Abstract
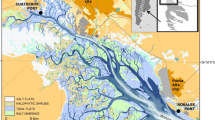
Bioindicators can be used to determine spatial and/or temporal variations of heavy metals in a certain coastal or marine environments. This study investigated the potential use of the burrowing crab Neohelice granulata from two different locations in the Bahía Blanca estuary, a moderately polluted ecosystem. Concentrations of zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), and lead (Pb) in soft tissues of male and female crabs were measured. In addition, concentrations of the three metals in eggs were compared with concentrations in female crabs. No geographical differences were found for any of the three metals, whereas sexual and seasonal differences were obtained for Zn and Ni, with the winter season posing lower concentrations. Moreover, the three metals were detectable in eggs and were lower than concentrations in female crabs (except for Zn). Finally, the usefulness of this species as a potential bioindicator of heavy-metal pollution within this estuarine ecosystem is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade JS, Pucci AE, Marcovecchio JE (2000) Cadmium concentrations in the Bahía Blanca estuary, (Argentina). Potential effects of dissolved cadmium on the diatom Thalassiosira curviseriata. Oceanologia 42(4):505–520
Barrento S, Marques A, Teixeira B, Carvalho ML, Vaz- Pires P, Nunes ML (2009) Accumulation of elements (S, As, Br, Sr, Cd, Hg, Pb) in two populations of Cancer pagurus: ecological implications to human consumption. Food Chem Toxicol 47:150–156
Beltrame MO (2008) Dinámica biogeoquímica de nutrientes y metales pesados en ambientes intermareales de la laguna costera de Mar Chiquita: Potenciales efectos ecotoxicológicos sobre especies claves del ecosistema. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Argentina
Beltrame MO, Marco SG, Marcovecchio JE (2008) Cadmium and zinc in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina): salinity effects on lethal toxicity in juveniles of the burrowing crab Chasmagnathus granulatus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55(1):78–85
Beltrame MO, De Marco SG, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Influences of sex, habitat, and seasonality on heavy-metal concentrations in the burrowing crab (Neohelice Granulata) from a coastal lagoon in Argentina. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58(3):746–756
Beltrame MO, De Marco SG, Marcovecchio JE (2011) The burrowing crab Neohelice granulata as potential bioindicator of heavy metals in estuarine systems of the Atlantic Coast of Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 172(1–4):379–389
Boschi EE (1964) Los crustáceos decápodos Brachyura del litoral bonaerense (R. A.). Bol Inst Biol Mar 6:1–75
Botté SE (2005) El rol de la vegetación en el ciclo biogeoquımico de los metales pesados en humedales del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Argentina
Botté SE, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2007) Dissolved heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations in surface water and porewater from Bahía Blanca Estuary Tidal Flats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:415–421
Botté SE, Arlenghi J, Del Blanco L, Asteasuain AA, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Variación entre pleamar y bajamar en la concentración de metales en el sedimento de planicie del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Primera Reunión Argentina de Geoquímica de la Superficie (IRAGSU). Córdoba, Argentina
Botté SE, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2010) Distribution of several heavy metals in tidal flats sediments within Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 210:371–388
Bryan GW, Langston WJ, Hummerstone LG, Burr GR (1985) A guide to the assessment of heavy metal contamination in estuaries using biological indicators. Mar Biol Assoc UK, Occasional Publication No. 4, pp 1–92
Chen M-H, Chen C-Y, Chou H-Y, Wen T-C (2005) Gender and size effects of metal bioaccumulation on the rock crab, Thalamita crenata, in Dapeng Bay, southwestern Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 50:463–484
Delhey JKV, Carrete M, Martinez MM (2001) Diet and feeding behavior of Olrog’s gull Larus atlanticus in Bahía Blanca. Argentina Ardea 89(2):319–329
Depledge MH, Fossi MC (1994) The role of biomarkers in environmental assessment. 2. Invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 3:161–172
Devescovi M, Lucu C (1995) Seasonal changes of the copper level in shore crabs Carcinus mediterraneus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 120:169–174
Escapa M, Perillo GME, Iribarne O (2008) Sediment dynamics modulated by burrowing crab activities in contrasting SW Atlantic intertidal habitats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 80:365–373
Fernández Severini MD, Botté SE, Hoffmeyer M, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of cadmium and copper in water and zooplankton in the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:57–66
Ferrer LD (2001) Estudio de los diversos metales pesados en sedimentos del estuario de Bahía Blanca y sus efectos tóxicos sobre el cangrejo Chasmagnathus granulata. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Argentina
