Abstract
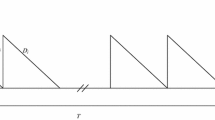
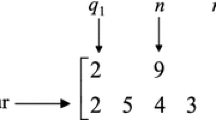
The aim of this paper is to investigate the vendor managed inventory (VMI) problem of a single-vendor single-buyer supply chain system, in which the vendor is responsible to manage the buyer’s inventory. To include an extended applicability in real-world environments, the multiproduct economic production quantity model with backordering under three constraints of storage capacity, number of orders, and available budget is considered. The nonlinear programming model of the problem is first developed to determine the near optimal order quantities along with the maximum backorder levels of the products in a cycle such that the total VMI inventory cost of the system is minimized. Then, a genetic algorithm (GA) based heuristic is proposed to solve the model. Numerical examples are given to both demonstrate the applicability of the proposed methodology and to fine tune the GA parameters. At the end, the performance of the proposed GA is compared to the one of the LINGO software using different problem sizes. The results of the comparison study show that, while the solutions do not differ significantly, the proposed GA reaches near optimum solutions in significantly less amount of CPU time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altiparmak F, Gen M, Lin L, Karaoglan I (2009) A steady-state genetic algorithm for multi-product supply chain network design. Comput Ind Eng 56:521–537
Ben-Daya M, Darwish M, Ertogral K (2008) The joint economic lot sizing problem: review and extensions. Eur J Oper Res 185:726–742
Cardenas-Barron LE (2001) The economic production quantity (EPQ) with shortage derived algebraically. Int J Prod Econ 70:289–292
Cetinkaya S, Lee CY (2000) Stock replenishment and shipment scheduling for vendor-managed inventory systems. Manag Sci 46:217–232
Chen X, Wan W, Xu X (1998) Modeling rolling batch planning as vehicle routing problem with time windows. Comput Oper Res 25:1127–1136
Cheung L, Lee HL (2002) The inventory benefit of shipment coordination and stock rebalancing in a supply chain. Manag Sci 48:300–306
Darwish MA (2009) Economic selection of process mean for single-vendor single-buyer supply chain. Eur J Oper Res 199:162–169
Disney SM, Towill DR (2003) The effect of vendor managed inventory (VMI) dynamics on the bullwhip effect in supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 85:199–215
Dong Y, Xu K (2002) A supply chain model of vendor managed inventory. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 38:75–95
Farahani RZ, Elahipanah M (2008) A genetic algorithm to optimize the total cost and service level for just-in-time distribution in a supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 111:229–243
Gen M (1997) Genetic algorithm and engineering design. Wiley, New York
Holland JH (1975) Adoption in neural and artificial systems. The University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Jasemi M (2006) A vendor-managed-inventory, Master of Science Thesis, Department of Industrial Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran (in Farsi)
Kaipia R, Holmstrom J, Tanskanen K (2002) VMI: What are you losing if you let your customer place orders? Prod Plan Control 13:17–25
Kleywegt AJ, Nori VS, Savelsbergh MWP (2004) Dynamic programming approximations for a stochastic inventory routing problem. Transp Sci 38:42–70
Lambert DM, Cooper MC (2000) Issues in supply chain management. Ind Mark Manag 29:65–83
Lee HL, So KC, Tang CS (2000) The value of information sharing in a two level supply chain. Manag Sci 46:626–643
Magee JF (1958) Production planning and inventory control. McGraw Hill, New York
Michalewicz Z (1994) Genetic algorithms + data structures = Evolution program. Springer, Berlin
Miller A (2002) Subset selection in regression, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Mitchell M (1999) An introduction to genetic algorithms. MIT Press, Boston
Myers RH, Montgomery DC (2002) Response surface methodology—process and product optimization using designed experiments. Wiley, New York
Nachiappan S, Jawahar N (2007) A genetic algorithm for optimal operating parameters of VMI system in a two-echelon supply chain. Eur J Oper Res 182:1433–1452
Park Y (2001) A hybrid genetic algorithm for the vehicle scheduling problem with due times and time deadlines. Int J Prod Econ 73:175–188
Pasandideh SHR, Niaki STA, Aryan-Yeganeh J (2010) A parameter-tuned genetic algorithm for multi-product economic production quantity model with space constraint, discrete delivery orders, and shortages. J Adv Eng Softw 41:306–314
Pasandideh SHR, Niaki STA, Mirhosseyni SS (2010) A parameter-tuned genetic algorithm to solve multi-products EPQ model with defective items, rework, and constrained space. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49:827–837
Pourakbar M, Farahani RZ, Asgari N (2007) A joint economic lot-size model for an integrated supply network using genetic algorithm. Appl Math Comput 189:583–596
Samal AR, Mohanty MK, Fifarek RH (2008) Backward elimination procedure for a predictive model of gold concentration. J Geochem Explor 97:69–82
Sofifard R, Hosseini SMM, Farahani RZ (2007) The study of vendor-managed-inventory in supply chain with mathematical model. Master of Science Thesis, Department of Industrial Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran (in Farsi)
Taleizadeh AA, Niaki STA, Aryanezhad MB, Fallah-Tafti A (2010) A genetic algorithm to optimize multi-product multi-constraint inventory control systems with stochastic replenishments and discount. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:311–323
Van Der Vlist P, Kuik R, Verheijen B (2007) Note on supply chain integration in vendor-managed inventory. Decis Support Syst 44:360–365
Yao YL, Evers PT, Dresner ME (2007) Supply chain integration in vendor-managed inventory. Decis Support Syst 43:663–674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasandideh, S.H.R., Niaki, S.T.A. & Hemmati Far, M. Optimization of vendor managed inventory of multiproduct EPQ model with multiple constraints using genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71, 365–376 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5476-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5476-x