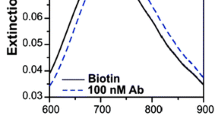
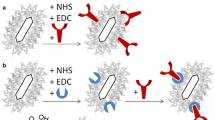
Abstract
In the last decade the use of anisotropic nanoparticles in analytical and bioanalytical applications has increased substantially. In particular, noble metal nanorods have unique optical properties that have attracted the interest of many research groups. The localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) generated by interaction of light at a specific wavelength with noble metal nanoparticles was found to depend on particle size and shape and on the constituting material and the surrounding dielectric solution. Because of their anisotropic shape, nanorods are characterized by two LSPR peaks: the transverse, fixed at approximately 530 nm, and the longitudinal, which is in the visible–near infra-red region of the spectrum and varies with nanorod aspect ratio. The intense surface plasmon band enables nanorods to absorb and scatter light in the visible and near infra-red regions, and fluorescence and two-photon induced luminescence are also observed. These optical properties, with the reactivity towards binding events that induce changes in the refractive index of the surrounding solution, make nanorods a useful tool for tracking binding events in different applications, for example assembly, biosensing, in-vivo targeting and imaging, and single-molecule detection by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. This review presents the promising strategies proposed for functionalizing gold nanorods and their successful use in a variety of analytical and biomedical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murray WA, Barnes W (2007) Plasmonic Materials. Adv Mater 19:3771–3782
Murphy CJ, Sau TK, Gole AM, Orendorff CJ, Gao J, Gou L, Hunyadi SE, Li T (2005) Anisotropic Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Assembly, and Optical Applications. J Phys Chem B 109:13857–13870
Pérez-Juste J, Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzán LM, Mulvaney P (2005) Gold nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord Chem Rev 249:1870–1901
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy and Sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297
Huang HJ, Yu C, Chang HC, Chiu KP, Ming Chen H, Liu RS, Tsai DP (2007) Plasmonic optical properties of a single gold nano-rod. Opt Express 15:7132–7139
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Lee K, El-Sayed MA (2006) Gold and Silver Nanoparticles in Sensing and Imaging: Sensitivity of Plasmon Response to Size, Shape, and Metal Composition. J Phys Chem B 110:19220–19225
Hu M, Novo C, Funston A, Wang H, Staleva H, Zou S, Mulvaney P, Xia Y, Hartland GV (2008) Dark-field microscopy studies of single metal nanoparticles: understanding the factors that influence the linewidth of the localized surface plasmon resonance. J Mater Chem 18:1949–1960
Chen H, Kou X, Yang Z, Ni W, Wang J (2008) Shape- and Size-Dependent Refractive Index Sensitivity of Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:5233–5237
Otte MA, Sepúlveda B, Ni W, Juste JP, Liz-Marzán LM, Lechuga LM (2010) Identification of the Optimal Spectral Region for Plasmonic and Nanoplasmonic Sensing. ACS Nano 4:349–357
Yang J, Wu J, Wu Y, Wang J, Chen C (2005) Organic solvent dependence of plasma resonance of gold nanorods: A simple relationship. Chem Phys Lett 416:215–219
Sepúlveda B, Angelomé PC, Lechuga LM, Liz-Marzán LM (2009) LSPR-based nanobiosensors. Nano Today 4:244–251
Huang H, He C, Zeng Y, Xia X, Yu X, Yi P, Chen Z (2009) A novel label-free multi-throughput optical biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2255–2259
