Abstract
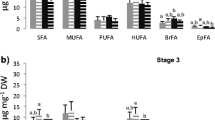
Cape hakes, Merluccius paradoxus and M. capensis, are important gadoid fish that are commercially harvested in the Benguela Current system off Namibia and South Africa. The aim of this study was to elucidate the nutritional condition and feeding preferences of their larvae. Hake eggs and larvae were sampled in austral spring of two consecutive years, 2007 and 2008, off the west coast of South Africa. They were identified to species using genetics, and total lipid content and fatty acid (FA) composition were analysed for each individual egg and larva to compare the condition of different early life stages of both hake species. Higher abundances of M. paradoxus eggs and larvae were consistently found compared to M. capensis. In both species, eggs contained wax esters (WE) and had significantly higher lipid content per dry mass than larvae. Lipid content as well as FA composition changed with the developmental stage of larvae. Quantities of essential fatty acid (EFA) increased with feeding of larvae due to dietary lipid incorporation. In 2007, yolk-sac larvae contained significantly lower total lipids than in 2008. It is argued that this was due to reduced lipid transfer by the spawning females to the eggs. These findings indicate that maternal effects are important in determining condition of hake larvae and that this may have an effect on their survival and subsequent recruitment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey K, Houde E (1989) Predation on eggs and larvae of marine fishes and the recruitment problem. Adv Mar Biol 25:1–83
Bell JG, Sargent JR (2003) Arachidonic acid in aquaculture feeds: current status and future opportunities. Aquaculture 218:491–499
Berkeley SA, Chapman C, Sogard SM (2004) Maternal age as a determinant of larval growth and survival in a marine fish, Sebastes melanops. Ecology 85:1258–1264
Blanchard JL, Frank KT, Simon JE (2003) Effects of condition on fecundity and total egg production of eastern Scotian Shelf haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 60:321–332
Botha L (1985) Occurrence and distribution of Cape hakes Merluccius capensis Cast and M. paradoxus Franca in the Cape of Good Hope area. S Afr J Mar Sci 3:179–190
Botha L (1986) Reproduction, sex ratio and rate of natural mortality of Cape hakes Merluccius capensis Cast and M. paradoxus Franca in the Cape of Good Hope area. S Afr J Mar Sci 4:23–35
Bustos CA, Landaeta MF, Bay-Schmith E, Lewis R, Moraga X (2007) Effects of temperature and lipid droplet adherence on mortality of hatchery-reared southern hake Merluccius australis larvae. Aquaculture 270:535–540
Butterworth DS, Rademeyer RA (2005) Sustainable management initiatives for the southern African hake fisheries over recent years. Bull Mar Sci 76:287–319
Copeman LA, Parrish CC, Brown JA, Harel M (2002) Effects of docosahexaenoic, eicosapentaenoic, and arachidonic acids on the early growth and pigmentation of yellowtail flounder (Limanda ferruginea): a live food enrichment experiment. Aquaculture 210:285–304
Cury P, Roy C (1989) Optimal environmental window and pelagic fish recruitment success in upwelling areas. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:670–680
Cushing DH (1975) Marine ecology and fisheries. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 278
Cutts CJ, Sawanboonchun J, Mazorra de Quero C, Bell JG (2006) Diet-induced differences in the essential fatty acid (EFA) compositions of larval Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L) with reference to possible effects of dietary EFAs on larval performance. ICES J Mar Sci 63:302–310
Dalsgaard J, St John M, Kattner G, Müller-Navarra D, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. Adv Mar Biol 46:225–340
de Figueiredo G, Nash R, Montagnes D (2005) The role of the generally unrecognised microprey source as food for larval fish in the Irish Sea. Mar Biol 148:395–404
