Abstract
Key message
Endogenous JA production is not necessary for wound-induced expression of JA-biosynthetic lipase genes such as DAD1 in Arabidopsis. However, the JA-Ile receptor COI1 is often required for their JA-independent induction.
Abstract
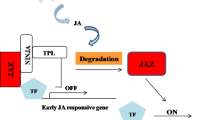
Wounding is a serious event in plants that may result from insect feeding and increase the risk of pathogen infection. Wounded plants produce high amounts of jasmonic acid (JA), which triggers the expression of insect and pathogen resistance genes. We focused on the transcriptional regulation of DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 and six of its homologs including DONGLE (DGL) in Arabidopsis, which encode lipases involved in JA biosynthesis. Plants constitutively expressing DAD1 accumulated a higher amount of JA than control plants after wounding, indicating that the expression of these lipase genes contributes to determining JA levels. We found that the expression of DAD1, DGL, and other DAD1-LIKE LIPASE (DALL) genes is induced upon wounding. Some DALLs were also expressed in unwounded leaves. Further experiments using JA-biosynthetic and JA-response mutants revealed that the wound induction of these genes is regulated by several distinct pathways. DAD1 and most of its homologs other than DALL4 were fully induced without relying on endogenous JA-Ile production and were only partly affected by JA deficiency, indicating that positive feedback by JA is not necessary for induction of these genes. However, DAD1 and DGL required CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 (COI1) for their expression, suggesting that a molecule other than JA might act as a regulator of COI1. Wound induction of DALL1, DALL2, and DALL3 did not require COI1. This differential regulation of DAD1 and its homologs might explain their functions at different time points after wounding.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boter M, Ruíz-Rivero O, Abdeen A, Prat S (2004) Conserved MYC transcription factors play a key role in jasmonate signaling both in tomato and Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 18:1577–1591
Böttcher C, Pollmann S (2009) Plant oxylipins: plant responses to 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid are governed by its specific structural and functional properties. FEBS J 276:4693–4704
Chini A, Fonseca S, Fernández G, Adie B, Chico JM, Lorenzo O, García-Casado G, López-Vidriero I, Lozano FM, Ponce MR, Micol JL, Solano R (2007) The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature 448:666–671
Delessert C, Wilson IW, Van Der Straeten D, Dennis ES, Dolferus R (2004) Spatial and temporal analysis of the local response to wounding in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Mol Biol 55:165–181
Dombrecht B, Xue GP, Sprague SJ, Kirkegaard JA, Ross JJ, Reid JB, Fitt GP, Sewelam N, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Kazan K (2007) MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2225–2245
Ellinger D, Kubigsteltig II (2010) Involvement of DAD1-like lipases in response to salt and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sig Behav 5:1269–1271
Ellinger D, Stingl N, Kubigsteltig II, Bals T, Juenger M, Pollmann S, Berger S, Schuenemann D, Mueller MJ (2010) DONGLE and DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 lipases are not essential for wound- and pathogen-induced jasmonate biosynthesis: redundant lipases contribute to jasmonate formation. Plant Physiol 153:114–127
Feys B, Benedetti CE, Penfold CN, Turner JG (1994) Arabidopsis mutants selected for resistance to the phytotoxin coronatine are male sterile, insensitive to methyl jasmonate, and resistant to a bacterial pathogen. Plant Cell 6:751–759
Glauser G, Dubugnon L, Mousavi SA, Rudaz S, Wolfender JL, Farmer EE (2009) Velocity estimates for signal propagation leading to systemic jasmonic acid accumulation in wounded Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 284:34506–34513
Hyun Y, Choi S, Hwang HJ, Yu J, Nam SJ, Ko J, Park JY, Seo YS, Kim EY, Ryu SB, Kim WT, Lee YH, Kang H, Lee I (2008) Cooperation and functional diversification of two closely related galactolipase genes for jasmonate biosynthesis. Dev Cell 14:183–192
Ishiguro S, Kawai-Oda A, Ueda J, Nishida I, Okada K (2001) The DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCIENCE1 gene encodes a novel phospholipase A1 catalyzing the initial step of jasmonic acid biosynthesis, which synchronizes pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and flower opening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2191–2209
Kallenbach M, Alagna F, Baldwin IT, Bonaventure G (2010) Nicotiana attenuata SIPK, WIPK, NPR1, and fatty acid-amino acid conjugates participate in the induction of jasmonic acid biosynthesis by affecting early enzymatic steps in the pathway. Plant Physiol 152:96–106
Kazan K, Manners JM (2013) MYC2: the master in action. Mol Plant 6:686–703
Lorenzo O, Chico JM, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Solano R (2004) JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1938–1950
Padham AK, Hopkins MT, Wang TW, McNamara LM, Lo M, Richardson LGL, Smith MD, Taylor CA, Thompson JE (2007) Characterization of a plastid triacylglycerol lipase from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1372–1384
Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C, Schwab R, Carrington JC, Weigel D (2003) Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 425:257–263
Park JH, Halitschke R, Kim HB, Baldwin IT, Feldmann KA, Feyereisen R (2002) A knock-out mutation in allene oxide synthase results in male sterility and defective wound signal transduction in Arabidopsis due to a block in jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 31:1–12
Reymond P, Weber H, Damond M, Farmer EE (2000) Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:707–719
