Abstract
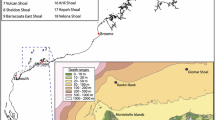
Deep-sea corals provide important habitat for many organisms; however, the extent to which fishes and other invertebrates are affiliated with corals or other physical variables is uncertain. The Cape Fear coral mound off North Carolina, USA (366–463 m depth, 33° 34.4′N, 76° 27.8′W) was surveyed using multibeam sonar and the Johnson-Sea-Link submersible. Multibeam bathymetric data (2006) were coupled with in situ video data (2002–2005) to define habitat associations of 14 dominant megafauna at two spatial scales. Results suggested greater habitat specificity of deep-reef fauna than previously documented, with fishes showing greater affinity for certain habitat characteristics than most invertebrates. High vertical profile, degree of coral coverage, and topographic complexity influenced distributions of several species, including Beryx decadactylus, Conger oceanicus, and Novodinia antillensis on the smaller scale (30 × 30 m). On the broad scale (170 × 170 m), several suspension feeders (e.g., N. antillensis, anemones), detritivores (Echinus spp.), and mesopelagic feeders (e.g., Beryx decadactylus, Eumunida picta) were most often found on the south-southwest facing slope near the top of the mound. Transient reef species, including Laemonema barbatulum and Helicolenus dactylopterus, had limited affiliations to topographic complexity and were most often on the mound slope and base. Megafauna at deep-water reefs behave much like shallow-water reef fauna, with some species strongly associated with certain fine-scale habitat attributes, whereas other species are habitat generalists. Documenting the degree of habitat specialization is important for understanding habitat functionality, predicting faunal distributions, and assessing the impacts of disturbance on deep-reef megafauna.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele LG, Patton WK (1976) The size of coral heads and the community biology of associated decapod crustaceans. J Biogeogr 3:35–47
Albani M, Klinkenberg B, Andison DW, Kimmins JP (2004) The choice of window size in approximating topographic surfaces from digital elevation models. Internat J Geogr Inform Sci 18:577–593
Alexander TJ, Barrett N, Haddon M, Edgar G (2009) Relationships between mobile macroinvertebrates and reef structure in a temperate marine reserve. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 389:31–44
Anker A, Nizinski M (2011) Description of a new deep-water species of Alpheus Fabricius, 1798 from the Gulf of Mexico (Crustacea, Decapoda, Alpheidae). Zootaxa 2925:49–56
Attrill MJ, Strong JA, Rowden AA (2000) Are macroinvertebrate communities influenced by seagrass structural complexity? Ecography 23:114–121
Ault TR, Johnson CR (1998a) Spatial variation in fish species richness on coral reefs: habitat fragmentation and stochastic structuring processes. Oikos 82:354–364
Ault TR, Johnson CR (1998b) Spatially and temporally predictable fish communities on coral reefs. Ecol Mono 68:25–50
Auster PJ (2005) Are deep-water corals important habitats for fishes? In: Freiwald A, Roberts JM (eds) Cold-water corals and ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, pp 747–760
Auster PJ, Malatesta RJ, LaRosa SC (1995) Patterns of microhabitat utilization by mobile megafauna on the southern New England (USA) continental shelf and slope. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 127:77–85
Beck MW (1995) Size-specific shelter limitation in stone crabs: a test of the demographic bottleneck hypothesis. Ecology 76:968–980
Bell JD, Galzin R (1984) Influence of live coral cover on coral reef fish communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 15:247–265
Brooks DA, Bane J (1983) Gulf Stream meanders off North Carolina during winter and summer 1979. J Geophys Res 88:4633–4650
Brooks RA, Nizinski MS, Ross SW, Sulak KJ (2007) Frequency of sublethal injury in a deepwater ophiuroid, Ophiacantha bidentata, an important component of western Atlantic Lophelia reef communities. Mar Biol 152:307–314
Buhl-Mortensen L, Vanreusel A, Gooday AJ, Levin LA, Priede IG, Buhl-Mortensen P, Gheerardyn H, King N, Raes M (2010) Biological structures as a source of habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity on the deep ocean margins. Mar Ecol 31:21–50
Campos-Creasey LS, Tyler PA, Gage JD, John AWG (1994) Evidence for coupling the vertical flux of phytodetritus to the diet and seasonal life history of the deep-sea echinoid Echinus affinis. Deep-Sea Res I 41:369–388