Huang H, Tang C, Zeng Y, Yu X, Liao B, Xia X, Yi P, Chu PK (2009) Label-free optical biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance of immobilized gold nanorods. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 71:96–101
Murphy CJ, Gole AM, Hunyadi SE, Stone JW, Sisco PN, Alkilany A, Kinard BE, Hankins P (2008) Chemical sensing and imaging with metallic nanorods. Chem Commun 544–557
Uechi I, Yamada S (2008) Photochemical and analytical applications of gold nanoparticles and nanorods utilizing surface plasmon resonance. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2411–2421
Nusz GJ, Curry AC, Marinakos SM, Wax A, Chilkoti A (2009) Rational Selection of Gold Nanorod Geometry for Label-Free Plasmonic Biosensors. ACS Nano 3:795–806
Chu M, Myroshnychenko V, Chen CH, Deng J, Mou C, García de Abajo FJ (2009) Probing Bright and Dark Surface-Plasmon Modes in Individual and Coupled Noble Metal Nanoparticles Using an Electron Beam. Nano Lett 9:399–404
Payne EK, Shuford KL, Park S, Schatz GC, Mirkin CA (2006) Multipole Plasmon Resonances in Gold Nanorods. J Phys Chem B 110:2150–2154
Brioude A, Jiang XC, Pileni MP (2005) Optical Properties of Gold Nanorods: DDA Simulations Supported by Experiments. J Phys Chem B 109:13138–13142
Chen C, Cheng S, Chau L, Wang CC (2007) Sensing capability of the localized surface plasmon resonance of gold nanorods. Biosens Bioelectron 22:926–932
Marinakos SM, Chen S, Chilkoti A (2007) Plasmonic Detection of a Model Analyte in Serum by a Gold Nanorod Sensor. Anal Chem 79:5278–5283
Li C, Male KB, Hrapovic S, Luong JHT (2005) Fluorescence properties of gold nanorods and their application for DNA biosensing. Chem Commun 3924–3926
Eustis S, El-Sayed M (2005) Aspect Ratio Dependence of the Enhanced Fluorescence Intensity of Gold Nanorods: Experimental and Simulation Study. J Phys Chem B 109:16350–16356
Alekseeva AV, Bogatyrev VA, Dykman LA, Khlebtsov BN, Trachuk LA, Melnikov AG, Khlebtsov NG (2005) Preparation and optical scattering characterization of gold nanorods and their application to a dot-immunogold assay. Appl Opt 44:6285–6295
Zhu J, Huang L, Zhao J, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Hao L, Lu Y (2005) Shape dependent resonance light scattering properties of gold nanorods. Mater Sci Eng, B 121:199–203
Imura K, Nagahara T, Okamoto H (2005) Near-Field Two-Photon-Induced Photoluminescence from Single Gold Nanorods and Imaging of Plasmon Modes. J Phys Chem B 109:13214–13220
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2003) Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem Mater 15:1957–1962
Sau TK, Murphy CJ (2004) Seeded High Yield Synthesis of Short Au Nanorods in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 20:6414–6420
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2001) Evidence for Bilayer Assembly of Cationic Surfactants on the Surface of Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 17:6368–6374
Connor E, Mwamuka J, Gole A, Murphy CJ, Wyatt MD (2005) Gold Nanoparticles Are Taken Up by Human Cells but Do Not Cause Acute Cytotoxicity13. Small 1:325–327
Huff TB, Hansen MN, Zhao Y, Cheng J, Wei A (2007) Controlling the Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 23:1596–1599
Shibu Joseph ST, Ipe BI, Pramod P, Thomas KG (2006) Gold Nanorods to Nanochains: Mechanistic Investigations on Their Longitudinal Assembly Using α, ω-Alkanedithiols and Interplasmon Coupling. J Phys Chem B 110:150–157
Yu C, Irudayaraj J (2007) Multiplex Biosensor Using Gold Nanorods. Anal Chem 79:572–579
Niidome T, Yamagata M, Okamoto Y, Akiyama Y, Takahashi H, Kawano T, Katayama Y, Niidome Y (2006) PEG-modified gold nanorods with a stealth character for in vivo applications. J Control Release 114:343–347
Pierrat S, Zins I, Breivogel A, Sonnichsen C (2007) Self-Assembly of Small Gold Colloids with Functionalized Gold Nanorods. Nano Lett 7:259–263
