Abstract
Although the use of TNF-α in the treatment of cancer is restricted due to its non-specific cytotoxicity and narrow range of applications to different cancers in clinical trials, we investigated a safe anti-cancer drug by the use of engineered bacterial capsule harboring TNF-α. The engineered bacterial capsule was designed to target cancer cells, promote a tumor-suppressive environment, and increase the efficacy of existing cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and cell therapy. The engineered bacterial capsule was constructed with Salmonella capsulizing TNF-α protein, which was produced and capsulized by Salmonella to reduce side effects of the protein. This bacterial capsule induced a tumor-suppressive environment through the activation of natural killer cells. Engineered bacterial capsule invaded tumor cells, released TNF-α, and induced apoptosis of tumor cells without apparent side effects. In a murine melanoma model, the bacterial capsule of TNF-α significantly inhibited tumor growth by 80–100% and prolonged the survival of the mice. When tested in combination with chemotherapy (cisplatin), antibiotics, and vaccine, recombinant microbial treatment increased the anti-tumor effects of existing therapies. The anti-tumor effects of the bacterial capsule of TNF-α were also observed in cervical cancer, melanoma, breast cancer, colon cancer, and renal carcinoma. These results suggest that the bacterial capsule of TNF-α is a promising strategy for TNF-α treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baselga J, Semiglazov V, van Dam P, Manikhas A, Bellet M, Mayordomo J, Campone M, Kubista E, Greil R, Bianchi G, Steinseifer J, Molloy B, Tokaji E, Gardner H, Phillips P, Stumm M, Lane HA, Dixon JM, Jonat W, Rugo HS (2009) Phase II randomized study of neoadjuvant everolimus plus letrozole compared with placebo plus letrozole in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:2630–2637
Beck CF, Ingraham JL, Neuhard J (1972) Location on the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium of genes governing pyrimidine metabolism. II. Uridine kinase, cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase. Mol Gen Genet 115:208–215
Bermudes D, Low B, Pawelek J (2000) Tumor-targeted Salmonella. Highly selective delivery vectors. Adv Exp Med Biol 465:57–63. doi:10.1007/0-306-46817-4_6
Bocci V (1988) Central nervous system toxicity of interferons and other cytokines. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2:107–118
Bouayadi K, Salles B (1995) Influence of DNA supercoiling on cisplatin toxicity in Escherichia coli K-12. Mutat Res 348:25–31
Braybrooke JP, Slade A, Deplanque G, Harrop R, Madhusudan S, Forster MD, Gibson R, Makris A, Talbot DC, Steiner J, White L, Kan O, Naylor S, Carroll MW, Kingsman SM, Harris AL (2005) Phase I study of MetXia-P450 gene therapy and oral cyclophosphamide for patients with advanced breast cancer or melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:1512–1520
Chen JT, Hasumi K, Masubuchi K (1992) Interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma and sizofiran in the adjuvant therapy in ovarian cancer—a preliminary trial. Biotherapy 5:275–280
Dietrich G, Spreng S, Gentschev I, Goebel W (2000) Bacterial systems for the delivery of eukaryotic antigen expression vectors. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 10:391–399
Fichtner I, Lemm M, Becker M, Tanneberger S (1990) Determination of antineoplastic activity and toxicity of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in animal experiments. Correlation to clinical findings. Neoplasma 37:301–315
Freytag SO, Movsas B, Aref I, Stricker H, Peabody J, Pegg J, Zhang Y, Barton KN, Brown SL, Lu M, Savera A, Kim JH (2007) Phase I trial of replication-competent adenovirus-mediated suicide gene therapy combined with IMRT for prostate cancer. Mol Ther 15:1016–1023
Goren MP, Wright RK, Horowitz ME (1986) Cumulative renal tubular damage associated with cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 18:69–73
Green S, Chiasson MA, Shah RG (1979) Evidence for the presence of an antitumor factor in serum of normal animals. Cancer Lett 6:235–240
Hanna N (1982) Inhibition of experimental tumor metastasis by selective activation of natural killer cells. Cancer Res 42:1337–1342