Caruso JH, Ross SW, Sulak KJ, Sedberry GR (2007) Deep-water chaunacid and lophiid anglerfishes (Pisces: Lophiiformes) off the south-eastern United States. J Fish Biol 70:1015–1026
Casazza TL, Ross SW (2008) Fishes associated with pelagic Sargassum and open water lacking Sargassum in the Gulf Stream off North Carolina. Fish Bull 106:348–363
Cordes EE, Hourdez S, Predmore BL, Redding ML, Fisher CR (2005) Succession of hydrocarbon seep communities associated with the long-lived foundation species Lamellibrachia luymesi. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 305:17–29
Cordes EE, McGinley MP, Podowski EL, Becker EL, Lessard-Pilon S, Viada ST, Fisher CR (2008) Coral communities of the deep Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Res I 55:777–787
Costello MJ, McCrea M, Freiwald A, Lundalv T, Jonsson L, Brett BJ, van Weering TCE, de Haas H, Roberts JM, Allen D (2005) Role of cold-water Lophelia pertusa coral reefs as fish habitat in the NE Atlantic. In: Freiwald A, Roberts JM (eds) Cold-water corals and ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, pp 771–805
Davies AJ, Duineveld GCA, Lavaleye MSS, Bergman MJN, vanHaren H, Roberts JM (2009) Downwelling and deep-water bottom currents as food supply mechanisms to the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia) at the Mingulay Reef complex. Limnol Oceanogr 54:620–629
Davies AJ, Duineveld GCA, van Weering TCE, Mienis F, Quattrini AM, Seim HE, Bane JE, Ross SW (2010) Short-term environmental variability in cold-water coral habitat at Viosca Knoll, Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Res I 57:199–212
Dolan MFJ, Grehan AJ, Guinan JC, Brown C (2008) Modeling the local distribution of cold-water corals in relation to bathymetric variables: adding spatial context to deep-sea video data. Deep-Sea Res I 55:1564–1579
Eastman JR (1997) Idrisi for windows. Version 2.0. Clark University Laboratory. Clark University Worcester, PA
Emson RH, Young CM (1994) Feeding mechanism of the brisingid starfish Novodinia antillensis. Mar Biol 118:433–442
Evans IS (1980) An integrated system of terrain analysis and slope mapping. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie Suppl-Bd 36:274–295
Fernholm B, Quattrini AM (2008) A new species of Hagfish (Myxinidae: Eptatretus) associated with deep-sea coral habitat in the Western North Atlantic. Copeia 2008:126–132
Frederiksen R, Jensen A, Westerberg H (1992) The distribution of the scerlactinian coral Lophelia pertusa around the Faeroe Islands and the relation to internal tidal mixing. Sarsia 77:157–171
Friedlander AM, Parrish JD (1998) Habitat characteristics affecting fish assemblages on a Hawaiian coral reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 222:1–30
Gartner JV, Crabtree RE, Sulak KJ (1997) Feeding at depth. In: Randall DJ, Farrel AP (eds) Deep-sea fishes. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 115–193
Gartner JV, Sulak KJ, Ross SW, Necaise AM (2008) Persistent near-bottom aggregations of mesopelagic animals along the North Carolina and Virginia continental slopes. Mar Biol 153:825–841
Genin AP, Dayton PK, Lonsdale PF, Spiess FN (1986) Corals on seamount peaks provide evidence of current acceleration over deep-sea topography. Nature 322:59–61
Goldman SF, Sedberry GR (2011) Feeding habits of some demersal fish on the Charleston Bump off the southeastern United States. ICES J Mar Sci 68:390–398
Gomes TM, Sola E, Gros MP, Menezes G, Pinho MR (1998) Trophic relationships and feeding habits of demersal fishes from the Azores: importance to multispecies assessment. ICES J Mar Sci 35:7–21
Gratwicke B, Speight MR (2005) The relationship between fish species richness, abundance and habitat complexity in a range of shallow tropical marine habitats. J Fish Biol 66:650–667
Harter SL, Ribera MM, Shepard AN, Reed JK (2009) Assessment of fish populations and habitat on Oculina Bank, a deep-sea coral marine protected area off eastern Florida. Fish Bull 107:195–206
Hartley S, Kunin WE, Lennon JJ, Pocock MJO (2004) Coherence and discontinuity in the scaling of species’ distribution patterns. Proc R Soc Lond B 271:81–88
Henkel TP, Pawlik JR (2005) Habitat use by sponge-dwelling brittlestars. Mar Biol 146:301–313
Henry LA, Nizinski MS, Ross SW (2008) Diversity, distribution, and biogeography of hydroid assemblages collected from deep-water coral habitats off the southeastern United States. Deep-Sea Res I 55:788–800
Hirzel AH, Hausser JDC, Perrin N (2002) Ecological-niche factor analysis: how to compute habitat-suitability maps without absence data? Ecology 83:2027–2036
