Abstract
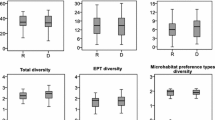
Native consumers play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem functioning, but species invasion may alter these processes. We hypothesized that the individual effects of large-bodied native and invasive consumers on ecosystem functioning and invertebrate community assemblages differ from the interactive effects. In the San Marcos River (Texas, USA), big claw river shrimp (Macrobrachium carcinus, Decapoda: Palemoides) is a large-bodied native freshwater shrimp species with low abundance, and armored catfish (Hypostomus plecostomus, Loricariidae) is an abundant, large-bodied invasive species. To examine natural distribution of these consumers, we conducted repeated field surveys of the river. Catfish had a wide range of distribution with high densities in the river, while shrimp with low densities had a patchy distribution in the open areas adjacent to openings and crevices. To investigate their individual and interactive effects, we performed a 2 × 2 factorial mesocosm stream channel experiment cross-classifying the presence and absence of catfish and shrimp for assessing their effects on ecosystem engineering and ecosystem functioning. Presence of invasive catfishes in mesocosms showed a significant influence on ecosystem functioning by decreasing periphyton biomass, altering periphyton nutrient ratios, and facilitating detrital decomposition. Catfish presence altered invertebrate community composition in leaf packs and produced ecosystem engineering effects by altering benthic habitat. The native big claw river shrimp had little effect on ecosystem functioning in mesocosms, but its presence appeared to mitigate the effects of catfish on periphyton and sediments. Our results suggest that native consumers can have the ability to mitigate the effects of invasive taxa, thus conservation of native species is critical to the preservation of ecosystem functioning in stream ecosystems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arango CP, Riley LA, Tank JL, Hall RO Jr (2009) Herbivory by an invasive snail increases nitrogen fixation in a nitrogen-limited stream. Can J Aquat Sci 66:1309–1317
Atkinson CL, Opsahl SP, Covich AP, Golladay SW, Conner LM (2010) Stable isotopic signatures, tissue stoichiometry, and nutrient cycling (C and N) of native and invasive freshwater bivalves. J North Am Benthological Soc 28:360–370
Bengston JR, Evans-White MA, Gido KB (2008) Effects of grazing minnows and crayfish on stream ecosystem structure and function. J North Am Benthological Soc 23:772–782
Berkenbusch K, Rowden AA, Myers TE (2007) Interactions between seagrasses and burrowing ghost shrimps and their influence on infaunal assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 341:70–84
Bertrand KN, Gido KB (2007) Effects of the herbivorous minnow, southern redbelly dace (Phoxinuserythrogaster), on stream productivity and ecosystem structure. Oecologia 151:69–81
Bowles DE, Aziz K, Knight CL (2000) Macrobrachium (Decapoda: Caridea : Palaemonidae) in the contiguous United States: a review of the species and an assessment of threats to their survival. J Crustac Biol 20:158–171
Burkholder JM, Wetzel RG, Klomparens KL (1990) Direct comparison of phosphate-uptake by adnate and loosely attached microalgae within an intact biofilm matrix. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2882–2890
Clavero M, Garcia-Berthou E (2005) Invasive species are a leading cause of animal extinctions. Trends Ecol Evol 20:110
Covich AP, McDowell WH (1996) The stream community. In: Reagan DP, Waide RB (eds) The food web of a tropical rain forest. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 433–459
Covich AP, Crowl TA, Johnson SL, Varza D, Certain DL (1991) Post-hurricane hugo increases in atyid shrimp abundances in a Puerto Rican montane stream. Biotropica 23:448–454
Covich AP, Crowl TA, Johnson SL, Pyron M (1996) Distribution and abundance of tropical freshwater shrimp along a stream corridor: response to disturbance. Biotropica 28:484–492
Covich AP, Austen MC, Barlocher F, Chauvet E, Cardinale BJ, Biles CL, Inchausti P, Dangles O, Solan M, Gessner MO, Statzner B, Moss B (2004) The role of biodiversity in the functioning of freshwater and marine benthic ecosystems. Bioscience 54:767–775
Crooks JA (2002) Characterizing ecosystem-level consequences of biological invasions: the role of ecosystem engineers. Oikos 97:153–166
Cross WF, Benstead JP, Frost PC, Thomas SA (2005) Ecological stoichiometry in freshwater benthic systems: recent progress and perspectives. Freshw Biol 50:1895–1912
Crowl TA, Covich AP (1994) Responses of a fresh-water shrimp to chemical and tactile stimuli from a large decapod predator. J North Am Benthological Soc 13:291–298