Hanna N (1983) Regulation of natural killer cell activation: implementation for the control of tumor metastasis. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul 3:22–33
He Q, Xu RZ, Shkarin P, Pizzorno G, Lee-French CH, Rothman DL, Shungu DC, Shim H (2003) Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of tumor metabolic markers for cancer diagnosis, metabolic phenotyping, and characterization of tumor microenvironment. Dis Markers 19:69–94
Hersh D, Monack DM, Smith MR, Ghori N, Falkow S, Zychlinsky A (1999) The Salmonella invasin SipB induces macrophage apoptosis by binding to caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2396–2401
Hoiseth SK, Stoker BAD (1981) Aromatic-dependent S. typhimunum are non-virulent and are effective as live vaccines. Nature 291:238–239
Huang Y, Hajishengallis G, Michalek SM (2000) Construction and characterization of a Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium clone expressing a salivary adhesin of Streptococcus mutans under control of the anaerobically inducible nirB promoter. Infect Immun 68:1549–1556
Jansen EP, Boot H, Dubbelman R, Verheij M, Cats A (2009) Postoperative chemoradiotherapy in gastric cancer—a phase I–II study of radiotherapy with dose escalation of weekly cisplatin and daily capecitabine chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 21:530–534
Jewett A, Bonavida B (1993) Pivotal role of endogenous TNF-alpha in the IL-2-driven activation and proliferation of the functionally immature NK free subset. Cell Immunol 151:257–269
Jewett A, Bonavida B (1994) Activation of the human immature natural killer cell subset by IL-12 and its regulation by endogenous TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma secretion. Cell Immunol 154:273–286
King I, Bermudes D, Lin S, Belcourt M, Pike J, Troy K, Le T, Ittensohn M, Mao J, Lang W, Runyan JD, Luo X, Li Z, Zheng LM (2002) Tumor-targeted Salmonella expressing cytosine deaminase as an anticancer agent. Hum Gene Ther 13:1225–1233
Le Pechoux C, Dunant A, Senan S, Wolfson A, Quoix E, Faivre-Finn C, Ciuleanu T, Arriagada R, Jones R, Wanders R, Lerouge D, Laplanche A (2009) Standard-dose versus higher-dose prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer in complete remission after chemotherapy and thoracic radiotherapy (PCI 99-01, EORTC 22003-08004, RTOG 0212, and IFCT 99-01): a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Oncol 10:467–474
Lejeune FJ, Lienard D, Matter M, Ruegg C (2006) Efficiency of recombinant human TNF in human cancer therapy. Cancer Immun 6:6
Lissoni P, Pittalis S, Ardizzoia A, Brivio F, Barni S, Tancini G, Pelizzoni F, Maestroni GJ, Zubelewicz B, Braczkowski R (1996) Prevention of cytokine-induced hypotension in cancer patients by the pineal hormone melatonin. Support Care Cancer 4:313–316
Lissoni P, Brivio F, Fumagalli L, Messina G, Meregalli S, Porro G, Rovelli F, Vigore L, Tisi E, D’Amico G (2009) Effects of the conventional antitumor therapies surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy on regulatory T lymphocytes in cancer patients. Anticancer Res 29:1847–1852
Luo X, Li Z, Lin S, Le T, Ittensohn M, Bermudes D, Runyab JD, Shen SY, Chen J, King IC, Zheng LM (2001) Antitumor effect of VNP20009, an attenuated Salmonella, in murine tumor models. Oncol Res 12:501–508
Moriya N, Miwa H, Orita K (1984) Antitumor effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in mice. Jpn J Surg 14:163–166
Ortaldo JR, Mason LH, Mathieson BJ, Liang SM, Flick DA, Herberman RB (1986) Mediation of mouse natural cytotoxic activity by tumour necrosis factor. Nature 321:700–702
Paglia P, Terrazzini N, Schulze K, Guzman CA, Colombo MP (2000) In vivo correction of genetic defects of monocyte/macrophages using attenuated Salmonella as oral vectors for targeted gene delivery. Gene Ther 7:1725–1730
Pajkos G, Bodoky G, Padi E, Izso J, Szanto J (1998) Low-dose leucovorin and interferon-alpha as modulators of 5-fluorouracil for adjuvant chemotherapy of colorectal cancer. Orv Hetil 139:1571–1575
Pawelek JM, Low KB, Bermudes D (1997) Tumor-targeted Salmonella as a novel anticancer vector. Cancer Res 57:4537–4544