Hirzel AH, Hausser J, Perrin N (2004) Biomapper 3.1. Lab. of conservation Biology, Department of Ecology and Evolution, University of Lausanne. URL: http://www.unil.ch/biomapper
Hixon MA (1991) Predation as a process structuring coral reef fish communities. In: Sale PF (ed) The ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 475–508
Hixon MA, Beets JP (1993) Predation, prey refuges, and the structure of coral reef fish assemblages. Ecol Mono 63:77–101
Jenness J (2002) Surface areas and ratios from elevation grid (surfgrids.avx) extension for ArcView 3.x-version 1.2. Jenness Enterprises http://www.jennessent.com/arcview/grid tools.htm
Jensen A, Frederiksen R (1992) The fauna associated with the bank-forming deep-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinaria) on the Faroe Shelf. Sarsia 77:53–69
Jonsson LG, Nilsson PG, Floruta F, Lundälv T (2004) Distributional patterns of macro-and megafauna associated with a reef of the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa on the Swedish west coast. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 284:163–171
Kendall MS, Bauer MJ, Jeffrey CFG (2009) Influence of hard bottom morphology on fish assemblages of the continental shelf off Georgia, southeastern USA. Bull Mar Sci 84:265–286
Kissling D, Taylor G (1977) Habitat factors for reef dwelling ophiuroids in the Florida Keys. In: Taylor DL (ed) Proceedings of 3rd international coral reef symposium, vol 1. University of Miami, Miami, pp 225–231
Lessard-Pilon SA, Podowski EL, Cordes EE, Fisher CR (2010) Megafauna community composition associated with Lophelia pertusa colonies in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Res II 57:1882–1890
Levin LA, Sibuet M, Gooday AJ, Smith CR, Vanreusel A (2010) The roles of habitat heterogeneity in generating and maintaining biodiversity on continental margins: an introduction. Mar Ecol 31:1–5
Levy A, Able KW, Grimes CB, Hood P (1988) Biology of the conger eel Conger oceanicus in the Mid-Atlantic Bight. Mar Biol 98:597–600
Luckhurst BE, Luckhurst K (1978) Analysis of the influence of the substrate variables on coral reef fish communities. Mar Biol 49:317–323
Lundblad E, Wright DJ, Miller J, Larkin EM, Rinehart R, Naar DF, Donahue BT, Anderson SM, Battista T (2006) A benthic terrain classification scheme for American Samoa. Mar Geodesy 29:89–111
Mah C, Nizinski M, Lundsten L (2010) Phylogenetic revision of the Hippasterinae (Goniasteridae; Asteroidea): systematics of deep-sea corallivores, including one new genus and three new species. Zool J Linn Soc 160:266–301
Mandelbrot BB (1983) The fractal geometry of nature. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York
McCosker JE, Ross SW (2007) A new deepwater species of the snake eel genus Ophichthus (Anguilliformes: Ophichthidae) from North Carolina. Copeia 2007:783–787
Menard A, Turgeon K, Kramer DL (2007) Selection of diurnal refuges by the nocturnal squirrelfish, Holocentrus rufus. Environ Biol Fish 82:59–70
Mortensen PB, Hovland M, Brattegard T, Farestveit R (1995) Deepwater bioherms of the scleractinian coral Lophelia pertusa (L.) at 64° N on the Norwegian Shelf: structure and associated megafauna. Sarsia 80:145–158
Mosher CV, Watling L (2009) Partners for life: a brittle star and its octocoral host. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 397:81–88
Munday PL, Jones GP, Caley MJ (1997) Habitat specialisation and the distribution and abundance of coral-dwelling gobies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 152:227–239
Nielsen JG, Ross SW, Cohen DM (2009) Atlantic occurrence of the genus Bellottia (Teleostei, Bythitidae) with two new species from the Western North Atlantic. Zootaxa 2018:45–57
Nizinski MS (1989) Ecological distribution, demography, and behavioral observations on Periclimenes anthophilus, an atypical symbiotic cleaner shrimp. Bull Mar Sci 45:174–188
Orth RJ, Heck KL Jr, van Montfrans J (1984) Faunal communities in seagrass beds: a review of the influence of plant structure and prey characteristics on predator: prey relationships. Estuaries 7:339–350
Partyka ML, Ross SW, Quattrini AM, Sedberry GR, Birdsong TW, Potter J (2007) Southeastern United States deep-sea corals (SEADESC) initiative: a collaborative effort to characterize areas of habitat-forming deep-sea corals. NOAA Tech Memo OER 1, Silver Spring, MD
Quattrini AM, Ross SW (2006) Fishes associated with North Carolina shelf-edge hardbottoms and initial assessment of a proposed marine protected area. Bull Mar Sci 79:137–163