Crowl TA, Mcdowell WH, Covich AP, Johnson SL (2001) Freshwater shrimp effects on detrital processing and nutrients in a tropical headwater stream. Ecology 82:775–783
Drenner RW, Mazumder A (1999) Microcosm experiments have limited relevance for community and ecosystem ecology: comment. Ecology 80:1081–1085
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Leveque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81:163–182
Evans-White MA, Dodds WK, Whiles MR (2003) Ecosystem significance of crayfishes and stonerollers in a prairie stream: functional differences between co-occurring omnivores. J North Am Benthological Soc 22:423–441
Flecker AS (1992) Fish trophic guilds and the structure of a tropical stream—weak direct vs strong indirect effects. Ecology 73:927–940
Flecker AS (1996) Ecosystem engineering by a dominant detritivore in a diverse tropical ecosystem. Ecology 77:1845–1854
Flecker AS, Taylor BW, Bernhardt ES, Hood JM, Cornwell WK, Cassatt SR, Vanni MJ, Altman NS (2002) Interactions between herbivorous fishes and limiting nutrients in a tropical stream ecosystem. Ecology 83:1831–1844
Frost PC, Hillebrand H, Kahlert M (2005) Low algal carbon content and its effect on the C:P stoichiometry of periphyton. Freshw Biol 50:1800–1807
Gribben PE, Byers JE, Clements M, Mckenzie LA, Steinberg PD, Wright JT (2009) Behavioural interactions between ecosystem engineers control community species richness. Ecol Lett 12:1127–1136
Groeger AW, Brown PF, Tietjen TE, Kelsey TC (1997) Water quality of the San Marcos River. Tex J Sci 49:279–294
Gutierrez JL, Jones CG (2006) Physical ecosystem engineers as agents of biogeochemical heterogeneity. Bioscience 56:227–236
Hargrave CW (2006) A test of three alternative pathways for consumer regulation of primary productivity. Oecologia 149:23–132
Higgins KA, Vanni MJ, Gonzalez MJ (2006) Detritivory and the stoichiometry of nutrient cycling by a dominant fish species in lakes of varying productivity. Oikos 114:419–430
Hillebrand H, Kahlert M (2001) Effect of grazing and nutrient supply on periphyton biomass and nutrient stoichiometry in habitats of different productivity. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1881–1898
Hillebrand H, Kahlert M, Haglund AL, Berninger UG, Nagel S, Wickham S (2002) Control of microbenthic communities by grazing and nutrient supply. Ecology 83:2205–2219
Hillebrand H, Frost P, Liess A (2008) Ecological stoichiometry of indirect grazer effects on periphyton nutrient content. Oecologia 155:619–630
Hood JM, Vanni MJ, Flecker AS (2005) Nutrient recycling by two phosphorus-rich grazing catfish: the potential for phosphorus-limitation of fish growth. Oecologia 146:247–257
Hoover TM, Richardson JS, Yonemitsu N (2006) Flow-substrate interactions create and mediate leaf litter resource patches in streams. Freshw Biol 51:435–447
Hubbs C (1995) Springs and spring runs as unique aquatic systems. Copeia 1995:989–991
Jones CG, Lawton JH, Shachak M (1994) Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 69:373–386
Kikkert DA, Crowl TA, Covich AP (2009) Upstream migration of amphidromous shrimps in the Luquillo Experimental Forest, Puerto Rico: temporal patterns and environmental cues. J North Am Benthological Soc 28:233–246
Knoll LB, Mcintyre PB, Vanni MJ, Flecker AS (2009) Feedbacks of consumer nutrient recycling on producer biomass and stoichiometry: separating direct and indirect effects. Oikos 118:1732–1742
Lodge DM, Stein RA, Brown KM, Covich AP, Bronmark C, Garvey JE, Klosiewski SP (1998) Predicting impact of freshwater exotic species on native biodiversity: challenges in spatial scaling. Aust J Ecol 23:53–67
Ludlam JP, Magoulick DD (2010) Effects of consumer identity and disturbance on stream mesocosm structure and function. Fundam Appl Limnol 177:143–149
Malmqvist B (2002) Aquatic invertebrates in landscapes. Freshw Biol 47:679–694
March JG, Benstead JP, Pringle CM, Ruebel MW (2001) Linking shrimp assemblages with rates of detrital processing along an elevational gradient in a tropical stream. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:470–478
Mather ME, Vanni MJ, Wissing TE, Davis SA, Schaus MH (1995) Regeneration of nitrogen and phosphorus by bluegill and gizzard shad: effect of feeding history. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:2327–2338
Mcintyre PB, Jones LE, Flecker AS, Vanni MJ (2007) Fish extinctions alter nutrient recycling in tropical freshwaters. In: Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:4461–4466
Merritt RW, Cummings KW, Berg MB (eds) (2007) An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. Kendall/Hunt publishing, Dubuque
Mooney HA, Hobbs RJ (eds) (2000) Invasive species in a changing world. Island Press, Washington, DC
Moore JW (2006) Animal ecosystem engineers in streams. Bioscience 56:237–246