Wang ZL, Mohamed MB, Link S, El-Sayed MA (1999) Crystallographic facets and shapes of gold nanorods of different aspect ratios. Surf Sci 440:L809–L814
Kim F, Song JH, Yang P (2002) Photochemical Synthesis of Gold Nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 124:14316–14317
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Wet Chemical Synthesis of High Aspect Ratio Cylindrical Gold Nanorods. J Phys Chem B 105:4065–4067
Khanal BP, Zubarev E (2007) Rings of Nanorods. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:2195–2198
Yang D, Cui D (2008) Advances and Prospects of Gold Nanorods. Chem Asian J 3:2010–2022
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Seed-Mediated Growth Approach for Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Spheroidal and Rod-like Gold Nanoparticles Using a Surfactant Template. Adv Mater 13:1389–1393
Yu CS, Lee C, Wang CRC (1997) Gold Nanorods: Electrochemical Synthesis and Optical Properties. J Phys Chem B 101:6661–6664
Wang H, Zou C, Yang B, Lu H, Tian C, Yang H, Li M, Liu C, Fu D, Liu J (2009) Electrodeposition of tubular-rod structure gold nanowires using nanoporous anodic alumina oxide as template. Electrochem Commun 11:2019–2022
Pérez-Juste J, Liz-Marzán L, Carnie S, Chan D, Mulvaney P (2004) Electric-Field-Directed Growth of Gold Nanorods in Aqueous Surfactant Solutions. Adv Funct Mater 14:571–579
Jiang X, Pileni M (2007) Gold nanorods: Influence of various parameters as seeds, solvent, surfactant on shape control. Colloids Surf, A 295:228–232
Gole A, Murphy CJ (2004) Seed-Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanorods: Role of the Size and Nature of the Seed. Chem Mater 16:3633–3640
Jiang X, Brioude A, Pileni M (2006) Gold nanorods: Limitations on their synthesis and optical properties. Colloids Surf, A 277:201–206
Johnson CJ, Dujardin E, Davis SA, Murphy CJ, Mann S (2002) Growth and form of gold nanorods prepared by seed-mediated, surfactant-directed synthesis. J Mater Chem 12:1765–1770
Gai PL, Harmer MA (2002) Surface Atomic Defect Structures and Growth of Gold Nanorods. Nano Lett 2:771–774
Hernandez J, Solla-Gullon J, Herrero E, Aldaz A, Feliu JM (2005) Characterization of the Surface Structure of Gold Nanoparticles and Nanorods Using Structure Sensitive Reactions. J Phys Chem B 109:12651–12654
Liu Guyot-Sionnest P (2005) Mechanism of Silver(I)-Assisted Growth of Gold Nanorods and Bipyramids. J Phys Chem B 109:22192–22200
Hubert F, Testard F, Spalla O (2008) Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide Silver Bromide Complex as the Capping Agent of Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 24:9219–9222
Jana NR (2005) Gram-Scale Synthesis of Soluble, Near-Monodisperse Gold Nanorods and Other Anisotropic Nanoparticles. Small 1:875–882
Niidome Y, Nakamura Y, Honda K, Akiyama Y, Nishioka K, Kawasaki H, Nakashima N (2009) Characterization of silver ions adsorbed on gold nanorods: surface analysis by using surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Chem Commun 1754–1756
Gao J, Bender CM, Murphy CJ (2003) Dependence of the Gold Nanorod Aspect Ratio on the Nature of the Directing Surfactant in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 19:9065–9070
Nie Z, Petukhova A, Kumacheva E (2010) Properties and emerging applications of self-assembled structures made from inorganic nanoparticles. Nature Nanotechnology 5:15–25
Sharma V, Park K, Srinivasarao M (2009) Colloidal dispersion of gold nanorods: Historical background, optical properties, seed-mediated synthesis, shape separation and self-assembly. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 65:1–38
Yu C, Irudayaraj J (2007) Quantitative Evaluation of Sensitivity and Selectivity of Multiplex NanoSPR Biosensor Assays. Biophys J 93:3684–3692