Pisters PW, Evans DB (2008) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, interferon-alpha, and radiation as adjuvant therapy for resected pancreatic cancer: is there a future for this regimen and/or should we change our approach to research and treatment of patients with pancreatic cancer? Ann Surg 248:152–153
Saif MW, Black G, Roy S, Bell D, Russo S, Eloubeidi MA, Steg A, Johnson MR, Zelterman D, Diasio RB (2007) Phase II study of capecitabine with concomitant radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: up-regulation of thymidine phosphorylase. Cancer J 13:247–256
Salles B, Calsou P (1992) Involvement of glutathione in cis-platinum toxicity in Escherichia coli K12. Toxicology 72:341–350
Salles B, Calsou P, Bouayadi K, Vinial H (1994) Multiple mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin toxicity in an Escherichia coli K12 mutant. Toxicology 93:235–247
Saltzman DA, Heise CP, Hasz DE, Zebede M, Kelly SM, Curtiss R 3rd, Leonard AS, Anderson PM (1996) Attenuated Salmonella typhimurium containing interleukin-2 decreases MC-38 hepatic metastases: a novel anti-tumor agent. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 11:145–153
Stewart F, Bohlken S, Begg A, Bartelink H (1986) Renal damage in mice after treatment with cisplatinum alone or in combination with X-irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 12:927–933
Stewart FA, Luts A, Oussoren Y, Begg AC, Dewit L, Bartelink H (1988) Renal damage in mice after treatment with cisplatin and X-rays: comparison of fractionated and single-dose studies. NCI Monogr 6:23–27
Stupp R, Mayer M, Kann R, Weder W, Zouhair A, Betticher DC, Roth AD, Stahel RA, Majno SB, Peters S, Jost L, Furrer M, Thierstein S, Schmid RA, Hsu-Schmitz SF, Mirimanoff RO, Ris HB, Pless M (2009) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy followed by surgery in selected patients with stage IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre phase II trial. Lancet Oncol 10:785–793
Terlikowski SJ (2002) Local immunotherapy with rhTNF-alpha mutein induces strong antitumor activity without overt toxicity—a review. Toxicology 174:143–152
Toso JF, Gill VJ, Hwu P, Marincola FM, Restifo NP, Schwartzentruber DJ, Sherry RM, Topalian SL, Yang JC, Stock F, Freezer LJ, Morton KE, Seipp C, Haworth L, Mavroukakis S, White D, MacDonald S, Mao J, Sznol M, Rosenberg SA (2002) Phase I study of the intravenous administration of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium to patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol 20:142–152
Weiss S (2003) Transfer of eukaryotic expression plasmids to mammalian hosts by attenuated Salmonella spp. Int J Med Microbiol 293:95–106
Yuhua L, Kunyuan G, Hui C, Yongmei X, Chaoyang S, Xun T, Daming R (2001) Oral cytokine gene therapy against murine tumor using attenuated Salmonella typhimurium. Int J Cancer 94:438–443
Zheng LM, Luo X, Feng M, Li Z, Le T, Ittensohn M, Trailsmith M, Bermudes D, Lin SL, King IC (2000) Tumor amplified protein expression therapy: Salmonella as a tumor-selective protein delivery vector. Oncol Res 12:127–135
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Moller A, Linke RP, Haas JG, Rieber EP, Riethmuller G (1986) Tumor necrosis factor as effector molecule in monocyte mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 46:5947–5952
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by KFDA and Korea Science & Engineering Foundation (Grant No. E00156).
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea. (A090228)
We are grateful to YuChang Park, YeSu Ju, and HaNa Nim for their expert, technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
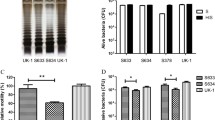
Survival of recombinant bacteria in tumor-bearing mice. B16F10 tumor-bearing C57BL6 mice were subcutaneously inoculated with 1 × 108 S. typhimurium harboring TNF-α next to tumor. At 1, 12, and 24 h after treatment, the tumor region was homogenized. Tumor cell lysates were cultivated and the percent survival of recombinant bacteria was calculated. (DOC 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, W.S., Chae, Y.S., Hong, J. et al. Antitumor therapeutic effects of a genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium harboring TNF-α in mice. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 1807–1819 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3006-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3006-4