Moyle PB, Light T (1996) Biological invasions of fresh water: empirical rules and assembly theory. Biol Conserv 78:149–161
Nico LG, Martin RT (2001) The South American suckermouth armored catfish, Pterygoplichthysanisitsi (Pisces: Loricariidae), in Texas, with comments on foreign fish introductions in the American southwest. Southwest Nat 46:98–104
Olsson K, Stenroth P, Nyström P, Granéli W (2009) Invasions and niche width: does niche width of an introduced crayfish differ from a native crayfish? Freshw Biol 54:1731–1740
Parker IM, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Goodell K, Wonham M, Kareiva PM, Williamson MH, Von Holle B, Moyle PB, Byers JE, Goldwasser L (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effects of invaders. Biol Invasions 1:3–19
Perkin JS, Shattuck ZR, Bean PT, Bonner TH, Saraeva E, Hardy TB (2010) Movement and Microhabitat Associations of Guadalupe Bass in Two Texas Rivers. North Am J Fish Manag 30:33–46
Polis GA, Strong DR (1996) Food web complexity and community dynamics. Am Nat 147:813–846
Pound KL, Bonner TH, Nowlin WH, Huffman DG (2011) Trophic ecology of a nonnative population of suckermouth catfishes (Hypostomus) in a central Texas spring-fed system. Environ Biol Fishes 90:277–285
Power ME (1984) Habitat quality and the distribution of algae-grazing catfish in a panamanian stream. J Anim Ecol 53:357–374
Power ME, Dudley TL, Cooper SD (1989) Grazing catfish, fishing birds, and attached algae in a Panamanian stream. Environ Biol Fishes 26:285–294
Revenga C, Campbell I, Abell R, De Villiers P, Bryer M (2005) Prospects for monitoring freshwater ecosystems towards the 2010 targets. Philos Trans R Soc B-Biol Sci 360:397–413
Rosemond AD, Pringle CM, Ramirez A (1998) Macroconsumer effects on insect detritivores and detritus processing in a tropical stream. Freshw Biol 39:515–523
Schaus MH, Vanni MJ, Wissing TE, Bremigan MT, Garvey JE, Stein RA (1997) Nitrogen and phosphorus excretion by detritivorous gizzard shad in a reservoir ecosystem. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1386–1397
Solorzano L (1969) Determination of ammonia in natural waters by phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol Oceanogr 14:799–801
Statzner B, Peltret W (2006) Assessing potential abiotic and biotic complications of crayfish-induced gravel transport in experimental streams. Geomorphology 74:245–256
Sterner RW (1990) The ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus resupplied by herbivores—zooplankton and the algal competitive arena. Am Nat 136:209–229
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Taylor BW, Flecker AS, Hall RO (2006) Loss of a harvested fish species disrupts carbon flow in a diverse tropical river. Science 313:833–836
Thorp JH, Covich AP (2001) Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
US Fish and Wildlife Service (1996) San Marcos and Comal Springs and associated aquatic ecosystems (revised) recovery plan. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Austin, Texas
Vanni MJ, Layne CD, Arnott SE (1997) “Top–down” trophic interactions in lakes: effects of fish on nutrient dynamics. Ecology 78:1–20
Vanni MJ, Flecker AS, Hood JM, Headworth JL (2002) Stoichiometry of nutrient recycling by vertebrates in a tropical stream: linking species identity and ecosystem processes. Ecol Lett 5:285–293
Vitousek PM (1990) Biological invasions and ecosystem processes—towards an integration of population biology and ecosystem studies. Oikos 57:7–13
Webster JR, Benfield EF (1986) Vascular plant breakdown in fresh-water ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 17:567–594
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (eds) (2000) Limnological analysis, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Zhang YX, Richardson JS, Negishi JN (2004) Detritus processing, ecosystem engineering, and benthic diversity: a test of predator-omnivore interference. J Anim Ecol 73:756–766
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Chad Thomas for his assistance in stream channel design, and Brad Caston, Josh Perkin, Zach Shattuck, Chekka Lash, Diego Araujo, Alex Smith, Clara Folb, Nathan Dammeyer, Casey Williams, Tom Heard, Alisa Abuzeineh, and Crystal LeBoeuf for assistance in the field. This work was supported by a Texas State University Research Enhancement Program grant and Texas Parks and Wildlife State Wildlife Grant to YZ and WHN. This experiment complies with all laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, S.E., Pray, C.L., Nowlin, W.H. et al. Effects of native and invasive species on stream ecosystem functioning. Aquat Sci 74, 793–808 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-012-0263-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-012-0263-6