Abstract
We describe trends in fast, high resolution elemental imaging by laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA–ICPMS). Recently developed low dispersion LA cells deliver quantitative transport of ablated aerosols within 10 ms and also provide enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional LA cells because the analyte ion signal becomes less diluted during aerosol transport. When connected to simultaneous ICPMS instruments, these low dispersion LA cells offer a platform for high speed and high lateral resolution shot-resolved LA–ICPMS imaging. Here, we examine the current paradigms of LA–ICPMS imaging and discuss how newly developed LA cell technology combined with simultaneous ICPMS instrumentation is poised to overcome current instrumental limitations to deliver faster, higher resolution elemental imaging.

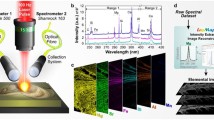
On means for obtaining high-speed, high-resolution, multielemental images is to combine new lowdispersion laser-ablation cell technology with an inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometer (ICP-TOFMS). Here, we show three selected-isotope LA-ICP-TOFMS images of a hetereogeneous Opalinus clay sample




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giesen C, Wang HAO, Schapiro D, Zivanovic N, Jacobs A, Hattendorf B, et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nat Methods. 2014;11(4):417–22.
Wang HA, Grolimund D, Giesen C, Borca CN, Shaw-Stewart JR, Bodenmiller B, et al. Fast chemical imaging at high spatial resolution by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2013;85(21):10107–16.
Van Malderen SJM, van Elteren JT, Vanhaecke F. Development of a fast laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry cell for sub-μm scanning of layered materials. J Anal At Spectrom. 2015;30(1):119–25.
Van Malderen SJ, van Elteren JT, Vanhaecke F. Submicrometer imaging by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry via signal and image deconvolution approaches. Anal Chem. 2015;87(12):6125–32.
Gundlach-Graham AW, Burger M, Allner S, Schwarz G, Wang HAO, Gyr L, et al. High-speed, high-resolution, multi-elemental LA–ICP–TOFMS imaging: Part I. instrumentation and two-dimensional imaging of geological samples. Anal Chem. 2015;87(16):8250–8.
Burger M, Gundlach-Graham A, Allner S, Schwarz G, Wang HAO, Gyr L, et al. High-speed, high-resolution, multielemental LA–ICP–TOFMS imaging: Part II. critical evaluation of quantitative three-dimensional imaging of major, minor, and trace elements in geological samples. Anal Chem. 2015;87(16):8259–67.
Kindness A, Sekaran CN, Feldmann J. Two-dimensional mapping of copper and zinc in liver sections by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2003;49(11):1916–23.
Woodhead JD, Hellstrom J, Hergt JM, Greig A, Maas R. Isotopic and elemental imaging of geological materials by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma‐mass spectrometry. Geostand Geoanal Res. 2007;31(4):331–43.
Sabine Becker J. Imaging of metals in biological tissue by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA–ICP–MS): state of the art and future developments. J Mass Spectrom. 2013;48(2):255–68.
Gray AL. Solid sample introduction by laser ablation for inductively coupled plasma source mass spectrometry. Analyst. 1985;110(5):551–6.
Günther D, Hattendorf B. Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2005;24(3):255–65.
Hattendorf B, Günther D. Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA–ICPMS). Handbook of spectroscopy. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2014. p. 647–98.
Longerich HP, Günther D, Jackson SE. Elemental fractionation in laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 1996;355(5–6):538–42.
Kuhn H-R, Guillong M, Günther D. Size-related vaporisation and ionisation of laser-induced glass particles in the inductively coupled plasma. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2004;378(4):1069–74.
Russo RE, Mao X, Gonzalez JJ, Zorba V, Yoo J. Laser ablation in analytical chemistry. Anal Chem. 2013;85(13):6162–77.
