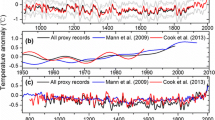
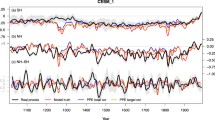
Abstract
Spatially resolved climate reconstructions are commonly derived from long instrumental series and proxy data via linear regression based approaches that use the main modes of the climate system. Such reconstructions have been shown to underestimate climate variability and are based upon the assumption that the main modes of climate variability are stationary back in time. Climate models simulate physically consistent climate fields but cannot be taken to represent the real past climate trajectory because of their necessarily simplified scope and chaotic internal variability. Here, we present sensitivity tests of, and a 200-year temperature reconstruction from, the PSR (Proxy Surrogate Reconstruction) method. This method simultaneously capitalizes on the individual strengths of instrumental/proxy data based reconstructions and model simulations by selecting the model states (analogs) that are most similar with proxy/instrumental data available at specific places and specific moments of time. Sensitivity experiments reveal an optimal PSR configuration and indicate that 6,500 simulation years of existing climate models provide a sufficient pool of possible analogs to skillfully reconstruct monthly European temperature fields during the past 200 years. Reconstruction verification based upon only seven instrumental stations indicates potential for extensions back in time using sparse proxy data. Additionally the PSR method allows evaluation of single time series, in this case the homogeneity of instrumental series, by identifying inconsistencies with the reconstructed climate field. We present an updated European temperature reconstruction including newly homogenized instrumental records performed with the computationally efficient PSR method that proves to capture the total variance of the target.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann CM, Joos F, Schimel DS, Otto-Bliesner BL, Tomas RA (2007) Solar influence on climate during the past millennium: results from transient simulations with the NCAR Climate System Model. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(10):3713–3718. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605064103
Auer I, Böhm R, Jurkovic A, Lipa W, Orlik A, Potzmann R, Schöner W, Ungersböck M, Matulla C, Briffa K, Jones P, Efthymiadis D, Brunetti M, Nanni T, Maugeri M, Mercalli L, Mestre O, Moisselin JM, Begert M, Müller-Westermeier G, Kveton V, Bochnicek O, Stastny P, Lapin M, Szalai S, Szentimrey T, Cegnar T, Dolinar M, Gajic-Capka M, Zaninovic K, Majstorovic Z, Nieplova E (2007) Histalp–historical instrumental climatological surface time series of the Greater Alpine Region. Int J Climatol 27(1):17–46. doi:10.1002/joc.1377
Barnett T, Preisendorfer R (1978) Multifield analog prediction of short-term climate fluctuations using a climate state vector. J Atmos Sci 35(10):1771–1787
Böhm R, Jones PD, Hiebl J, Frank D, Brunetti M, Maugeri M (2010) The early instrumental bias: a solution for long central European temperature series 1760–2007. Clim Change. doi:10.1007/s10584-009-9649-4 (in press)
Brohan P, Kennedy J, Harris I, Tett S, Jones P (2006) Uncertainty estimates in regional and global observed temperature changes: a new data set from 1850. J Geophys Res Atmos 111(D12):D12106. doi:10.1029/2005JD006548
Büntgen U, Wilson R, Franke J, Frank D, Esper J (2010) Proxy number and location to reconstruct European climate variability. Clim Res (in press)
Bürger G, Cubasch U (2005) Are multiproxy climate reconstructions robust. Geophys Res Lett 58:227–235
Bürger G, Fast I, Cubasch U (2006) Climate reconstruction by regression-32 variations on a theme. Tellus A 32:L23–71. doi:10.1029/2005GL024155
Christiansen B, Schmith T, Thejll P (2009) A surrogate ensemble study of climate reconstruction methods: stochasticity and robustness. J Clim 22(4):951–976
