Abstract
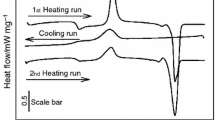
Two new synthetic silico-metallic mineral particles like TOT–TOT swelling interstratified (SSMMP) produced with distinct hydrothermal processes (talc 7 h/315 °C and talc 24 h/205 °C) were used to synthesize polyurethane nanocomposites by in situ polymerization technique. These fillers were added in a range of 0.5–5 wt% related to the mass of the pure polymer. The dispersion and interaction between the fillers and the polymeric matrix were evaluated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The X-ray analysis indicated that the synthetic SSMMP are well dispersed/or exfoliated into the polymer matrix. The high surface area of the synthetic SSMMP was significant for the increase in the crystallinity and thermal properties of the nanocomposites. In the case of Young’s modulus, for nanocomposites PU/SSMMP 24 h and the pristine PU, a similar behavior was observed. However, for the nanocomposites PU/SSMMP 7 h, an increase in the Young´s modulus values until 3 % of filler addition when compared to pure PU was noticed. The creep-recovery test showed that both SSMMP behave as a mechanical restraint of the polyurethane chains. The results evidenced the importance of the SSMMP syntheses conditions to obtain nanocomposites with desired properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zilg C, Thomann R, Mülhaupt R, Finter J (1999) Polyurethane nanocomposites containing laminated anisotropic nanoparticles derived from organophilic layered silicates. Adv Mater 11:49–52
Zhang X, Xu R, Wu Z, Zhou C (2003) The synthesis and characterization of polyurethane/clay nanocomposites. Polym Int 52:790–794
Esteves ACC, Barros-Timmons A, Trindade T (2004) Nanocompósitos de matriz polimérica: estratégias de síntese de materiais híbridos. Quim Nova 27:798–806
Jiang-Ping H, Hua-Ming L, Xia-Yu W, Yong G (2006) In situ preparation of poly (ethylene terephthalate)–SiO2 nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 42:1128–1134
Gacitua WE, Ballerini AA, Zhang J (2005) Polymer nanocomposites: synthetic and natural fillers a review. Cienc y Tec 7:159–178
Dumas A, Martin F, Le Roux C, Micoud P, Petit S, Ferrage E, Brendlé J, Grauby O, Greenhill-Hooper M (2013) Phyllosilicates synthesis: a way of accessing edges contributions in NMR and FTIR spectroscopies. Example of synthetic talc. Phys Chem Miner 40:361–373
Dumas A, Martin F, Ferrage E, Micoud P, Le Roux C, Petit S (2013) Synthetic talc advances: coming closer to nature, added value, and industrial requirements. Appl Clay Sci 85:8–18
Yousfi M, Livi S, Dumas A, Le Roux C, Crépin-Leblond J, GreenHill-Hooper M, Duchet-Rumeau J (2013) Use of new synthetic talc as reinforcing nanofillers for polypropylene and polyamide 6 systems: thermal and mechanical properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 403:29–42
Mehrjerdi AK, Adl-Zarrabi B, Cho SW, Skrifvars M (2013) Mechanical and thermo-physical properties of high-density polyethylene modified with talc. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/APP.38945
Balamurugan GP, Maiti SN (2010) Effects of nanotalc inclusion on mechanical, microstructural, melt shear rheological, and crystallization behavior of polyamide 6-based binary and ternary nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci. doi:10.1002/pen.21724
Yu F, Liu T, Zhao X, Yu X, Lu A, Wang J (2012) Effects of talc on the mechanical and thermal properties of polylactide. J Appl Polym Sci 125:E99–E109
Zhao G, Wang T, Wang Q (2012) Studies on wettability, mechanical and tribological properties of the polyurethane composites filled with talc. Appl Surf Sci 258:3557–3564
Bajsic EG, Rek V, Pavic BO (2013) The influence of talc content on the thermal and mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane/polypropylene blends. J Elast Plast. doi:10.1177/0095244312458602
Bajsic EG, V Rek, Cosic I (2014) Preparation and characterization of talc filled thermoplastic polyurethane/polypropylene blends. J Polym. pp 1–8. Article ID 289283. doi:10.1155/2014/289283
Shakoor A, Thomas NL (2013) Talc as a nucleating agent and reinforcing filler in poly (lactic acid) composites. Polym Eng Sci. doi:10.1002/pen
Jain S, Misra M, Mohanty AK, Ghosh AK (2012) Thermal, mechanical and rheological behavior of poly (lactic acid)/talc composites. J Polym Environ 20:1027–1037
Fiorentino B, Fulchiron R, Duchet-Rumeau J, Bounor-Regaré V, Majesté JC (2013) Controlled shear-induced molecular orientation and crystallization in polypropylene/talc microcomposites—effects of the talc nature. Polymer 54:2764–2775
Wang K, Bahlouli N, Addiego F, Ahzi S, Rémond Y, Ruch D, Muller R (2013) Effect of talc content on the degradation of re-extruded polypropylene/talc composites. Polym Degrad Stab 98:1275–1286
