: when a negative (positive) phase of February–March SAM occurs, it gives rise to an anomalous meridional circulation in a longitudinally locked air–sea coupled system over the central Pacific that persists up to the subsequent boreal summer and propagates from the sub-polar latitudes to the equatorial latitudes inducing a warming (cooling) effect over the central equatorial Pacific region. In turn, this effect concomitantly weakens (strengthens) the monsoon rainfall over the Indian sub-continent. Thus, the February–March SAM could possibly serve as a new precursor to foreshadow the subsequent behavior of the Indian summer monsoon.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arblaster JM, Meehl GA (2006) Contributions of external forcings to Southern Annular Mode trends. J Clim 19:2896–2905
Ashok K, Guan Z, Saji NH, Yamagata T (2004) Individual and combined influences of ENSO and the Indian ocean dipole on the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 17:3141–3155
Ashok K, Behera SK, Rao SA, Weng H, Yamagata T (2007) El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J Geophys Res 112:C11007. doi:10.1029/2006JC003798
Blanford HF (1884) On the connection of Himalayan snowfall with dry winds and seasons of drought in India. Proc R Soc Lond 37:3–22
Butler AH, Thompson DWJ, Gurney KR (2007) Observed relationships between the Southern Annular Mode and atmospheric carbon dioxide. Global Biogeochem Cycles 21:GB4014. doi:10.1029/2006GB002796
Cai WJ, Whetton PH, Karoly DJ (2003) The response of the Antarctic Oscillation to increasing and stabilized atmospheric CO2. J Clim 16:1525–1538
Cai W, Shi G, Cowan T, Bi D, Ribbe J (2005) The response of the Southern Annular Mode, the East Australian Current, and the southern mid-latitude ocean circulation to global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32:L23706. doi:10.1029/2005GL024701
Cai W, Sullivan A, Cowan T (2011) Interactions of ENSO, the IOD, and the SAM in CMIP3 Models. J Clim 24:1688–1704. doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3744.1
Ciasto LM, Thompson DWJ (2008) Observations of large-scale ocean–atmosphere interaction in the Southern Hemisphere. J Clim 21:1244–1259. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1809.1
Ciasto L, Simpkins GR, England MH (2015) Teleconnections between tropical Pacific SST anomalies and extratropical Southern Hemisphere climate. J Clim 28:56–65. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00438.1
Ding Q, Steig EJ, Battisti DS, Wallace JM (2012) Influence of the tropics on the Southern Annular Mode. J Clim 25:6330–6348
Ding H, Richard J, Greatbatch Gollan G (2015) Tropical impact on the interannual variability and long-term trend of the Southern Annular Mode during austral summer from 1960/1961 to 2001/2002. Clim Dyn 44:2215–2228. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2299-x
Fogt RL, Bromwich DH, Hines KM (2011) Understanding the SAM influence on the South Pacific ENSO teleconnection. Clim Dyn 36:1555–1576
Gong DY, Wang SW (1998) Antarctic oscillation: concept and applications. Chin Sci Bull 43:734–738
Gong D, Wang S (1999) Definition of Antarctic oscillation index. Geophys Res Lett 26:459–462. doi:10.1029/1999GL900003
Hendon HH, Lim E-P, Arblaster JM, Anderson DTL (2014) Causes and predictability of the record wet spring over Australia in 2010. Clim Dyn 42:1155–1174
Ho M, Kiem AS, Verdon-Kidd DC (2012) The Southern Annular Mode: a comparison of indices. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:967–982
Ivchenko VO, Zalesny VB, Drinkwater MR (2004) Can the equatorial ocean quickly respond to Antarctica sea ice/salinity anomalies? Geophys Res Lett 31:L15310. doi:10.1029/2004GL020472.79521.18
Ivchenko VO, Zalesny VB, Drinkwater MR, Schröter J (2006) A quick response of the equatorial ocean to Antarctic sea ice/salinity anomalies. J Geophys Res 111:C10018. doi:10.1029/2005JC003061
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Leetama A, Reynolds B, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo KC, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Jenne R, Joseph D (1996) The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:437–471
Kendall MG, Stuart A (1979) The advanced theory of statistics, volume 2: inference and relationship, 4th edn. Hodder Arnold, Griffin, pp 758, ISBN: 0852642555
Kidson JW, Sinclair MR (1995) The influence of persistent anomalies on Southern Hemisphere storm tracks. J Clim 8:1938–1950
Kiem AS, Franks SW (2001) On the identification of ENSO induced rainfall and runoff variability: a comparison of methods and indices. Hydrol Sci J 46:715–727
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni AA, Inamdar SR, Prasad KD (1999) Teleconnections: Northern Hemisphere lower stratospheric geopotential heights and Indian monsoon rainfall. Meteorol Atmos Phys 69:195–203
Krishna Kumar K, Rajagopalan B, Hoerting M, Bates G, Cane M (2006) Unraveling the mystery of Indian monsoon failure during El-Niño. Science 314:115–119
Kushner PJ, Held IM, Delworth TL (2001) Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation response to global warming. J Clim 14:2238–2249
L’Heureux M, Thompson D (2006) Observed relationships between the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and the extra-tropical zonal-mean circulation. J Clim 19:276–287
Larkin NK, Harrison DE (2005) On the definition of El Niño and associated seasonal average U.S. weather anomalies. Geophys Res Lett 32:L13705. doi:10.1029/2005GL022738