Collins M, Tett S, Cooper C (2001) The internal climate variability of HadCM3, a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments. Clim Dyn 17(1):61–81
Cook E, D’Arrigo R, Mann M (2002) A well-verified, multiproxy reconstruction of the winter North Atlantic Oscillation index since AD 1400. J Clim 15(13):1754–1764
Cook E, Woodhouse C, Eakin C (2004) Long-term aridity changes in the western United States. Science 306:1015–1018
Crespin E, Goosse H, Fichefet T, Mann ME (2009) The 15th century Arctic warming in coupled model simulations with data assimilation. Clim Past 5:389–401
Cubasch U, von Storch H, Waszkewitz J, Zorita E (1996) Estimates of climate change in Southern Europe derived from dynamical climate model output. Clim Res 7:129–149
Della-Marta PM, Luterbacher J, von Weissenfluh H, Xoplaki E, Brunet M, Wanner H (2007) Summer heat waves over western Europe 1880 2003, their relationship to large-scale forcings and predictability. Clim Dyn 29:251–275. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0233-1
ECMWF (2006) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ERA-40 Re-Analysis data. http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/ecmwf-e40, British Atmospheric Data Centre. June 2009
Esper J, Cook E, Schweingruber F (2002) Low-frequency signals in long tree-ring chronologies for reconstructing past temperature variability. Science 295(5563):2250–2253
Frank D, Büntgen U, Böhm R, Maugeri M, Esper J (2007) Warmer early instrumental measurements versus colder reconstructed temperatures: shooting at a moving target. Quat Sci Rev 26(25-28):3298–3310
Frank DC, Esper J, Raible CC, Buentgen U, Trouet V, Stocker B, Joos F (2010) Ensemble reconstruction constraints on the global carbon cycle sensitivity to climate. Nature 463(7280):527–530. doi:10.1038/nature08769
Franke J, Paul A, Schulz M (2008) Modeling variations of marine reservoir ages during the last 45,000 years. Clim Past 4:125–136
Gavin D, Oswald W, Wahl E, Williams J (2003) A statistical approach to evaluating distance metrics and analog assignments for pollen records. Quat Res 60(3):356–367
González-Rouco J, Zorita E, Cubasch U, von Storch H, Fisher-Bruns I, Valero F (2003) Simulating the climate since 1000 AD with the AOGCM ECHO-G. In: Wilson A (ed) Solar variability as an input to the Earth’s environment, International Solar Cycle Studies (ISCS) Symposium, Noordwijk: ESA Publications Division, Tatranská Lomnica, Slovak Republic, pp 329–338, ISBN 92-9092-845-X
González-Rouco JF, Beltrami H, Zorita E, von Storch H (2006) Simulation and inversion of borehole temperature profiles in surrogate climates: spatial distribution and surface coupling. Geophys Res Lett 33(1):L01–703. doi:10.1029/2005GL024693
González-Rouco JF, Beltrami H, Zorita E, Stevens MB (2009) Borehole climatology: a discussion based on contributions from climate modeling. Clim Past 5:97–127
Goosse H, Renssen H, Timmermann A, Bradley RS, Mann ME (2006) Using paleoclimate proxy-data to select optimal realisations in an ensemble of simulations of the climate of the past millennium. Clim Dyn 27(2-3):165–184. doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0128-6
Goosse H, Crespin E, de Montety A, Mann M, Renssen H, Timmermann A (2010) Reconstructing surface temperature changes over the past 600 years using climate model simulations with data assimilation. J Geophys Res Atmos (in press). doi:10.1029/2009JD012737
Graham NE, Hughes MK, Ammann CM, Cobb KM, Hoerling MP, Kennett DJ, Kennett JP, Rein B, Stott L, Wigand PE, Xu T (2007) Tropical pacific–mid-latitude teleconnections in medieval times. Clim Change 83(1-2):241–285. doi:10.1007/s10584-007-9239-2
Hegerl GC, Crowley TJ, Hyde WT, Frame DJ (2006) Climate sensitivity constrained by temperature reconstructions over the past seven centuries. Nature 440(7087):1029–1032. doi:10.1038/nature04679
Jansen E, J Overpeck KRB, Duplessy JC, Joos F, Masson-Delmotte V, Olago D, Otto-Bliesner B, Peltier WR, Rahmstorf S, Ramesh R, Raynaud D, Rind D, Solomina O, Villalba R, Zhang D (2007) Palaeoclimate. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