Ferrer LD, Contardi ET, Andrade JS, Asteasuain RO, Pucci AE, Marcovecchio JE (2000) Environmental cadmium and lead concentrations in the Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina). Potential toxic effects of Cd and Pb on crab larvae. Oceanologia 42(4):493–504
Fialkowski W, Rainbow PS, Smith BD, Zmudzinski L (2003) Seasonal variation in trace metal concentrations in three talitrid amphipods from the Gulf of Gdansk, Poland. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 288:81–93
Förstner U, Wittmann GTW (1983) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer, Berlin
Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2004) Oceanografía química. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer M (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía (IADO-CONICET), Bahía Blanca, pp 69–78
Freije RH, Spetter CV, Marcovecchio JE, Popovich CA, Botté SE, Negrín V et al (2008) Water chemistry and nutrients of the Bahía Blanca Estuary. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 241–254
Hempel M, Botté SE, Negrin VL, Chiarello MN, Marcovecchio JE (2008) The role of the smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora and associated sediments in the heavy metal biogeochemical cycle within Bahía Blanca estuary salt marshes. J Soils Sed 8:289–297
Iribarne O, Bortolus A, Botto F (1997) Between-habitat differences in burrow characteristics and trophic modes in the southwestern Atlantic burrowing crab Chasmagnathus granulata. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 155:132–145
Ituarte R, Spivak E, Luppi T (2004) Female reproductive cycle of the Southwestern Atlantic estuarine crab Chasmagnathus granulatus (Brachyura: Grapsoidea: Varunidae). Sci Mar 68:127–137
Jeckel WH, Roth RR, Ricci L (1996) Patterns of trace-metal distribution in tissues of Pleoticus muelleri (Crustacea: Decapoda: Solenoceridae). Mar Biol 125:297–306
Jones RP, Clarke JU (2005) Analytical chemistry detection limits and the evaluation of dredged sediment. ERDC/TN EEDP-04–36. United States Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Vicksburg
Kannan K, Yasunaga Y, Iwata H, Ichihashi H, Tanabe S, Tatsukawa R (1995) Concentrations of heavy metals, organochlorines, and organotins in Horseshoe Crab, Tachypleus tridentatus, from Japanese coastal waters. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 28:40–47
Limbozzi F, Leitao TE (2008) Characterization of Bahia Blanca main existing pressures and their effects on the state indicators for surface and groundwater quality. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 315–331
Louis Y, Garnier C, Lenoble V, Omanović D, Mounier S, Pizěta I (2009) Characterisation and modelling of marine dissolved organic matter interactions with major and trace cations. Mar Environ Res 67:100–107
MacFarlane GR, Booth DJ, Brown KR (2000) The semaphore crab, Heloecius cordiformis: Bio-indication potential for heavy metals in estuarine systems. Aquat Toxicol 50:153–166
Marcovecchio JE (1994) Trace metals residues in several tissues of two crustacean species from the Bahía Blanca estuary in Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 29:65–73
Marcovecchio JE, Ferrer L (2005) Distribution and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. J Coastal Res 21:826–834
Marcovecchio JE, Freije RH (2004) Efectos de la intervención antrópica sobre sistemas marinos costeros: El estuario de Bahía Blanca. Anales de la Academia Nacional de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales (ANCEFN). Argentina 56:115–132
Marcovecchio JE, Moreno VJ, Perez A (1988a) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in biota of Bahia Blanca, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 75:181–190
Marcovecchio JE, Moreno VJ, Perez A (1988b) The sole, Paralichthys sp., as an indicator species of heavy metal pollution in the Bahía Blanca estuary trophic web. In: Seeliger U, Lacerda LD, Patchineelam SR (eds) Metals in coastal environments of Latin America. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 122–129
Marcovecchio JE, Moreno VJ, Perez A (1996) Bio-magnification of total mercury in Bahía Blanca estuary shark. Mar Pollut Bull 17:276–278
Marcovecchio JE, Spetter CV, Botté SE, Delucchi F, Arias AH, Fernández Severini MD et al (2009) Inorganic nutrients and organic matter tidal time-scale variation in a mesotidal estuary: Bahía Blanca, Argentina. J Chem Ecol 25(6):453–465
Markert B (2007) Definitions and principles for bioindication and biomonitoring of trace metals in the environment. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21(Suppl 1):77–82
McPherson R, Brown K (2001) The bioaccumulation of cadmium by the Blue Swimmer Crab Portunus pelagicus L. Sci Total Environ 279:223–230
Negrin VL (2010) El rol de las marismas del estuario de Bahía Blanca en el ciclo bio-geoquímico de nutrientes inorgánicos y de materia orgánica. Doctoral thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca, Argentina
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC, Parodi E, Freije RH (2001) The Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. In: Seeliger U, Kjerfve B (eds) Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 205–217
Petracci PF (2002) Diet of sanderling in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Waterbirds 25(3):366–370