Lear J, Hare D, Adlard P, Finkelstein D, Doble P. Improving acquisition times of elemental bio-imaging for quadrupole-based LA–ICP–MS. J Anal At Spectrom. 2012;27(1):159–64.
Holland JF, Enke CG, Allison J, Stults JT, Pinkston JD, Newcome B, et al. Mass spectrometry on the chromatographic time scale: realistic expectations. Anal Chem. 1983;55(9):997A–1012.
Schilling GD, Andrade FJ, Barnes JH, Sperline RP, Denton MB, Barinaga CJ, et al. Continuous simultaneous detection in mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2007;79(20):7662–8.
Bleiner D, Belloni F, Doria D, Lorusso A, Nassisi V. Overcoming pulse mixing and signal tailing in laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry depth profiling. J Anal At Spectrom. 2005;20(12):1337–43.
Bleiner D, Gunther D. Theoretical description and experimental observation of aerosol transport processes in laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2001;16(5):449–56.
Plotnikov A, Vogt C, Wetzig K, Kyriakopoulos A. A theoretical approach to the interpretation of the transient data in scanning laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: consideration of the geometry of the scanning area. Spectrochim Acta B. 2008;63(4):474–83.
Triglav J, van Elteren JT, Šelih VS. Basic modeling approach to optimize elemental imaging by laser ablation ICPMS. Anal Chem. 2010;82(19):8153–60.
Wang HAO, Grolimund D, Van Loon LR, Barmettler K, Borca CN, Aeschlimann B, et al. Quantitative chemical imaging of element diffusion into heterogeneous media using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, synchrotron micro-x-ray fluorescence, and extended x-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2011;83(16):6259–66.
Elteren J, Izmer A, Sala M, Orsega EF, Selih VS, Panighello S, et al. 3D laser ablation-ICP–mass spectrometry mapping for the study of surface layer phenomena – a case study for weathered glass. J Anal At Spectrom. 2013;28:994–1004.
Chirinos JR, Oropeza DD, Gonzalez JJ, Hou HM, Morey M, Zorba V, et al. Simultaneous 3-dimensional elemental imaging with LIBS and LA–ICP–MS. J Anal At Spectrom. 2014;29(7):1292–8.
Jakubowski N, Prohaska T, Rottmann L, Vanhaecke F. Inductively coupled plasma- and glow discharge plasma-sector field mass spectrometry Part I. Tutorial: fundamentals and instrumentation. J Anal At Spectrom. 2011;26(4):693–726.
Wehe C, Thyssen G, Herdering C, Raj I, Ciarimboli G, Sperling M, et al. Elemental bioimaging by means of fast scanning laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2015;26(8):1274–82.
Dziewatkoski MP, Daniels LB, Olesik JW. Time-resolved inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry measurements with individual, monodisperse drop sample introduction. Anal Chem. 1996;68(7):1101–9.
Heinrich C, Pettke T, Halter W, Aigner-Torres M, Audétat A, Günther D, et al. Quantitative multi-element analysis of minerals, fluid and melt inclusions by laser-ablation inductively-coupled-plasma mass-spectrometry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2003;67(18):3473–97.
Borovinskaya O, Hattendorf B, Tanner M, Gschwind S, Gunther D. A prototype of a new inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometer providing temporally resolved, multi-element detection of short signals generated by single particles and droplets. J Anal At Spectrom. 2013;28(2):226–33.
Myers DP, Li G, Yang P, Hieftje GM. An inductively coupled plasma–time-of-flight mass spectrometer for elemental analysis. Part I: optimization and characteristics. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1994;5(11):1008–16.
Burgoyne TW, Hieftje GM, Hites RA. Design and performance of a plasma-source mass spectrograph. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1997;8(4):307–18.
Hieftje GM, Barnes JH, Grøn OA, Leach AM, McClenathan DM, Ray SJ, et al. Evolution and revolution in instrumentation for plasma-source mass spectrometry. Pure Appl Chem. 2001;73(10):1579–88.