Jones P, Mann M (2004) Climate over past millennia. Rev Geophys 42:RG2002
Jones P, Moberg A (2003) Hemispheric and large-scale surface air temperature variations: an extensive revision and an update to 2001. J Clim 16(2):206–223
Jones P, Briffa K, Osborn T, Lough J, van Ommen T, Vinther B, Luterbacher J, Wahl E, Zwiers F, Mann M (2009) High-resolution palaeoclimatology of the last millennium: a review of current status and future prospects. The Holocene 19(1):3–49
Juckes M, Allen M, Briffa K, Esper J, Hegerl G, Moberg A, Osborn T, Weber S, Zorita E (2007) Millennial temperature reconstruction intercomparison and evaluation. Clim Past 3(4):591–609
Jungclaus JH, Lorenz SJ, Timmreck C, Reick CH, Brovkin V, Six K, Segschneider J, Giorgetta MA, Crowley TJ, Pongratz J, Krivova NA, Vieira LE, Solanki SK, Klocke D, Botzet M, Esch M, Gayler V, Haak H, Raddatz TJ, Roeckner E, Schnur R, Widmann H, Claussen M, Stevens B, Marotzke J (2010) Climate and carbon-cycle variability over the Last Millennium. Proc Natl Acad Sci (submitted)
Krivova N, Balmaceda L, Solanki S (2007) Reconstruction of solar total irradiance since 1700 from the surface magnetic flux. Astron Astrophys 467(1):335–346
Kruizinga S, Murphy A (1983) Use of an analogue procedure to formulate objective probabilistic temperature forecasts in the Netherlands. Mon Weather Rev 111(11):2244–2254
Küttel M, Xoplaki E, Gallego D, Luterbacher J, García-Herrera R, Allan R, Barriendos M, Jones P, Wheeler D, Wanner H (2010) The importance of ship log data: reconstructing North Atlantic, European and Mediterranean sea level pressure fields back to 1750. Clim Dyn (in press). doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0577-9
Lee TCK, Zwiers FW, Tsao M (2008) Evaluation of proxy-based millennial reconstruction methods. Clim Dyn 31(2-3):263–281. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0351-9
Lefohn A, Husar J, Husar R (1999) Estimating historical anthropogenic global sulfur emission patterns for the period 1850–1990. Atmos Environ 33:3435–3444
Lorenz E (1969) Studies of atmospheric predictability. Tech. rep., Massachusetts Institute of Technology, project No. 8604
Luterbacher J, Xoplaki E, Dietrich D, Rickli R, Jacobeit J, Beck C, Gyalistras D, Schmutz C, Wanner H (2002) Reconstruction of sea level pressure fields over the Eastern North Atlantic and Europe back to 1500. Clim Dyn 18:545–561
Luterbacher J, Dietrich D, Xoplaki E, Grosjean M, Wanner H (2004) European seasonal and annual temperature variability, trends, and extremes since 1500. Science 303(5663):1499–1503
Luterbacher J, König SJ, Franke J, van der Schrier G, Della-Marta PM, Jacobeit J, Kttel M, González-Rouco FJ, Zorita E, Xoplaki E, Stssel M, Rutishauser T, Wanner H, Pfister C, Brázdil R, Dobrovolny P, Camuffo D, Bertolin C, Moberg A, Leijonhufvud L, Soderberg J, Allan R, Wilson R, Wheeler D, Barriendos M, Glaser R, Riemann D, Nordli O, Limanwka D, van Engelen A, Zerefos CS (2010) Circulation dynamics and its influence on European and Mediterranean january-april climate over the past half millennium: results and insights from instrumental data, documentary proxy evidence and coupled climate models. Clim Change. doi:10.1007/s10584-009-9782-0 (in press)
MacFarling Meure C, Etheridge D, Trudinger C (2006) Law Dome CO2CH4 and N2O ice core records extended to 2000 years BP. Geophys Res Lett 33:L14810. doi:10.1029/2006GL026152
Mann M, Rutherford S (2002) Climate reconstruction using ‘Pseudoproxies’. Geophys Res Lett 29(10):1501. doi:10.1029/2001GL014554
Mann M, Bradley R, Hughes M (1998) Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries. Nature 392(6678):779–787
Mann M, Rutherford S, Wahl E, Ammann C (2005) Testing the fidelity of methods used in proxy-based reconstructions of past climate. J Clim 18(20):4097–4107