Nusz GJ, Marinakos SM, Curry AC, Dahlin A, Hook F, Wax A, Chilkoti A (2008) Label-Free Plasmonic Detection of Biomolecular Binding by a Single Gold Nanorod. Anal Chem 80:984–989
Orendorff CJ, Gearheart L, Jana NR, Murphy CJ (2006) Aspect ratio dependence on surface enhanced Raman scattering using silver and gold nanorod substrates. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:165–170
Wang C, Irudayaraj J (2008) Gold Nanorod Probes for the Detection of Multiple Pathogens. Small 4:2204–2208
Rayavarapu RG, Petersen W, Ungureanu C, Post JN, Leeuwen TGV, Manohar S (2007) Synthesis and Bioconjugation of Gold Nanoparticles as Potential Molecular Probes for Light-Based Imaging Techniques. Int J Biomed Imaging 2007:29817
Eghtedari M, Liopo AV, Copland JA, Oraevsky AA, Motamedi M (2009) Engineering of Hetero-Functional Gold Nanorods for the in vivo Molecular Targeting of Breast Cancer Cells. Nano Lett 9:287–291
Fourkal E, Velchev I, Taffo A, Ma C, Khazak V, Skobeleva N (2009) Photo-Thermal Cancer Therapy Using Gold Nanorods. World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, September 7 – 12, 2009, Munich, Germany
Huff TB, Tong L, Zhao Y, Hansen MN, Cheng J, Wei A (2007) Hyperthermic effects of gold nanorods on tumor cells. Nanomedicine 2:125–132
Salem AK, Searson PC, Leong KW (2003) Multifunctional nanorods for gene delivery. Nat Mater 2:668–671
Yu C, Varghese L, Irudayaraj J (2007) Surface Modification of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide-Capped Gold Nanorods to Make Molecular Probes. Langmuir 23:9114–9119
Caswell KK, Wilson JN, Bunz UHF, Murphy CJ (2003) Preferential End-to-End Assembly of Gold Nanorods by Biotin−Streptavidin Connectors. J Am Chem Soc 125:13914–13915
Thomas KG, Barazzouk S, Ipe BI, Joseph STS, Kamat PV (2004) Uniaxial Plasmon Coupling through Longitudinal Self-Assembly of Gold Nanorods. J Phys Chem B 108:13066–13068
Chang J, Wu H, Chen H, Ling Y, Tan W (2005) Oriented assembly of Au nanorods using biorecognition system. Chem Commun 1092–1094
Rostro-Kohanloo BC, Bickford LR, Payne CM, Day ES, Anderson LJE, Zhong M, Lee S, Mayer KM, Zal T, Adam L, Dinney CPN, Drezek RA, West JL, Hafner JH (2009) The stabilization and targeting of surfactant-synthesized gold nanorods. Nanotechnology 20:434005
Thierry B, Ng J, Krieg T, Griesser HJ (2009) A robust procedure for the functionalization of gold nanorods and noble metal nanoparticles. Chem Commun 1724–1726
Liao H, Hafner JH (2005) Gold Nanorod Bioconjugates. Chem Mater 17:4636–4641
Takahashi H, Niidome Y, Niidome T, Kaneko K, Kawasaki H, Yamada S (2006) Modification of Gold Nanorods Using Phosphatidylcholine to Reduce Cytotoxicity. Langmuir 22:2–5
Orendorff CJ, Alam TM, Sasaki DY, Bunker BC, Voigt JA (2009) Phospholipid−Gold Nanorod Composites. ACS Nano 3:971–983
Dai Q, Coutts J, Zou J, Huo Q (2008) Surface modification of gold nanorods through a place exchange reaction inside an ionic exchange resin. Chem Commun 2858–2860
Huang H, Liu X, Zeng Y, Yu X, Liao B, Yi P, Chu PK (2009) Optical and biological sensing capabilities of Au2S/AuAgS coated gold nanorods. Biomaterials 30:5622–5630
Gole A, Murphy CJ (2008) Azide-Derivatized Gold Nanorods: Functional Materials for “Click” Chemistry. Langmuir 24:266–272
Jain PK, Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Plasmon Coupling in Nanorod Assemblies: Optical Absorption, Discrete Dipole Approximation Simulation, and Exciton-Coupling Model. J Phys Chem B 110:18243–18253
Gluodenis M, Foss CA (2002) The Effect of Mutual Orientation on the Spectra of Metal Nanoparticle Rod−Rod and Rod−Sphere Pairs. J Phys Chem B 106:9484–9489