Domínguez-Petit R, Saborido-Rey F, Medina I (2009) Changes of proximate composition, energy storage and condition of European hake (Merluccius merluccius, L. 1758) through the spawning season. Fish Res 104:73–82
Ederington MC, McManus GB, Harvey HR (1995) Trophic transfer of fatty acids, sterols, and a triterpenoid alcohol between bacteria, a ciliate, and the copepod Acartia tonsa. Limnol Oceanogr 40:860–867
Fernández-Palacios H, Izquierdo MS, Robaina L, Valencia A, Salhi M, Vergara JM (1995) Effect of n-3 HUFA level in broodstock diets on egg quality of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L). Aquaculture 132:325–337
Field JG, Moloney CL, du Buisson L, Jarre A, Stroemme T, Lipinski MR, Kainge P (2008) Exploring the BOFFFF hypothesis using a model of Southern African deepwater hake (Merluccius paradoxus). In: Tsukamoto K, Kawamura T, Takeuchi T, Beard TD Jr, Kaiser MJ (eds) Fisheries for global welfare and environment, 5th World Fisheries Congress, pp 17–26
Fukami K, Watanabe A, Fujita S, Yamaoka K, Nishijima T (1999) Predation on naked protozoan microzooplankton by fish larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 185:285–291
Govoni JJ, Ortner PB, Al-Yamani F, Hill LC (1986) Selective feeding of spot, Leiostomus xanthurus, and Atlantic croaker, Micropogonias undulatus, larvae in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 28:175–183
Grote B, Ekau W, Hagen W, Huggett JA, Verheye HM (2007) Early life-history strategy of Cape hake in the Benguela upwelling region. Fish Res 86:179–187
Hislop JRG (1988) The influence of maternal length and age on the size and weight of the eggs and the relative fecundity of the haddock, Melanogrammus aeglefinus, in British waters. J Fish Biol 32:923–930
Hjort J (1914) Fluctuations in the great fisheries of northern Europe viewed in the light of biological research. Rapp P-V Reun Cons Int Explo Mer 20:1–228
Hollowed AB, Bailey KM (1989) New perspectives on the relationships between recruitment of Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) in the ocean environment. In: Beamish RJ, McFarlane GA (eds) Effects of ocean variability on recruitment and an evaluation of parameters used in stock assessment models. Can Spec Public Fish Aquat Sci, pp 207–220
Houde ED (2008) Emerging from Hjort’s shadow. J Northwest Atl Fish Sci 41:53–70
Izquierdo MS, Fernandez-Palacios H, Tacon AGJ (2001) Effect of broodstock nutrition on reproductive performance of fish. Aquaculture 197:25–42
Jennings S, Kaiser MJ, Reynolds JD (2001) Marine fisheries ecology. Blackwell Science, Oxford, p 417
Kaitaranta JK (1981) Total lipids and lipid classes of fish roe. Comp Biochem Physiol 69B
Kattner G, Fricke HSG (1986) Simple gas-liquid chromatography method for simultaneous determination of fatty acids and alcohols in wax esters of marine organisms. J Chromatogr A 361:263–268
Kayama M, Horii I, Ikeda Y (1974) Studies on fish roe, especially on mullet roe wax esters. Yukagaku 23:290–295
Klungsøyr J, Tilseth S, Wilhelmsen S, Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR (1989) Fatty acid composition as an indicator of food intake in cod larvae Gadus morhua from Lofoten, Northern Norway. Mar Biol 102:183–188
Lloret J, Demestre M, Sanchez-Pardo J (2008) Lipid (energy) reserves of European hake (Merluccius merluccius) in the north-western Mediterranean. Vie Milieu 58:75–85
Lochmann SE, Maillet GL, Frank KT, Taggart CT (1995) Lipid class composition as a measure of nutritional condition in individual larval Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:1294–1306
Longhurst A (2002) Murphy’s law revisited: longevity as a factor in recruitment to fish populations. Fish Res 56:125–131
Macchi GJ, Pájaro M, Militelli MI, Radovani N, Rivas L (2006) Influence of size, age and maternal condition on the oocyte dry weight of Argentine hake (Merluccius hubbsi). Fish Res 80:345–349
