Abstract
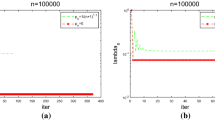
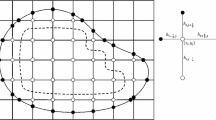
The first-order div least squares finite element methods provide inherent a posteriori error estimator by the elementwise evaluation of the functional. In this paper we prove Q-linear convergence of the associated adaptive mesh-refining strategy for a sufficiently fine initial mesh with some sufficiently large bulk parameter for piecewise constant right-hand sides in a Poisson model problem. The proof relies on some modification of known supercloseness results to non-convex polygonal domains plus the flux representation formula. The analysis is carried out for the lowest-order case in two-dimensions for the simplicity of the presentation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, J.H., Manteuffel, T.A., McCormick, S.F., Nolting, J.W., Ruge, J.W., Tang, L.: Efficiency based adaptive local refinement for first-order system least-squares formulations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33(1), 1–24 (2011)
Arnold, D., Brezzi, F.: Mixed and nonconforming finite element methods: implementation, postprocessing and error estimates. RAIRO Model. Math. Anal. Numer. 19(1), 7–32 (1985)
Berndt, M., Manteuffel, T.A., McCormick, S.F.: Local error estimates and adaptive refinement for first-order system least squares (FOSLS). Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 6, 35–43 (1997). ((electronic) Special issue on multilevel methods (Copper Mountain, CO, 1997))
Binev, P., Dahmen, W., DeVore, R.: Adaptive finite element methods with convergence rates. Numer. Math. 97(2), 219–268 (2004)
Binev, P., DeVore, R.: Fast computation in adaptive tree approximation. Numer. Math. 97(2), 193–217 (2004)
Bochev, P.B., Gunzburger, M.D.: Least-squares Finite Element Methods, volume 166 of Applied Mathematical Sciences. Springer, New York (2009)
Braess, D.: Finite Elements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2007). third edition
Brandts, J., Chen, Y., Yang, J.: A note on least-squares mixed finite elements in relation to standard and mixed finite elements. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 26(4), 779–789 (2006)
Brenner, S.C.: Two-level additive Schwarz preconditioners for nonconforming finite element methods. Math. Comp. 65(215), 897–921 (1996)
Brenner, S.C., Scott, L.R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 15, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2008)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods, volume 15 of Springer Series in Computational Mathematics. Springer, New York (1991)
Carstensen, C., Feischl, M., Page, M., Praetorius, D.: Axioms of adaptivity. Comput. Math. Appl. 67(6), 1195–1253 (2014)
Carstensen, C., Hoppe, R.W.H.: Error reduction and convergence for an adaptive mixed finite element method. Math. Comp. 75, 1033–1042 (2006)
Carstensen, C., Hoppe, R.W.H., Eigel, M., Löbhard, C.: A review of unified a posteriori finite element error control. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 5, 509–558 (2012)
Carstensen, C., Park, E.-J.: Convergence and optimality of adaptive least squares finite element methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53(1), 43–62 (2015)
Carstensen, C., Peterseim, D., Schedensack, M.: Comparison results of finite element methods for the Poisson model problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(6), 2803–2823 (2012)
Carstensen, C., Rabus, H.: An optimal adaptive mixed finite element method. Math. Comp. 80(274), 649–667 (2011)
Carstensen, C., Rabus, H.: Axioms of adaptivity for separate marking. (2016). arXiv:1606.02165 [math.NA] (Submitted)
Cascon, J.M., Kreuzer, Ch., Nochetto, R.H., Siebert, K.G.: Quasi-optimal convergence rate for an adaptive finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46, 2524–2550 (2008)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems. Classics in Applied Mathematics, vol. 40. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Philadelphia (2002)
Dörfler, W.: A convergent adaptive algorithm for Poisson’s equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33(3), 1106–1124 (1996)
Ferraz-Leite, C., Ortner, S., Praetorius, D.: Convergence of simple adaptive Galerkin schemes based on \(h-h/2\) error estimators. Numer. Math. 116(2), 291–316 (2010)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.-A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations, volume 5 of Springer Series in Computational Mathematics. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Marini, L.D.: An inexpensive method for the evaluation of the solution of the lowest order Raviart–Thomas mixed method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22(3), 493–496 (1985)
Nochetto, R.H., Siebert, K.G., Veeser, A.: Theory of Adaptive Finite Element Methods: An Introduction Multiscale Nonlinear and Adaptive Approximation. Springer, Berlin (2009). (electronic)
Scott, L.R., Zhang, S.: Finite element interpolation of nonsmooth functions satisfying boundary conditions. Math. Comput. 54(190), 483–493 (1990)
Starke, G.: An adaptive least-squares mixed finite element method for elasto-plasticity. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(1), 371–388 (2007)
Stevenson, R.: Optimality of a standard adaptive finite element method. Found. Comput. Math. 7(2), 245–269 (2007)
Verfürth, R.: A Review of a Posteriori Error Estimation and Adaptive Mesh-Refinement Techniques. Wiley and Teubner, New York (1996)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Eunjung Lee of the Department of Computational Science and Engineering of Yonsei University in Seoul, Korea, and Gerhard Starke from the Faculty of Mathematics of the University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany, for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft in the Priority Program 1748 “Reliable simulation techniques in solid mechanics. Development of non- standard discretization methods, mechanical and mathematical analysis” under the project “Foundation and application of generalized mixed FEM towards nonlinear problems in solid mechanics” (CA 151/22-1). This research was supported in part by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology NRF 2011-0030934 and NRF-2015R1A5A1009350.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carstensen, C., Park, EJ. & Bringmann, P. Convergence of natural adaptive least squares finite element methods. Numer. Math. 136, 1097–1115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-017-0866-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-017-0866-x