Xu Z, Shen C, Xiao C, Yang T, Chen S, Li H, Gao H (2006) Fabrication of gold nanorod self-assemblies from rod and sphere mixtures via shape self-selective behavior. Chem Phys Lett 432:222–225
Orendorff CJ, Hankins PL, Murphy CJ (2005) pH-Triggered Assembly of Gold Nanorods. Langmuir 21:2022–2026
Varghese N, Vivekchand S, Govindaraj A, Rao C (2008) A calorimetric investigation of the assembly of gold nanorods to form necklaces. Chem Phys Lett 450:340–344
Sudeep PK, Joseph STS, Thomas KG (2005) Selective Detection of Cysteine and Glutathione Using Gold Nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 127:6516–6517
Nie FD, Rubinstein M, Kumacheva E (2008) “Supramolecular” Assembly of Gold Nanorods End-Terminated with Polymer “Pom-Poms”: Effect of Pom-Pom Structure on the Association Modes. J Am Chem Soc 130:3683–3689
Nakashima H, Furukawa K, Kashimura Y, Torimitsu K (2008) Self-Assembly of Gold Nanorods Induced by Intermolecular Interactions of Surface-Anchored Lipids. Langmuir 24:5654–5658
Gole A, Murphy CJ (2005) Biotin−Streptavidin-Induced Aggregation of Gold Nanorods: Tuning Rod−Rod Orientation. Langmuir 21:10756–10762
Pan B, Ao L, Gao F, Tian H, He R, Cui D (2005) End-to-end self-assembly and colorimetric characterization of gold nanorods and nanospheres via oligonucleotide hybridization. Nanotechnology 16:1776–1780
Dujardin E, Mann S, Hsin L, Wang CRC (2001) DNA-driven self-assembly of gold nanorods. Chem Commun 1264–1265
Huang H, Koria P, Parker SM, Selby L, Megeed Z, Rege K (2008) Optically Responsive Gold Nanorod−Polypeptide Assemblies. Langmuir 24:14139–14144
Walker DA, Gupta VK (2008) Reversible end-to-end assembly of gold nanorods using a disulfide-modified polypeptide. Nanotechnology 19:435603
Reynolds RA, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL (2000) Homogeneous, Nanoparticle-Based Quantitative Colorimetric Detection of Oligonucleotides. J Am Chem Soc 122:3795–3796
Aslan K, Holley P, Davies L, Lakowicz JR, Geddes CD (2005) Angular-Ratiometric Plasmon-Resonance Based Light Scattering for Bioaffinity Sensing. J Am Chem Soc 127:12115–12121
Aslan K, Lakowicz JR, Geddes CD (2005) Nanogold Plasmon Resonance-Based Glucose Sensing. 2. Wavelength-Ratiometric Resonance Light Scattering. Anal Chem 77:2007–2014
Dai Q, Liu X, Coutts J, Austin L, Huo Q (2008) A One-Step Highly Sensitive Method for DNA Detection Using Dynamic Light Scattering. J Am Chem Soc 130:8138–8139
Liu ZD, Li YF, Ling J, Huang CZ (2009) A Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Light-Scattering Assay of Mercury (II) on the Basis of Hg2+−DNA Complex Induced Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 43:5022–5027
Liu X, Dai Q, Austin L, Coutts J, Knowles G, Zou J, Chen H, Huo Q (2008) A One-Step Homogeneous Immunoassay for Cancer Biomarker Detection Using Gold Nanoparticle Probes Coupled with Dynamic Light Scattering. J Am Chem Soc 130:2780–2782
He W, Huang CZ, Li YF, Xie JP, Yang RG, Zhou PF, Wang J (2008) One-Step Label-Free Optical Genosensing System for Sequence-Specific DNA Related to the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Based on the Measurements of Light Scattering Signals of Gold Nanorods. Anal Chem 80:8424–8430
Mayer KM, Lee S, Liao H, Rostro BC, Fuentes A, Scully PT, Nehl CL, Hafner JH (2008) A Label-Free Immunoassay Based Upon Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanorods. ACS Nano 2:687–692
York J, Spetzler D, Xiong F, Frasch WD (2008) Single-molecule detection of DNA via sequence-specific links between F1-ATPase motors and gold nanorod sensors. Lab Chip 8:415–419
Eum N, Yeom S, Kwon D, Kim H, Kang S (2010) Enhancement of sensitivity using gold nanorods—Antibody conjugator for detection of E. coli O157:H7. Sens Actuators, B 143:784–788
