Abstract
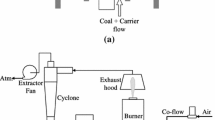
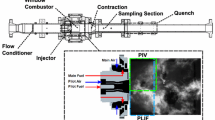
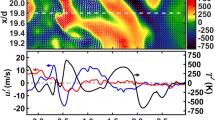
This paper demonstrates the application of laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) and particle image velocimetry (PIV) techniques to a particle-laden reacting flow of pulverized coal. A laboratory-scale open-type annular burner is utilized to generate velocity profiles of coal particles and micrometric alumina particles. Pair-wise two-component LDV measurements and high-speed stereo PIV measurements provide three-dimensional velocity components of the flow field. A detailed comparison of velocities for alumina and coal particle seeding revealed differences attributed to the wide size distribution of coal particles. In addition, the non-spherical shape and high flame luminosity associated with coal particle combustion introduces noise to the Mie scatter images. The comparison of mean and RMS velocities measured by LDV and PIV techniques showed that PIV measurements are affected by the wide size distribution of coal particles, whereas LDV measurements become biased toward the velocity of small particles, as signals from large particles are rejected. This small-particle bias is also reflected in the spectral characteristics for both techniques, which are in good agreement within the range of frequencies accessible. PIV measurements showed an expected lack of response of large coal particles to the turbulence fluctuations. The overall good agreement between LDV and PIV measurements demonstrates the applicability of the high-speed PIV technique to a particle-laden, high luminosity coal flame while highlighting some of its limitations.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (2005) Twenty years of particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 39(2):159–169
Benedict LH, Gould RD (1996) Towards better uncertainty estimates for turbulence statistics. Exp Fluids 22(2):129–136
Benedict LH, Nobach H, Tropea C (2000) Estimation of turbulent velocity spectra from laser Doppler data. Meas Sci Technol 11(8):1089–1104
Buhre BJP, Elliott LK, Sheng CD, Gupta RP, Wall TF (2005) Oxy-fuel combustion technology for coal-fired power generation. Prog Energy Combust Sci 31(4):283–307
Cant RS, Mastorakos E (2008) An introduction to turbulent reacting flows. Imperial College Press, London, ISBN 978-1-86094-778-0
Chen L, Yong SZ, Ghoniem AF (2012) Oxy-fuel combustion of pulverized coal: characterization, fundamentals, stabilization and cfd modeling. Prog Energy Combust Sci 38(2):156–214
Costa M, Silva P, Azevedo JLT (2003) Measurements of gas species, temperature, and char burnout in a low-no x pulverized-coal-fired utility boiler. Combust Sci Technol 175(2):271–289
Edge P, Gharebaghi M, Irons R, Porter R, Porter RTJ, Pourkashanian M, Smith D, Stephenson P, Williams A (2011) Combustion modelling opportunities and challenges for oxy-coal carbon capture technology. Chem Eng Res Des 89(9):1470–1493
el Gendy H, Preciado I, Ring T, Eddings E (2010) Particle image velocimetry of pulverized oxy-coal flames. In: AIChE annual meeting, Salt Lake City, Utah
Heil P, Toporov D, Stadler H, Tschunko S, Förster M, Kneer R (2009) Development of an oxycoal swirl burner operating at low o2 concentrations. Fuel 88(7):1269–1274
Hwang SM, Kurose R, Akamatsu F, Tsuji H, Makino H, Katsuki M (2005) Application of optical diagnostics techniques to a laboratory-scale turbulent pulverized coal flame. Energy Fuels 19(2):382–392
Hwang SM, Kurose R, Akamatsu F, Tsuji H, Makino H, Katsuki M (2006) Observation of detailed structure of turbulent pulverized-coal flame by optical measurement- (part 1, time-averaged measurement of behavior of pulverized-coal particles and flame structure). JSME Int J Ser B 49:1316–1327
IEA (ed) (2012) Medium-term coal market report 2012—market trends and projections to 2017. International Energy Agency, Paris, ISBN 978-92-64-17795-6
Jensen PA, Ereaut PR, Clausen S, Rathmann O (1994) Local measurements of velocity, temperature and gas composition in a pulverized-coal flame. J Inst Energy 67(470):37–46
Kihm KD, Sun F, Chigier N (1990) Laser Doppler velocimetry investigation of swirler flowfields. J Propul Power 6(4):364–374
Kurose R, Watanabe H, Makino H (2009) Numerical simulations of pulverized coal combustion. KONA Powder Part J 27:144–156
Lee SL, Durst F (1982) On the motion of particles in turbulent duct flows. Int J Multiph Flow 8(2):125–146
Mattern P, Sieber S, Dues M, Caglar S, Gabi M (2012) Simultaneous high speed stereo piv and lda measurements in the highly transient vortical wake of an axial fan. In: 16th International symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal
Most JM, Trouillet P, Jallais S, Mandin P, Marchand F, Le-Masson C, Witwicki P, Rampelberg D (2000) Development of a LDV probe for velocity measurements in a 600 mw pulverized coal power plant. In: Proceeding of 10th international symposium on laser technique techniques and applications, Lisbon, Portugal
Pickett LM, Jackson RE, Tree DR (1999) Lda measurements in a pulverized coal flame at three swirl ratios. Combust Sci Technol 143(1):79–107
Schnell U, Kaess M, Brodbek H (1993) Experimental and numerical investigation of NOx formation and its basic interdependences on pulverized coal flame characteristics. Combust Sci Technol 93(1):91–109
Spencer A, Hollis D (2005) Correcting for sub-grid filtering effects in particle image velocimetry data. Meas Sci Technol 16(11):2323–2335
Toftegaard MB, Brix J, Jensen PA, Glarborg P, Jensen AD (2010) Oxy-fuel combustion of solid fuels. Prog Energy Combust Sci 36(5):581–625
Toporov D, Bocian P, Heil P, Kellermann A, Stadler H, Tschunko S, Förster M, Kneer R (2008) Detailed investigation of a pulverized fuel swirl flame in co2/o2 atmosphere. Combust Flame 155(4):605–618
Tropea C, Yarin AL, Foss JF (eds) (2007) Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics. Springer, Berlin, ISBN 978-3-540-25141-5
Wall T, Liu Y, Spero C, Elliott L, Khare S, Rathnam R, Zeenathal F, Moghtaderi B, Buhre B, Sheng C, Gupta R, Yamada T, Makino K, Yu J (2009) An overview on oxyfuel coal combustion—state of the art research and technology development. Chem Eng Res Des 87(8):1003–1016
Wall TF (2007) Combustion processes for carbon capture. Proc Combust Inst 31(1):31–47
Zhou R, Balusamy S, Hochgreb S (2012) A tool for the spectral analysis of the laser Doppler anemometer data of the Cambridge stratified swirl burner. Tech. Rep. CUED/A-TURBO/TR.135, Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge. http://www.dspace.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/243258
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. M. Pourkashanian, Prof. A. Hayhurst, Dr. S. Scott for their valuable guidance on coal handling and Dr W. Nimmo for the supply of coal samples. This work is supported by EPSRC research grant (#EP/G062153/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balusamy, S., Schmidt, A. & Hochgreb, S. Flow field measurements of pulverized coal combustion using optical diagnostic techniques. Exp Fluids 54, 1534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-013-1534-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-013-1534-2