Mann M, Zhang Z, Hughes M, Bradley R, Miller S, Rutherford S, Ni F (2008) Proxy-based reconstructions of hemispheric and global surface temperature variations over the past two millennia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(36):13252–13257
Mann ME, Rutherford S, Wahl E, Ammann C (2007) Robustness of proxy-based climate field reconstruction methods. J Geophys Res 112(D12):D12109. doi:10.1029/2006JD008272
Mann ME, Zhang Z, Rutherford S, Bradley RS, Hughes MK, Shindell D, Ammann C, Faluvegi G, Ni F (2009) Global signatures and dynamical origins of the little ice age and medieval climate anomaly. Science 326(1256):1256–1260. doi:10.1126/science.1177303
Mitchell TD, Jones PD (2005) An improved method of constructing a database of monthly climate observations and associated high-resolution grids. Int J Climatol 25(6):693–712. doi:10.1002/joc.1181
Moberg A, Bergström H, Krigsman JR (2002) Daily air temperature and pressure series for Stockholm (1756–1998). Clim Change 53:171–212
Osborn TJ, Briffa KR (2006) The spatial extent of 20th-century warmth in the context of the past 1200 years. Science 311(5762):841–844. doi:10.1126/science.1120514
Parker D, Legg T, Folland C (1992) A new daily central England temperature series, 1772-1991. Int J Climatol 12(4):317–342
Pauling A, Luterbacher J, Casty C, Wanner H (2006) Five hundred years of gridded high-resolution precipitation reconstructions over Europe and the connection to large-scale circulation. Clim Dyn 26(4):387–405
Peixoto JP, Oort AH (1992) Physics of climate. Springer, New York
Peterson T, Vose R, Schmoyer R (1998) Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN) quality control of monthly temperature data. Int J Climatol 18:1169–1179
Petoukhov V, Claussen M, Berger A, Crucifix M, Eby M, Eliseev A, Fichefet T, Ganopolski A, Goosse H, Kamenkovich I, Mokhov I, Montoya M, Mysak L, Sokolov A, Stone P, Wang Z, Weaver A (2005) EMIC Intercomparison Project (EMIP-CO2): comparative analysis of EMIC simulations of climate, and of equilibrium and transient responses to atmospheric CO2 doubling. Clim Dyn 25(4):363–385. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0042-3
Pongratz J, Reick C, Raddatz T, Claussen M (2008) A reconstruction of global agricultural areas and land cover for the last millennium. Global Biogeochem Cycles 22(3):GB3018. doi:10.1029/2007GB003153
Raible CC, Casty C, Luterbacher J, Pauling A, Esper J, Frank DC, Büntgen U, Roesch AC, Tschuck P, Wild M, Vidale PL, Schär C, Wanner H (2006) Climate variability-observations, reconstructions, and model simulations for the Atlantic-European and Alpine Region from 1500–2100 AD. Clim Change 79(1–2):9–29. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9061-2
Riedwyl N, Küttel M, Luterbacher J, Wanner H (2009) Comparison of climate field reconstruction techniques: application to Europe. Clim Dyn 32(2–3):381–395. doi:10.1007/s00382-008-0395-5
Smerdon JE, Kaplan A (2007) Comments on Testing the fidelity of methods used in proxy-based reconstructions of past climate: the role of the standardization interval. J Clim 20(22):5666–5670. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1794.1
Smerdon JE, Kaplan A, Chang D (2008) On the origin of the standardization sensitivity in RegEM climate field reconstructions. J Clim 21(24):6710–6723. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2182.1
Stendel M, Mogensen I, Christensen J (2006) Influence of various forcings on global climate in historical times using a coupled atmosphere ocean general circulation model. Clim Dyn 26:1–15. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0041-4
Tanré D, Geleyn JF, Slingo J (1984) First results of the introduction of an advanced aerosolradiation interaction in ECMWF low resolution global model. In: Gerber HE, Deepak A (eds) Aerosols and their climatic effects. Deepak Publishing, Hampton, VA, pp 133–177
Tett S, Betts R, Crowley T, Gregory J, Johns T, Jones A, Osborn T, Öström E, Roberts D, Woodage M (2007) The impact of natural and anthropogenic forcings on climate and hydrology since 1550. Clim Dyn 28(1):3–34