Lee S, Feldstein SB (2013) Detecting ozone- and greenhouse-gas-driven wind trends with observational data. Science 339:6119. doi:10.1126/science.1225154
Limpasuvan V, Hartmann DL (1999) Eddies and the annular modes of climate variability. Geophys Res Lett 26:3133–3136
Limpasuvan V, Hartmann DL (2000) Wave-maintained annular modes of climate variability. J Clim 13:4414–4429
Marshall G (2003) Trends in the southern annular mode from observations and reanalysis. J Clim 16:4134–4143
Meneghini B, Simmonds I, Smith I (2007) Association between Australian rainfall and the Southern Annular Mode. Int J Clim 27:109–121
Nan S, Li J (2003) The relationship between summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley and the previous Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode. Geophys Res Lett 30(24):2266. doi:10.1029/2003GL018381
Nan S, Li JP, Yuan X, Zhao P (2008) Boreal spring Southern Hemisphere annual mode, Indian Ocean SST and East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res 114:D02103. doi:10.1029/2008JD010045
Nan S, Li J, Yuan X, Zhao P (2009) Boreal spring southern hemisphere annular mode, Indian Ocean sea surface temperature, and East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res 114:D02103. doi:10.1029/2008JD010045
Reason CJC, Rouault M (2005) Links between the Antarctic Oscillation and winter rainfall over western South Africa. Geophys Res Lett 32:L07705. doi:10.1029/2005GL022419
Reynolds RW, Rayner NA, Smith TM, Stokes DC, Wang W (2002) An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J Clim 15:1609–1625
Rogers JC, van Loon H (1982) Spatial variability of sea level pressure and 500mb height anomalies over the Southern Hemisphere. Mon Weather Rev 110:1375–1392
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363
Samanta D, Dash MK, Goswami BN, Pandey PC (2015) Extratropical anticyclonic Rossby wave breaking and Indian summer monsoon failure. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2661-7
Schneider U, Becker A, Finger P, Meyer-Christoffer A, Ziese M, Rudolf B (2014) GPCC’s new land surface precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in situ data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle. Theor Appl Climatol 115:15–40. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0860-x
Sen Gupta A, England M (2006) Coupled ocean–atmosphere feedback in the Southern Annular Mode. J Clim 20:3677–3692
Silvestri GE, Vera CS (2003) Antarctic Oscillation signal on precipitation anomalies over southeastern South America. Geophys Res Lett 30:2115. doi:10.1029/2003GL018277
Silvestri G, Vera C (2009) Nonstationary impacts of the Southern Annular Mode on Southern Hemisphere climate. J Clim. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI3036.1
Thompson DWJ, Wallace JM (2000a) Annular modes in the extratropical circulation. Part I: month-to-month variability. J Clim 13:1000–1016
Thompson DWJ, Wallace JM (2000b) Annular modes in the extratropical circulation. Part II: trends. J Clim 13:1018–1036
Viswambharan NK, Mohanakumar K (2013) Signature of a southern hemisphere extratropical influence on the summer monsoon over India. Clim Dyn 41(2):367–379
Walker GT (1924) Correlation in seasonal variations of weather, IV. A further study of world weather. Mem India Meteorol Dept 24:275–332
Wang G, Cai W (2013) Climate-change impact on the 20th-century relationship between the Southern Annular Mode and global mean temperature. Sci Rep 3:2039. doi:10.1038/srep02039
Wilson AB, Bromwich DH, Hines KM, Wang S-H (2014) El Niño flavors and their simulated impacts on atmospheric circulation in the high-southern latitudes. J Clim 27:8934–8955. doi:10.1175/JCLID-14-00296.1
Wu Z, Li J, Wang B, Liu X (2009) Can the Southern Hemisphere annular mode affect China winter monsoon? J Geophys Res 114:D11107. doi:10.1029/2008JD011501
Wu Z, Dou J, Lin H (2015) Potential influence of the November–December Southern Hemisphere annular mode on the East Asian winter precipitation: a new mechanism. Clim Dyn 44:1215–1226. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2241-2
Zheng F, Li JP (2012) Impact of preceeding boreal winter southern hemisphere annular mode on spring precipitation over south China and related mechanism. Chin J Geophys 55(11):3542–3557
Zheng F, Li J, Clark RT, Ding R, Li F, Wang L (2014) Influence of the boreal spring Southern Annular Mode on summer surface air temperature over northeast China. Atmos Sci Lett. doi:10.1002/asl2.541
Zhou T, Yu R (2004) Sea-surface temperature induced variability of the Southern Annular Mode in an atmospheric general circulation model. Geophys Res Lett 912(31):L24206. doi:10.1029/2004GL021473
Acknowledgments
Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) is fully supported by Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India. The authors wish to acknowledge the support of M. Rajeevan, Director, for providing all the facilities at IITM. Authors are also grateful to NCEP-NCAR, NOAA and NASA for providing the atmospheric, ocean and precipitation datasets respectively. Figures are prepared using GrADS. The comments and suggestions of two anonymous reviewers are appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhu, A., Kripalani, R.H., Preethi, B. et al. Potential role of the February–March Southern Annular Mode on the Indian summer monsoon rainfall: a new perspective. Clim Dyn 47, 1161–1179 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2894-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2894-5