Abstract
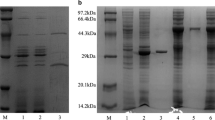
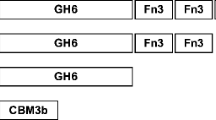
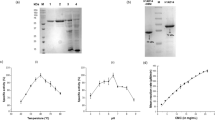
Cel9B from Paenibacillus barcinonensis is a modular endoglucanase with a novel molecular architecture among family 9 enzymes that comprises a catalytic domain (GH9), a family 3c cellulose-binding domain (CBM3c), a fibronectin III-like domain repeat (Fn31,2), and a C-terminal family 3b cellulose-binding domain (CBM3b). A series of truncated derivatives of endoglucanase Cel9B have been constructed and characterized. Deletion of CBM3c produced a notable reduction in hydrolytic activity, while it did not affect the cellulose-binding properties as CBM3c did not show the ability to bind to cellulose. On the contrary, CBM3b exhibited binding to cellulose. The truncated forms devoid of CBM3b lost cellulose-binding ability and showed a reduced activity on crystalline cellulose, although activity on amorphous celluloses was not affected. Endoglucanase Cel9B produced only a small ratio of insoluble products from filter paper, while most of the reducing ends produced by the enzyme were released as soluble sugars (91%), indicating that it is a processive enzyme. Processivity of Cel9B resides in traits contained in the tandem of domains GH9–CBM3c, although the slightly reduced processivity of truncated form GH9–CBM3c suggests a minor contribution of domains Fn31,2 or CBM3b, not contained in it, on processivity of endoglucanase Cel9B.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai T, Ohara H, Karita S, Kimura T, Sakka K, Ohmiya K (2001) Sequence of celQ and properties of CelQ, a component of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:660–666
Bayer EA, Belaich JP, Shoham Y, Lamed R (2004) The cellulosomes: multienzyme machines for degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:521–554
Bayer EA, Shoham Y, Lamed R (2006) Cellulose-decomposing bacteria and their enzyme systems. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds) The Prokaryotes, vol 2. Springer, New York, pp 578–617
Béguin P, Aubert JP (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:25–58
Blanco A, Vidal T, Colom JF, Pastor FIJ (1995) Purification and properties of xylanase A from alkali-tolerant Bacillus sp. strain BP-23. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4468–4470
Blanco A, Díaz P, Martínez J, Vidal T, Torres AL, Pastor FIJ (1998) Cloning of a new endoglucanase gene from Bacillus sp. BP-23 and characterisation of the enzyme. Performance in paper manufacture from cereal straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:48–54
Blanco A, Díaz P, Zueco J, Parascandola P, Pastor FIJ (1999) A multidomain xylanase from a Bacillus sp. with a region homologous to thermostabilizing domains of thermophilic enzymes. Microbiology 145:2163–2170
Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2004) Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J 382:769–781
Burstein T, Shulman M, Jindou S, Petkun S, Frolow F, Shoham Y, Bayer EA, Lamed R (2009) Physical association of the catalytic and helper modules of a family-9 glycoside hydrolase is essential for activity. FEBS Lett 583:879–874
Carrard G, Koivula A, Söderlund H, Béguin P (2000) Cellulose-binding domains promote hydrolysis of different sites on crystalline cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:10342–10347
Gal L, Gaudin C, Belaich A, Pages S, Tadif C, Belaich JP (1997) CelG from Clostridium thermocellum: a multidomain endoglucanase acting efficiently on crystalline cellulose. J Bacteriol 179:6595–6601
Gilad R, Rabinovich L, Yaron S, Bayer EA, Lamed R, Gilbert HJ, Shoham Y (2003) CelI, a noncellulosomal family 9 enzyme from Clostridium thermocellum, is a processive endoglucanase that degrades crystalline cellulose. J Bacteriol 185:391–398
Heckman KL, Pease LR (2007) Gene splicing and mutagenesis by PCR-driven overlap extension. Nat Protocol 2:924–932
Irwin DC, Spezio M, Walker LP, Wilson DW (1993) Activity studies of eight purified cellulases: specificity, synergism, and binding domain effects. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:1002–1013
Irwin D, Shin DH, Zhang S, Barr BK, Sakon J, Karplus PA, Wilson DB (1998) Roles of the catalytic domain and two cellulose binding domains of Thermomonospora fusca E4 in cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 180:1709–1714
Jindou S, Xu Q, Kenig R, Shulman M, Shoham Y, Bayer EA, Lamed R (2006) Novel architectural theme of family-9 glycoside hydrolases identified in cellulosomal enzymes of Acetivibrio cellulolyticus and Clostridium thermocellum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:308–316
Kataeva IA, Seidel RD III, Shah A, West LT, Li XL, Ljungdahl LG (2002) The fibronectin type 3-like repeat from the Clostridium thermocellum cellobiohydrolase CbhA promotes hydrolysis of cellulose by modifying its surface. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4292–4300
