Abstract
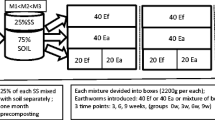
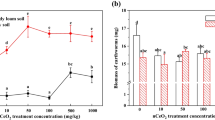
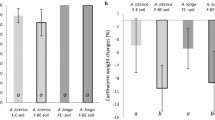
The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of engineered nanoparticles (NPs) on soil microbial biomass C (MBC) and on earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. An artificial soil was incubated for 4 weeks with earthworms fed with vegetable residues contaminated by NPs, consisting of Ag, Co, Ni and TiO2. After the treatments, soils were analysed for MBC and total and water soluble metal-NPs, whereas earthworms were purged for 28 days and then analysed for fatty acids (FAs) and total metal-NPs. Longitudinal sections of earthworms were investigated by environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM), equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), to provide insights about the retention and localization of NPs within earthworms. The nanoparticles reduced the MBC content in the following order Ag > Co > Ni, whereas TiO2 did not affect it. The ESEM-EDS analysis confirmed NP retention in earthworm guts and tissues. The solid/water coefficient of partition suggested that NPs interfered with living organisms due to their presence in suspension. Among the 27 FAs identified in earthworm tissues, the eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5ω3) was the most abundant. The degree of unsaturation of FAs was reduced by supplying NP-contaminated food.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams L, Lyon DY, Alvarez PJJ (2006) Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res 40:3527–3532
Ahamed M (2011) Toxic response of nickel nanoparticles in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25:930–936
Alt V, Bechert T, Steinrucke P, Wagener M, Seidel P, Dingeldein E, Domann E, Schnettler R (2004) An in vitro assessment of the antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity of nanoparticulate silver bone cement. Biomaterials 25:4383–4391
Asensio V, Rodríguez-Ruiz A, Garmendia L, Andre J, Kille P, Morgan AJ, Soto M, Marigómez I (2013) Towards an integrative soil health assessment strategy: a three tier (integrative biomarker response) approach with Eisenia fetida applied to soils subjected to chronic metal pollution. Sci Total Environ 442:344–365
Barnes RJ, Riba O, Gardner MN, Scott TB, Jackman SA, Thompson IP (2010) Optimization of nano-scale nickel/iron particles for the reduction of high concentration chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbon solutions. Chemosphere 79:448–454
Bigorgne E, Foucaud L, Lapied E, Labille J, Botta C, Sirguey C, Falla J, Rose J, Joner EJ, Rodius F, Nahmani J (2011) Ecotoxicological assessment of TiO2 byproducts on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 159:2698–2705
Blaser P, Zimmermann S, Luster J, Shotyk W (2000) Critical examination of trace element enrichments and depletions in soils: As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Swiss forest soils. Sci Total Environ 249:257–280
Burke DJ, Zhu S, Pablico-Lansigan MP, Hewins CR, Samia ACS (2014) Titanium oxide nanoparticle effects on composition of soil microbial communities and plant performance. Biol Fertil Soils. doi:10.1007/s00374-014-0938-3
Calisi A, Zaccarelli N, Lionetto MG, Schettino T (2012) Integrated biomarker analysis in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris: application to the monitoring of soil heavy metal pollution. Chemosphere 90:2637–2644
Chaperon S, Sauvé S (2007) Toxicity interaction of metals (Ag, Cu, Hg, Zn) to urease and dehydrogenase activities in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2329–2338
Collins JM, Dominey RN, Grogan WM (1990) Shape of the fluidity gradient in the plasma membrane of living HeLa cells. J Lipid Res 31:261–270
Crockett EL, Dougherty BE, McNamer AN (2001) Effects of acclimation temperature on enzymatic capacities and mitochondrial membranes from the body wall of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Comp Biochem Phys B 130:419–426
Dinesh R, Anandaraj M, Srinivasan V, Hamza S (2012) Engineered nanoparticles in the soil and their potential implications to microbial activity. Geoderma 173–174:19–27
Du W, Sun Y, Ji R, Zhu J, Wu J, Guo H (2011) TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles negatively affect wheat growth and soil enzyme activities in agricultural soil. J Environ Monit 13:822–828
Duarte AP, Freitas Melo V, Brown GG, Pauletti V (2014) Earthworm (Pontoscolex corethrurus) survival and impacts on properties of soils from a lead mining site in Southern Brazil. Biol Fertil Soils 50:851–860
Frostegård Å, Tunlid A, Bååth E (1993) Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. App Environ Microb 59:3605–3617
García JJ, Martinez-Ballariin E, Millan-Plano S, Allué JL, Albendea C, Fuentes L, Escanero JF (2005) Effects of trace elements on membrane fluidity. J Trace Elem Med Bio 19:19–22
Ge Y, Schimel JP, Holden PA (2011) Evidence for negative effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on soil bacterial communities. Environ Sci Technol 45:1659–1664
Hänsch M, Emmerling C (2010) Effects of silver nanoparticles on the microbiota and enzyme activity in soil. J Plant NutrSoil Sci 173:554–558
Howlett NG, Avery SV (1997) Relationship between cadmium sensitivity and degree of plasma membrane fatty acid unsaturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. App Microbiol Biotechnol 48:539–545
Jain D, Daima HK, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2009) Synthesis of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using papaya fruit extract and evaluation of their anti-microbial activities. Dig J Nanomater Bios 4:557–563