Mock JJ, Hill RT, Degiron A, Zauscher S, Chilkoti A, Smith DR (2008) Distance-Dependent Plasmon Resonant Coupling between a Gold Nanoparticle and Gold Film. Nano Lett 8:2245–2252
Eghtedari M, Oraevsky A, Copland JA, Kotov NA, Conjusteau A, Motamedi M (2007) High Sensitivity of In Vivo Detection of Gold Nanorods Using a Laser Optoacoustic Imaging System. Nano Lett 7:1914–1918
Song KH, Kim C, Maslov K, Wang LV (2009) Noninvasive in vivo spectroscopic nanorod-contrast photoacoustic mapping of sentinel lymph nodes. Eur J Radiol 70:227–231
Wang H, Huff TB, Zweifel DA, He W, Low PS, Wei A, Cheng J (2005) In vitro and in vivo two-photon luminescence imaging of single gold nanorods. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15752–15756
Durr NJ, Larson T, Smith DK, Korgel BA, Sokolov K, Ben-Yakar A (2007) Two-Photon Luminescence Imaging of Cancer Cells Using Molecularly Targeted Gold Nanorods. Nano Lett 7:941–945
Moskovits M (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a brief retrospective. J Raman Spectrosc 36:485–496
Chaney SB, Shanmukh S, Dluhy RA, Zhao Y (2005) Aligned silver nanorod arrays produce high sensitivity surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates. Appl Phys Lett 87:031908
Leverette CL, Villa-Aleman E, Jokela S, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Smith SA (2009) Trace detection and differentiation of uranyl(VI) ion cast films utilizing aligned Ag nanorod SERS substrates. Vib Spectrosc 50:143–151
Shanmukh S, Jones L, Driskell J, Zhao Y, Dluhy R, Tripp RA (2006) Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Respiratory Virus Molecular Signatures Using a Silver Nanorod Array SERS Substrate. Nano Lett 6:2630–2636
Chu H, Huang Y, Zhao Y (2008) Silver nanorod arrays as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate for foodborne pathogenic bacteria detection. Appl Spectrosc 62:922–931
Wang Y, Lee K, Irudayaraj J (2010) SERS aptasensor from nanorod-nanoparticle junction for protein detection. Chem Commun 46:613–615
Lee SJ, Morrill AR, Moskovits M (2006) Hot Spots in Silver Nanowire Bundles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 128:2200–2201
Yun S, Park Y, Kim SK, Park S (2007) Linker-Molecule-Free Gold Nanorod Layer-by-Layer Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Anal Chem 79:8584–8589
Fabris L, Dante M, Braun G, Lee SJ, Reich NO, Moskovits M, Nguyen T, Bazan GC (2007) A Heterogeneous PNA-Based SERS Method for DNA Detection. J Am Chem Soc 129:6086–6087
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Ministry of Science and Innovation (contract number DEP2007-73224-C03-01) and by ENIAC Joint Undertaking Action (ENIAC-2010-120215). The AMR group is a Grup de Recerca de la Generalitat de Catalunya and has support from the Departament d’Universitats, Recerca i Societat de la Informació la Generalitat de Catalunya (expedient 2009 SGR 1343). CIBER-BBN is an initiative funded by the VI National R&D&I Plan 2008-2011, Iniciativa Ingenio 2010, Consolider Program, CIBER Actions and financed by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III with assistance from the European Regional Development Fund. Ilaria Mannelli thanks the JAE-doc action, founded by Junta para la Ampliación de Estudios e Investigaciones Científicas.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special issue on Focus on Bioanalysis with Guest Editors Antje J. Baeumner, Günter Gauglitz and Frieder W. Scheller.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4590-y
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannelli, I., Marco, MP. Recent advances in analytical and bioanalysis applications of noble metal nanorods. Anal Bioanal Chem 398, 2451–2469 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3937-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3937-8