Phillips DJH (1977) The use of biological indicator organisms to monitor trace metal pollution in marine and estuarine environments—a review. Environ Pollut 13:281–317
Phillips DJH (1980) Quantitative aquatic biological indicators: their use to monitor trace metal and organochlorine pollution. Applied Science Publishers, London
Phillips DJH, Rainbow PS (1988) Barnacles and mussels as biomonitors of trace elements: a comparative study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 49:83–93
Phillips DJH, Rainbow PS (1993) Biomonitoring of trace aquatic contaminants. Chapman and Hall, London
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Melo W (2008) The Bahía Blanca estuary: an integrated overview of its geomorphology and dynamics. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 219–229
Pratolongo PD, Perillo GME, Piccolo MC (2010) Combined effects of waves and plants on a mud deposition event at a mudflat–saltmarsh edge in the Bahía Blanca estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87:207–212
Rainbow PS (1995a) Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 31:183–192
Rainbow PS (1995b) Physiology, physiochemistry and metal uptake—a crustacean perspective. Mar Pollut Bull 31(1–3):55–59
Rainbow PS (1997) Trace metal accumulation in marine invertebrates: marine biology or marine chemistry? J Mar Biol Assoc UK 77:195–210
Rainbow PS (2002) Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: why and so what? Environ Pollut 120:497–507
Rainbow PS (2007) Trace metal bioaccumulation: models, metabolic availability and toxicity. Environ Int 33:576–582
Rainbow PS, Phillips DJH (1993) Cosmopolitan biomonitors of trace metals. Mar Pollut Bull 26(11):593–601
Rainbow PS, White SL (1989) Comparative strategies of heavy metal accumulation by crustaceans: zinc, copper and cadmium in a decapod, an amphipod and a barnacle. Hydrobiologia 174:245–262
Salomons W, Förstner U (1984) Metals in the Hydrocycle. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, p 349
Sastre MP, Reyes P, Ramos H, Romero R, Rivera J (1999) Heavy metal bioaccumulation in Puerto Rican Blue Crabs (Callinectes spp.). Bull Mar Sci 64(2):209–217
Shank GC, Skrabal SA, Whitehead RF, Kieber RJ (2004) Strong copper complexation in an organic-rich estuary: the importance of allochthonous dissolved organic matter. Mar Chem 88:21–39
Simonetti P, Botté SE, Fiori SM, Marcovecchio JE (2012) Heavy metals concentration in soft tissues of the burrowing crab, Neohelice granulata, in the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62(2):243–253
Spivak ED (1997) Cangrejos estuariales del Atlántico sudoccidental (25–41°S) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura). Invest Mar Valparaíso 25:105–120
Spivak E, Anger K, Luppi TA, Bas C, Ismael D (1994) Distribution and habitat preferences of two grapsid crab species in Mar Chiquita Lagoon (Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina). Helgol Mar Res 48:59–78
Swaileh KM, Adelung D (1995) Effect of body size and season on the concentrations of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in Diastylis rathkei from Keil Bay, Western Baltic. Mar Pollut Bull 31(1–3):103–107
Tombesi NB, Pistonesi MF, Freije RH (2000) Physico-chemical characterization improvement evaluation of primary treated municipal waste water in the City of Bahía Blanca (Argentina). Ecol Environ Conserv 6(2):147–151
Town RM, Filella M (2002) Implications of natural organic matter binding heterogeneity on understanding lead (II) complexation in aquatic systems. Sci Total Environ 300:143–154
Turoczy NJ, Mitchell BD, Levings AH, Rajendram VS (2001) Cadmium, copper, mercury, and zinc concentrations in tissues of the King Crab (Pseudocarcinus gigas) from southeast Australian waters. Environ Int 27:327–334
Villares R, Puente X, Carballeira A (2002) Seasonal variation and background levels of heavy metals in two green seaweeds. Environ Pollut 119:79–90
White S, Rainbow PS (1982) Regulation and accumulation of copper, zinc and cadmium by the shrimp Palaemon elegans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 8:95–101
White SL, Rainbow PS (1985) On the metabolic requirements for copper and zinc in molluscs and crustaceans. Mar Environ Res 16:215–229
White SL, Rainbow PS (1987) Heavy metal concentrations and size effects in the mesopelagic decapod crustacean Systellaspis debilis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 37:147–151
Zauke GP, Clason B, Savinov VM, Savinova T (2003) Heavy metals of inshore benthic invertebrates from the Barents Sea. Sci Total Environ 306(1–3):99–110
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606:135–150
Acknowledgments
The authors thank M. Nedda Chiarello and Javier Arlenghi (IADO) for valuable help in the laboratory analyses. This research was supported by a grant funded by the National Council of Scientific and Technological Researches (CONICET–Argentina) and with the 2008 Latin America E. Alexander Bergstrom Memorial Research Award from the Association of Field Ornithologists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonetti, P., Botté, S.E., Fiori, S.M. et al. Burrowing Crab (Neohelice granulata) as a Potential Bioindicator of Heavy Metals in the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64, 110–118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9804-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9804-1