Jenkinson DS, Brookes PC, Powlson DS (2004) Measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 36:5–7
Kennedy AC (1994) Carbon utilization and fatty acid profiles for characterization of bacteria. In Weaver RW, Angle S, Bottomley P, Bezdicek D, Smith S, Tabatabai A, Wollum A (Eds), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: microbiological and biochemical properties, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp. 543–556
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY, Mahendra S, McLaughlin MJ, Lead JR (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behaviour, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1825–1851
Kool PL, Diez Ortiz M, van Gestel CAM (2011) Chronic toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles, non-nano ZnO and ZnCl2 to Folsomia candida (Collembola) in relation to bioavailability in soil. Environ Pollut 159:2713–2719
Lavelle P, Bignell D, Lepage M, Wolters V, Roger P, Ineson P, Heal OW, Dhillion S (1997) Soil function in a changing world: the role of invertebrate ecosystem engineers. Eur J Soil Biol 33:159–193
Massey PA, Creamer RE, Schulte RPO, Whelan MJ, Ritz K (2013) The effects of earthworms, botanical diversity and fertiliser type on the vertical distribution of soil nutrients and plant nutrient acquisition. Biol Fertil Soils 49:1189–1201
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramirez TJ, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
OECD (1984) Guideline for testing of chemicals No. 207, Earthworm acute toxicity test. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Paris, France
Paoletti MG, Buscardo E, VanderJagt DJ, Pastuszyn A, Pizzoferrato L, Huang YS, Chuang LT, Millson M, Cerda H, Torres F, Glew RH (2003) Nutrient content of earthworms consumed by Ye’Kuana Amerindians of the Alto Orinoco of Venezuela. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 270:249–257
Paraszkiewicz K, Bernat P, Dlugonski J (2009) Effect of nickel, copper, and zinc on emulsifier production and saturation of cellular fatty acids in the filamentous fungus Curvularia lunata. Int Biodeter Biodegr 63:100–105
Park J, Kang E, Son SU, Park HM, Lee MK, Kim J, Kim KW, Noh HJ, Park JH, Bae CJ, Park JG, Hyeon T (2005) Monodisperse nanoparticles of Ni and NiO: synthesis, characterization, self-assembled superlattices, and catalytic applications in the Suzuki coupling reaction. Adv Mater 17:429–434
Percival SL, Bowler PG, Dolman J (2007) Antimicrobial activity of silver-containing dressings on wound microorganisms using an in vitro biofilm model. Int Wound J 4:186–191
Petersen SO, Holmstrup M (2000) Temperature effects on lipid composition of the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Eisenia nordenskioeldi. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1787–1791
Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Munaro B, Broggi F, Marmorato P, Franchini F, Colognato R, Rossi F (2009) Genotoxicity and morphological transformation induced by cobalt nanoparticles and cobalt chloride: an in vitro study in Balb/3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Mutagenesis 24:439–445
Reinecke AJ (1992) A review of ecotoxicological test methods using earthworms. In Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (Eds.), Ecotoxicology of Earthworms. Intercept, Andover, MA, (pp. 7–19)
Sampedro L, Jeannotte R, Whalen JK (2006) Trophic transfer of fatty acids from gut microbiota to the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2188–2198
Sanchez-Hernandez JC (2006) Earthworm biomarkers in ecological risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam T 188:85–126
Schlich K, Klawonn T, Terytze K, Hund-Rinke K (2013) Effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate in the earthworm reproduction test. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:181–188
Schrand AM, Rahman MF, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Smith DA, Syed AF (2010) Metal-based nanoparticles and their toxicity assessment. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2:544–568
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Krogh PH, Schaefer M, Johansen A (2008) The toxicity testing of double-walled nanotubes-contaminated food to Eisenia veneta earthworms. Ecotox Environ Safe 71:616–619
Simonet BM, Valcárcel M (2009) Monitoring nanoparticles in the environment. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:7–21
Tourinho PS, Cornelis AM, Van Gestel AM, Lofts S, Svnedsen C, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2012) Metal-based nanoparticles in soil: fate, behaviour, and effects on soil invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1679–1692
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vittori Antisari L, Carbone S, Gatti A, Fabrizi A, Vianello G (2012a) Toxicological effects of engineered nanoparticles on earthworms (Lumbricus rubellus) in short exposure. Environ Qual 8:51–60
Vittori Antisari L, Carbone S, Gatti A, Vianello G, Nannipieri P (2012b) Toxicity of metal oxide (CeO2, Fe3O4, SnO2) engineered nanoparticles on soil microbial biomass and their distribution in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 60:87–94
Yang H, Wu Q, Tang M, Kong L, Lu Z (2009) Cell membrane injury induced by silica nanoparticles in mouse macrophage. J Biomed Nanotechnol 5:528–535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antisari, L.V., Laudicina, V.A., Gatti, A. et al. Soil microbial biomass carbon and fatty acid composition of earthworm Lumbricus rubellus after exposure to engineered nanoparticles. Biol Fertil Soils 51, 261–269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0972-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0972-1