Marteinsdottir G, Begg GA (2002) Essential relationships incorporating the influence of age, size and condition on variables required for estimation of reproductive potential in Atlantic cod Gadus morhua. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 235:235–256
Marteinsdottir G, Steinarsson A (1998) Maternal influence on the size and viability of cod (Gadus morhua L) eggs and larvae. J Fish Biol 52:1241–1258
Masuda R (2003) The critical role of docosahexaenoic acid in marine and terrestrial ecosystems: from bacteria to human behavior. Big fish bang, pp 249–256
Méndez E, Fernández M, Pazo G, Grompone MA (1992) Hake roe lipids: composition and changes following cooking. Food Chem 45:179–181
Mourente G (2003) Accumulation of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid; 22:6n-3) in larval and juvenile fish brain. In: Browman HI, Skiftesvik AB (eds) The big fish bang, Proceedings of the 26th Annual Larval Fish Conference, Bergen, pp 239–248
Murua H, Motos L (2006) Reproductive strategy and spawning activity of the European hake Merluccius merluccius (L.) in the Bay of Biscay. J Fish Biol 69:1288–1303
Nagano N, Iwatsuki Y, Kamiyama T, Nakata H (2000) Effects of marine ciliates on survivability of the first-feeding larval surgeonfish, Paracanthurus hepatus: laboratory rearing experiments. Hydrobiologia 432:149–157
Nevenzel JC (1970) Occurrence, function and biosynthesis of wax esters in marine organisms. Lipids 5:308–319
Olivar MP, Fortuño JM (1991) Guide to Ichthyoplankton of the Southeast Atlantic (Benguela Current Region). Sci Mar 55:383
Olsen RE, Henderson RJ (1989) The rapid analysis of neutral and polar marine lipids using double-development HPTLC and scanning densitometry. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 129:189–197
Olsen RE, Henderson RJ, Pedersen T (1991) The influence of dietary lipid classes on the fatty acid composition of small cod Gadus morhua L reared in an enclosure in northern Norway. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 148:59–76
Payne AIL (1989) Cape hakes. In: Payne AIL, Crawford RJM, Van Dalsen AP (eds) Oceans of life off Southern Africa. Vlaeberg Publication, Cape Town, pp 136–147
Peters J, Renz J, Van Beusekom J, Boersma M, Hagen W (2006) Trophodynamics and seasonal cycle of the copepod Pseudocalanus acuspes in the Central Baltic Sea (Bornholm Basin): evidence from lipid composition. Mar Biol 149:1417–1429
Pickova J, Dutta PC, Larsson P-O, Kiessling A (1997) Early embryonic cleavage pattern, hatching success, and egg-lipid fatty acid composition: comparison between two cod (Gadus morhua) stocks. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:2410–2416
Plante S, Pernet F, Haché R, Ritchie R, Ji B, McIntosh D (2007) Ontogenetic variations in lipid class and fatty acid composition of haddock larvae Melanogrammus aeglefinus in relation to changes in diet and microbial environment. Aquaculture 263:107–121
Porebski J (1975) Application of the surface adhesion test to identify the eggs of the hake Merluccius spp. Colln Sci Pap Int Commun SE Atl Fish 2:102–106
Probst WN, Kraus G, Rideout RM, Trippel EA (2006) Parental effects on early life history traits of haddock Melanogrammus aeglefinus. ICES J Mar Sci 63:224–234
Rainuzzo J, Reitan K, Olsen Y (1997) The significance of lipids at early stages of marine fish: a review. Aquaculture 155:103–115
Rossi S, Sabatés A, Latasa M, Reyes E (2006) Lipid biomarkers and trophic linkages between phytoplankton, zooplankton and anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) larvae in the NW Mediterranean. J Plankton Res 28:551–562
Sargent JR, Parkes RJ, Mueller-Harvey I, Henderson RJ (1987) Lipid biomarkers in marine ecology. In: Sleigh MA (ed) Microbes in the sea. Ellis Horwood, Chichester, pp 119–533
Sargent JR, McEvoy L, Estevez A, Bell G, Bell M, Henderson J, Tocher D (1999) Lipid nutrition of marine fish during early development: current status and future directions. Aquaculture 179:217–229