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (Lond) 227:680–685
Li Y, Irwin DC, Wilson DB (2007) Processivity, substrate binding, and mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis by Thermobifida fusca Cel9A. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3165–3172
Linder M, Teeri TT (1997) The roles and function of cellulose-binding domains. J Biotechnol 57:15–28
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Oliveira OV, Freitas LCG, Straatsma TP, Lins RD (2009) Interaction between the CBM of Cel9A from Thermobifida fusca and cellulose fibers. J Mol Recognit 22:38–45
Pastor FIJ, Pujol X, Blanco A, Vidal T, Torres AL, Diaz P (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a multidomain endoglucanase from Paenibacillus sp. BP-23: evaluation o fits performance in pulp refining. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:61–68
Reverbel-Leroy C, Pages S, Belaich A, Belaich JP, Tardif C (1997) The processive endocellulase CelF, a major component of the Clostridium cellulolyticum cellulosome: purification and characterization of the recombinant form. J Bacteriol 179:46–52
Riedel K, Ritter J, Bauer S, Bronnenmeier K (1998) The modular cellulase CelZ of the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium stercorarium contains a thermostabilizing domain. FEMS Microbiol Lett 164:261–267
Sakon J, Irwin D, Wilson DB, Karplus PA (1997) Structure and mechanism of endo/exocellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusca. Nat Struct Biol 4:810–818
Sánchez MM, Pastor FIJ, Diaz P (2003) Exo-mode of action of cellobiohydrolase Cel48C from Paenibacillus sp. BP-23, a unique type of cellulase among Bacillales. Eur J Biochem 270:2913–2919
Sánchez MM, Irwin DC, Pastor FIJ, Wilson DB, Diaz P (2004) Synergistic activity of Paenibacillus sp. BP-23 cellobiohydrolase Cel48C in association with the contiguous endoglucanase Cel9B and with endo- or exo-acting glucanases from Thermobifida fusca. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:161–169
Sánchez MM, Fritze D, Blanco A, Spröer C, Tindall BJ, Schumann P, Kroppenstedt RM, Diaz P, Pastor FIJ (2005) Paenibacillus barcinonensis sp. nov., a xylanase-producing bacterium isolated from a rice field in the Ebro River delta. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:935–939
Schwarz WH (2001) The cellulosome and cellulose degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:634–649
Spiro RG (1966) The Nelson–Somogyi copper reduction method. Analysis of sugars found in glycoprotein. Methods Enzymol 8:3–26
Teeri TT (1997) Crystalline cellulose degradation: new insight into the function of cellobiohydrolases. Trends Biotechnol 15:160–167
Tomme P, Boraston A, McLean B, Kormos J, Creagh AL, Sturch K, Gilkes NR, Haynes CA, Warren RAJ, Kilburn DG (1998) Characterization and affinity applications of cellulose-binding domains. J Chromatogr B 715:283–296
Tormo J, Lamed R, Chirino AJ, Morag E, Bayer EA, Shoham Y, Steitz TA (1996) Crystal structure of a bacterial family-III cellulose-binding domain: a general mechanism for attachment to cellulose. EMBO J 15:5739–5751
Watson BJ, Zhang H, Longmire AG, Moon YH, Hutcheson SW (2009) Processive endoglucanases mediate degradation of cellulose by Saccharophagus degradans. J Bacteriol 191:5697–5705
Wood TM (1988) Preparation of crystalline, amorphous, and dyed cellulase substrates. Methods Enzymol 160:19–25
Zhang YHP, Cui J, Lynd LR, Kuang LR (2006) A transition from cellulose swelling to cellulose dissolution by o-phosphoric acid: evidence from enzymatic hydrolysis and supramolecular structure. Biomacromolecules 7:644–648
Zhou W, Irwin DC, Escovar-Kousen J, Wilson DB (2004) Kinetic studies of Thermobifida fusca Cel9A active site mutant enzymes. Biochemistry 43:9655–9663
Zverlov VV, Velikodvorskaya GA, Schwarz WH (2003) Two new cellulosome components encoded downstream of celI in the genome of Clostridium thermocellum: the non-processive endoglucanase CelN and the possibly structural protein CseP. Microbiology 149:515–524
Zverlov VV, Schantz N, Schwarz WH (2005) A major new component in the cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum is a processive endo-β-1, 4-glucanase producing cellotetraose. FEMS Microbiol Lett 249:353–358
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, grant no. CTQ2007-68003-CO2-01-02/PPQ. Iulia Chiriac held a FI grant from Generalitat de Catalunya. The experiments described in this article have been performed in compliance with Spanish current laws.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiriac, A.I., Cadena, E.M., Vidal, T. et al. Engineering a family 9 processive endoglucanase from Paenibacillus barcinonensis displaying a novel architecture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1125–1134 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2350-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2350-8