Castillo LA, Barbosa SE, Capiati NJ (2013) Influence of talc morphology on the mechanical properties of talc filled polypropylene. J Polym Res 20:152
Lapcik L Jr, Jindrova P, Lapcikova B, Tamblyn R, Greenwood R, Rowson N (2008) Effect of the talc filler content on the mechanical properties of polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci 110:2742–2747
Leong YW, Abu Bakar MB, Mohd Ishak ZA, Ariffin A, Pukansky B (2004) Comparison of the mechanical properties and interfacial interactions between talc, kaolin, and calcium carbonate filled polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci 91:3315–3326
Zhou Y, Rangari V, Mahfuz H, Jeelani S, Mallick PK (2005) Experimental study on thermal and mechanical behavior of polypropylene, talc/polypropylene and polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng A 402:109–117
Castillo LA, Barbosa SE, Capiati NJ (2012) Influence of talc genesis and particle surface on the crystallization kinetics of polypropylene/talc composites. J Appl Polym Sci 126:1763–1772
Zhou XP, Xie XL, Yu ZZ, Mai YW (2007) Intercalated structure of polypropylene/in situ polymerization-modified talc composites via melt compounding. Polymer 48:3555–3564
Abu Bakar MB, Leong YW, Ariffin A, Mohd. Ishak ZA (2007) Mechanical, flow, and morphological properties of talc- and kaolin-filled polypropylene hybrid composites. J Appl Polym Sci 104:434–441
Leong YW, Mohd-Ishak ZA, Ariffin A (2004) Mechanical and thermal properties of talc and calcium carbonate filled polypropylene hybrid composites. J Appl Polym Sci 91:3327–3336
Yousfi M, Livi S, Dumas A, Crépin-Leblond J, GreenHill-Hooper M, Duchet-Rumeau J (2014) Compatibilization of polypropylene/polyamide 6 blends using new synthetic nanosized talc fillers: morphology, thermal and mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.40453
Prado MA, Dias G, Carone C, Ligabue R, Dumas A, Le Roux C, Micoud P, Martin F, Einloft S (2014) Synthetic Ni-talc as filler for producing polyurethane nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.41854
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Sinha Ray S, Okamoto M (2003) Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing. Prog Polym Sci 28:1539–1641
Wang G, Ma G, Hou C, Guan T, Ling L, Wang B (2014) Preparation and properties of waterborne polyurethane/nanosilica composites: a diol as extender with triethoxysilane group. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/APP.40526
Martin F et al (1999) The structural formula of talc from the trimouns deposit, Pyrenees, France. Can Miner 37:997–1006
Zhang M et al (2006) Dehydroxylation, proton migration, and structural changes in heated talc: an infrared spectroscopic study. Am Miner 91:816–825
Russell JD, Farmer VC, Velde B (1970) Replacement of OH by OD in layer silicates, and identification of the vibrations of these groups in infra-red spectra. Miner Mag 37:292
Demétrio da Silva V, Moreira dos Santos LM, Subda SM, Ligabue R, Seferin M, Carone CLP, Einloft S (2013) Synthesis and characterization of polyurethane/titanium dioxide nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization. Polym Bull 70:1819–1833
Polizos G, Tuncer E, Agapov AL, Stevens D, Sokolov AP, Kidder MK, Jacobs JD, Koerner H, Vaia RA, More KL, Sauers I (2012) Effect of polymer–nanoparticle interactions on the glass transition dynamics and the conductivity mechanism in polyurethane titanium dioxide nanocomposites. Polymer 53:595–603. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2011.11.050
Rogers M, Long T (2003) Synthetic methods in step-growth polymers. Wiley
Amico SC, Freitag CPM, Riegel IC, Pezzin SH (2011) Efeito da incorporação do talco nas características térmicas, mecânicas e dinâmico-mecânicas de poliuretanos termoplásticos. Rev Mat 16:597–605
Liu ZW, Chou HC, Chen SH, Tsao CT, Chuang CN, Cheng CN, Yang CH, Wang CK, Hsieh KH (2014) Mechanical and thermal properties of thermoplastic polyurethane-toughened polylactide-based nanocomposites. Polym Compos 35:1744–1757
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank FAPERGS for financial support. GD and MP thank FAPERGS and CAPES for their master scholarship. SE and RL acknowledge CNPq for DT grant and CC CAPES for PNPD post-doc fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dias, G., Prado, M.A., Carone, C. et al. Synthetic silico-metallic mineral particles (SSMMP) as nanofillers: comparing the effect of different hydrothermal treatments on the PU/SSMMP nanocomposites properties. Polym. Bull. 72, 2991–3006 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1449-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1449-6