Tingley M, Huybers P (2010a) A bayesian algorithm for reconstructing spatially arrayed temperatures. Part 1: development and applications to paleoclimate reconstruction problems. J Clim (in press)
Tingley M, Huybers P (2010b) A bayesian algorithm for reconstructing spatially arrayed temperatures. Part 2: comparison with the regularized expectation-maximization algorithm. J Clim (in press)
Trenberth K (1995) Atmospheric circulation climate changes. Clim Change 31(2):427–453
Trouet V, Esper J, Graham NE, Baker A, Scourse JD, Frank DC (2009) Persistent positive north Atlantic oscillation mode dominated the medieval climate anomaly. Science 324(5923):78–80. doi:10.1126/science.1166349
van den Dool H (1994) Searching for analogues, how long must we wait? Tellus A 46:314–324
van der Schrier G, Barkmeijer J (2005) Bjerknes’ hypothesis on the coldness during AD 1790–1820 revisited. Clim Dyn 25(5):537–553. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0053-0
von Storch H, Zwiers FW (2002) Statistical analysis in climate research. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
von Storch H, Cubasch U, González-Rouco J, Jones JM, Voss R, Widmann M, Zorita E (2000) Combining paleoclimatic evidence and GCMs by means of Data Assimilation Through Upscaling and Nudging(DATUN). 11th Symposium on Global Change Studies Long Beach, CA
von Storch H, Zorita E, Jones J, Dimitriev Y, Gonzalez-Rouco F, Tett S (2004) Reconstructing past climate from noisy data. Science 306(5696):679–682
Widmann M, Goosse H, van der Schrier G, Schnur R, Barkmeijer J (2009) Using data assimilation to study extratropical Northern Hemisphere climate over the last millennium. Clim Past Discuss 5:2115–2156
Xoplaki E, González-Rouco J, Gyalistras D, Luterbacher J, Rickli R, Wanner H (2003) Interannual summer air temperature variability over Greece and its connection to the large-scale atmospheric circulation and Mediterranean SSTs 1950–1999. Clim Dyn 20:537–554
Zhang Z, Mann M, Cook E (2004) Alternative methods of proxy-based climate field reconstruction: application to summer drought over the conterminous United States back to AD1700 from tree-ring data. The Holocene 14(4):502–516. doi:10.1191/0959683604hl727rp
Zorita E, von Storch H (1999) The analog method as a simple statistical downscaling technique: comparison with more complicated methods. J Clim 12(8):2474–2489
Zorita E, Hughes J, Lettemaier D, von Storch H (1995) Stochastic characterization of regional circulation patterns for climate model diagnosis and estimation of local precipitation. J Clim 8(5):1023–1042
Zorita E, González-Rouco F, Legutke S (2003) Testing the Mann et al. (1998) approach to paleoclimate reconstructions in the context of a 1000-yr control simulation with the ECHO-G coupled climate model. J Clim 16:1378–1390
Zorita E, González-Rouco F, von Storch H (2007) Comments on “Testing the fidelity of methods used in proxy-based reconstructions of past climate”. J Clim 20(14):3693–3698
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the EU project MILLENNIUM (#017008-GOCE) and by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) through its National Center of Competence in Research on Climate (NCCR Climate). We are thankful to all data-contributors: Johann Jungclaus et al. from the MPI in Hamburg; Simon Tett and Phil Brohan from Hadley Centre, Exeter; Jürg Luterbacher from the University of Gießen and Geert Jan van Oldenborgh from the KNMI (Climate-Explorer: http://climexp.knmi.nl). We also very much appreciated discussions with Ed Cook, Anders Moberg, Eduardo Zorita and Jan Esper. Finally we want to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franke, J., González-Rouco, J.F., Frank, D. et al. 200 years of European temperature variability: insights from and tests of the proxy surrogate reconstruction analog method. Clim Dyn 37, 133–150 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0802-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0802-6