Roberts JM (2005) Reef-aggregating behaviour by symbiotic eunicid polychaetes from cold-water corals: do worms assemble reefs? J Mar Biol Ass UK 85:813–819
Roberts JM, Wheeler AJ, Freiwald A (2006) Reefs of the deep: the biology and geology of cold-water coral ecosystems. Science 312:543–547
Roberts JM, Henry LA, Long D, Hartley JP (2008) Cold-water coral reef frameworks, megafaunal communities and evidence for coral carbonate mounds on the Hatton Bank, north east Atlantic. Facies 54:297–316
Roberts JM, Wheeler A, Freiwald A, Cairns SD (2009) Cold-water corals: the biology and geology of deep-sea coral habitats. Cambridge University Press, UK
Robertson DR, Gaines SD (1986) Interference competition structures habitat use in a local assemblage of coral reef surgeonfishes. Ecology 67:1372–1383
Ross SW, Quattrini AM (2007) The fish fauna associated with deep coral banks off the southeastern United States. Deep-Sea Res I 54:975–1007
Ross SW, Quattrini AM (2009) Deep-sea reef fish assemblage patterns on the Blake Plateau (Western North Atlantic Ocean). Mar Ecol 30:74–92
Stevens GC (1989) The latitudinal gradient in geographical range: how so many species coexist in the tropics. Am Nat 133:240–256
Sulak KJ, Brooks RA, Luke KE, Norem AD, Randall M, Quaid AJ, Yeargin GE, Miller JM, Harden WM, Caruso JH, Ross SW (2007) Demersal fishes associated with Lophelia pertusa coral and hard-substrate biotopes on the continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico. In: George RY, Cairns SD (eds) Conservation and adaptive management of seamount and deep-Sea coral ecosystems. University of Miami, Florida, pp 65–92
ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecol 67:1167–1179
ter Braak CJF (1996) Unimodal methods to relate species to environment. Centre for Biometry Wageningen (DLO Agricultural Mathematics Group), Wageningen
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Thiem Ø, Ravagnan E, Fosså JH, Berntsen J (2006) Food supply mechanisms for cold-water corals along a continental shelf edge. J Mar Syst 60:207–219
Tissot BN, Yoklavich MM, Love MS, York K, Amend M (2006) Benthic invertebrates that form habitat on deep banks off southern California, with special reference to deep-sea coral. Fish Bull 104:167–181
Weaver DC, Sedberry GR (2001) Trophic subsidies at the Charleston Bump: food web structure of reef fishes on the continental slope of the southeastern United States. Am Fish Soc Symp 25:137–152
Wilson SK (2001) Multiscale habitat associations of detrivorous blennies (Blenniidae: Salariini). Coral Reefs 20:245–251
Wilson MFJ, O’Connell B, Brown C, Guinan JC, Grehan AJ (2007) Multiscale terrain analysis of multibeam bathymetry data for habitat mapping on the continental slope. Mar Geodesy 30:3–35
Wilson SK, Burgess SC, Cheal AJ, Emslie M, Fisher R, Miller I, Polunin NVC, Sweatman HPA (2008) Habitat utilization by coral reef fish: implications for specialists versus generalists in a changing environment. J An Ecol 77:220–228
Wood J (1996) The geomorphological characterisation of digital elevation models. PhD Thesis, University of Leicester
Wood J (2005) Landserf version 2.2. http://www.landserf.org
Acknowledgments
The NOAA Undersea Research Center at UNCW provided funds (to S.W. Ross, PI) for the multibeam mapping cruise on the NOAA vessel Nancy Foster. NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration largely funded (to S.W. Ross, lead PI) submersible fieldwork and some data analyses. Environmental Defense Fund (through D.N. Rader) and NOAA Habitat Conservation Division (through Miles Croom) supplied substantial funds for this project. Friends of the NC Museum of Natural Sciences administered funds and the South Atlantic Fishery Management Council provided support. We thank the personnel of the NOAA vessel Nancy Foster, the R/V Seward Johnson and Johnson-Sea-Link submersible. We also thank M.L. Partyka, A.M. Necaise, J.P. McClain-Counts, M. Rhode, E. Cordes and A. Davies for their helpful contributions. Finally, we acknowledge support of US Geological Survey and particularly thank G.D. Brewer for facilitating this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. P. Grassle.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quattrini, A.M., Ross, S.W., Carlson, M.C.T. et al. Megafaunal-habitat associations at a deep-sea coral mound off North Carolina, USA. Mar Biol 159, 1079–1094 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1888-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1888-7