St John MA, Lund T (1996) Lipid biomarkers: linking the utilization of frontal plankton biomass to enhanced condition of juvenile North Sea cod. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 131:75–85
St John M, Clemmesen C, Lund T, Köster T (2001) Diatom production in the marine environment: implications for larval fish growth and condition. ICES J Mar Sci 58:1106–1113
Stenevik EK, Verheye HM, Lipinski MR, Ostrowski M, Strømme T (2008) Drift routes of Cape hake eggs and larvae in the southern Benguela Current system. J Plankton Res 30:1147–1156
Sundby S, Boyd AJ, Hutchings L, O’Toole MJ, Thorisson K, Thorsen A (2001) Interaction between Cape hake spawning and the circulation in the Northern Benguela upwelling ecosystem. S Afr J Mar Sci 23:317–336
Tocher DR (2003) Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Sci 11:107–184
Trippel EA, Kraus G, Köster FW (2005) Maternal and paternal influences on early life history traits and processes of Baltic cod Gadus morhua. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 303:259–267
Voges E, Gordoa A, Bartholomae CH, Field JG (2002) Estimating the probability of different levels of recruitment for Cape hakes Merluccius capensis off Namibia using environmental indices. Fish Res 58:333–340
Von der Heyden S, Lipinski MR, Matthee CA (2007) Species-specific genetic markers for identification of early life history stages of Cape hakes, Merluccius capensis and M. paradoxus in the southern Benguela Current. J Fish Biol 70:262–268
Wickham SA (1995) Trophic relations between cyclopoid copepods and ciliated protists: complex interactions link the microbial and classic food webs. Limnol Oceanogr 40:1173–1181
Wiegand MD (1996) Composition, accumulation and utilization of yolk lipids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 6:259–286
Yanes-Roca C, Rhody N, Nystrom M, Main KL (2009) Effects of fatty acid composition and spawning season patterns on egg quality and larval survival in common snook (Centropomus undecimalis). Aquaculture 287:335–340
Zhang W, Xu K, Wan R, Zhang G, Meng T, Xiao T, Wang R, Sun S, Choi JK (2002) Spatial distribution of ciliates, copepod nauplii and eggs, Engraulis japonicus post-larvae and microzooplankton herbivorous activity in the Yellow Sea, China. Aquat Microb Ecol 27:249–259
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the captains and crew of RV Dr. Fridtjof Nansen and RV Ellen Khuzwayo, and scientists and technicians from the South African Departments of Environmental Affairs (DEA) and Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (DAFF) and from the National Marine Information and Research Centre (NatMIRC) of Namibia for their support during the cruises. We are also grateful to Dr. S. von der Heyden (Univ. of Stellenbosch, South Africa) and Prof. M. Kochzius and the working group ‘Biotechnology and Molecular Genetics’, University of Bremen, headed by Prof. D. Blohm, for scientific and logistic assistance. Logistic and financial support was generously provided by the Nansen Programme, particularly Dr. T. Strømme, the Benguela Current Large Marine Ecosystem Programme (BCLME), DEA and DAFF, the Norway-South Africa Fisheries Cooperation Agreement (NORSA) and the German National Academic Foundation (Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes). This paper formed part of a PhD thesis at the University of Bremen, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Righton.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grote, B., Hagen, W., Lipinski, M.R. et al. Lipids and fatty acids as indicators of egg condition, larval feeding and maternal effects in Cape hakes (Merluccius paradoxus and M. capensis). Mar Biol 158, 1005–1017 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1626-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1626-6