Ribot C, Zimmerli C, Farmer EE, Reymond P, Poirier Y (2008) Induction of the Arabidopsis PHO1;H10 gene by 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid but not jasmonic acid via a CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1-dependent pathway. Plant Physiol 147:696–706
Richmond GS, Smith TK (2011) Phospholipases A1. Int J Mol Sci 12:588–612
Ryu SB (2004) Phospholipid-derived signaling mediated by phospholipase A in plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:229–235
Sanders PM, Lee PY, Biesgen C, Boone JD, Beals TP, Weiler EW, Goldberg RB (2000) The Arabidopsis DELAYED DEHISCENCE1 gene encodes an enzyme in the jasmonic acid synthesis pathway. Plant Cell 12:1041–1061
Sasaki-Sekimoto Y, Jikumaru Y, Obayashi T, Saito H, Masuda S, Kamiya Y, Ohta H, Shirasu K (2013) Basic Helix-Loop-Helix transcription factors JASMONATE-ASSOCIATED MYC2-LIKE1 (JAM1), JAM2, and JAM3 are negative regulators of jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 163:291–304
Schaller A, Stintzi A (2009) Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis—structure, function, regulation. Phytochemistry 70:1532–1538
Schilmiller AL, Koo AJ, Howe GA (2007) Functional diversification of acyl-coenzyme A oxidases in jasmonic acid biosynthesis and action. Plant Physiol 143:812–824
Schommer C, Palatnik JF, Aggarwal P, Chételat A, Cubas P, Farmer EE, Nath U, Weigel D (2008) Control of jasmonate biosynthesis and senescence by miR319 targets. PLoS Biol 6:e230
Seo YS, Kim EY, Kim JH, Kim WT (2009) Enzymatic characterization of class I DAD1-like acylhydrolase members targeted to chloroplast in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett 583:2301–2307
Staswick PE, Tiryaki I (2004) The oxylipin signal jasmonic acid is activated by an enzyme that conjugates it to isoleucine in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2117–2127
Stintzi A, Browse J (2000) The Arabidopsis male-sterile mutant, opr3, lacks the 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductase required for jasmonate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10625–10630
Stintzi A, Weber H, Reymond P, Browse J, Farmer EE (2001) Plant defense in the absence of jasmonic acid: the role of cyclopentenones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12837–12842
Stotz HU, Jikumaru Y, Shimada Y, Sasaki E, Stingl N, Mueller MJ, Kamiya Y (2011) Jasmonate-dependent and COI1-independent defense responses against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Arabidopsis thaliana: auxin is part of COI1-independent defense signaling. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1941–1956
Stotz HU, Mueller S, Zoeller M, Mueller MJ, Berger S (2013) TGA transcription factors and jasmonate-independent COI1 signalling regulate specific plant responses to reactive oxylipins. J Exp Bot 64:963–975
Tabata R, Ikezaki M, Fujibe T, Aida M, Tian CE, Ueno Y, Yamamoto KT, Machida Y, Nakamura K, Ishiguro S (2010) Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR6 and 8 regulate jasmonic acid biosynthesis and floral organ development via repression of class 1 KNOX genes. Plant Cell Physiol 51:164–175
Taki N, Sasaki-Sekimoto Y, Obayashi T, Kikuta A, Kobayashi K, Ainai T, Yagi K, Sakurai N, Suzuki H, Masuda T, Takamiya K, Shibata D, Kobayashi Y, Ohta H (2005) 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid triggers expression of a distinct set of genes and plays a role in wound-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:1268–1283
Thines B, Katsir L, Melotto M, Niu Y, Mandaokar A, Liu G, Nomura K, He SY, Howe GA, Browse J (2007) JAZ repressor proteins are targets of the SCFCOI1 complex during jasmonate signalling. Nature 448:661–665
Vick BA, Zimmerman DC (1984) Biosynthesis of jasmonic acid by several plant species. Plant Physiol 75:458–461
von Malek B, van der Graaff E, Schneitz K, Keller B (2002) The Arabidopsis male-sterile mutant dde2-2 is defective in the ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE gene encoding one of the key enzymes of the jasmonic acid biosynthesis pathway. Planta 216:187–192
Wasternack C, Hause B (2013) Jasmonates: biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in annals of botany. Ann Bot 111:1021–1058
Wasternack C, Xie D (2010) The genuine ligand of a jasmonic acid receptor: improved analysis of jasmonates is now required. Plant Sig Behav 5:337–340
Yan J, Zhang C, Gu M, Bai Z, Zhang W, Qi T, Cheng Z, Peng W, Luo H, Nan F, Wang Z, Xie D (2009) The Arabidopsis CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 protein is a jasmonate receptor. Plant Cell 21:2220–2236
Zheng XY, Spivey NW, Zeng W, Liu PP, Fu ZQ, Klessig DF, He SY, Dong X (2012) Coronatine promotes Pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation. Cell Host Microbe 11:587–596
Acknowledgments
The mutant coi1-51 was identified and provided by Dr. Takashi Araki (Kyoto University). We thank Dr. Yusuke Jikumaru and Ms. Tomoe Nose of RIKEN for JA measurement, and Dr. Kenichiro Maeo, Dr. Ryo Tabata, Dr. Tomoko Niwa, and Ms. Kanako Nakano of Nagoya University for materials, comments, and helpful discussion. This work was financed by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research no. 21•09098 to I.R. and S.I.). I.R. was a recipient of the Postdoctoral Fellowships for Foreign Researchers from JSPS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Sato.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruduś, I., Terai, H., Shimizu, T. et al. Wound-induced expression of DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 and DAD1-like lipase genes is mediated by both CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1-dependent and independent pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Cell Rep 33, 849–860 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1561-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1561-8