Mahoney PP, Li G, Hieftje GM. Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a time-of-flight mass analyser. J Anal At Spectrom. 1996;11(6):401–5.
Bleiner D, Hametner K, Günther D. Optimization of a laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma “time of flight” mass spectrometry system for short transient signal acquisition. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 2000;368(1):37–44.
Leach AM, Hieftje GM. Standardless semiquantitative analysis of metals using single-shot laser ablation inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2001;73(13):2959–67.
Borovinskaya O, Gschwind S, Hattendorf B, Tanner M, Günther D. Simultaneous mass quantification of nanoparticles of different composition in a mixture by microdroplet generator-ICPTOFMS. Anal Chem. 2014;86(16):8142–8.
Leach AM, Hieftje GM. Factors affecting the production of fast transient signals in single shot laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Appl Spectrosc. 2002;56(1):62–9.
Liu XR, Horlick G. In-situ laser-ablation sampling for inductively-coupled plasma-atomic emission-spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B. 1994;50(4–7):537–48.
Tanner M, Gunther D. In torch laser ablation sampling for inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2005;20(9):987–9.
Tabersky D, Nishiguchi K, Utani K, Ohata M, Dietiker R, Fricker MB, et al. Aerosol entrainment and a large-capacity gas exchange device (Q-GED) for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in atmospheric pressure air. J Anal At Spectrom. 2013;28(6):831–42.
Pisonero J, Fliegel D, Gunther D. High efficiency aerosol dispersion cell for laser ablation-ICP–MS. J Anal At Spectrom. 2006;21(9):922–31.
Gurevich EL, Hergenroder R. A simple laser ICP–MS ablation cell with wash-out time less than 100 ms. J Anal At Spectrom. 2007;22(9):1043–50.
Lindner H, Autrique D, Pisonero J, Gunther D, Bogaerts A. Numerical simulation analysis of flow patterns and particle transport in the HEAD laser ablation cell with respect to inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom. 2010;25(3):295–304.
Douglas DN, Managh AJ, Reid HJ, Sharp BL. A high-speed, integrated ablation cell and dual concentric injector plasma torch for laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2015;87(22):11285–94.
Bandura DR, Baranov VI, Ornatsky OI, Antonov A, Kinach R, Lou X, et al. Mass cytometry: technique for real time single cell multitarget immunoassay based on inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81(16):6813–9822.
Gundlach-Graham A, Dennis EA, Ray SJ, Enke CG, Barinaga CJ, Koppenaal DW, et al. First inductively coupled plasma-distance-of-flight mass spectrometer: instrument performance with a microchannel plate/phosphor imaging detector. J Anal At Spectrom. 2013;28(9):1385–95.
Borovinskaya O, Tanner M, Cubison M, Günther D (2015) A new commercial ICP–TOFMS for the anaylsis of nanoparticles. European winter conference on plasma spectrochemistry, Münster, Germany, 23 February 2015.
Acknowledgments
Alex Gundlach-Graham would like to acknowledge financial support through the Marie Curie International Incoming Fellowship: the research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. 624280. A.G.-G. thanks Gunnar Schwarz for helpful critiques and comments on an early version of this manuscript. We would also like the acknowledge the work of Marcel Burger, Steffen Allner, Luzia Gyr, and Dr. Hao Wang for contribution to collection and analysis of the LA–ICP–TOFMS data presented here, and Dr. Daniel Grolimund for providing the cesium-infiltrated Opalinus clay sample.
Compliance with ethical standards
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection featuring Young Investigators in Analytical and Bioanalytical Science with guest editors S. Daunert, A. Baeumner, S. Deo, J. Ruiz Encinar, and L. Zhang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gundlach-Graham, A., Günther, D. Toward faster and higher resolution LA–ICPMS imaging: on the co-evolution of LA cell design and ICPMS instrumentation. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 2687–2695 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9251-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9251-8