Abstract.
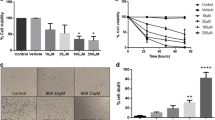
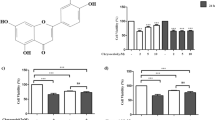
Recently, we have shown that the non-psychoactive cannabinoid compound cannabidiol (CBD) induces apoptosis of glioma cells in vitro and tumor regression in vivo. The present study investigated a possible involvement of caspase activation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction in the apoptotic effect of CBD. CBD produced a gradual, time-dependent activation of caspase-3, which preceded the appearance of apoptotic death. In addiction, release of cytochrome c and caspase-9 and caspase-8 activation were detected. The exposure to CBD caused in glioma cells an early production of ROS, depletion of intracellular glutathione and increase activity of glutathione reductase and glutathione peroxidase enzymes. Under the same experimental condition, CBD did not impair primary glia. Thus, we found a different sensitivity to the anti-proliferative effect of CBD in human glioma cells and non-transformed cells that appears closely related to a selective ability of CBD in inducing ROS production and caspase activation in tumor cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 6 April 2006; received after revision 31 May 2006; accepted 22 June 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massi, P., Vaccani, A., Bianchessi, S. et al. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol triggers caspase activation and oxidative stress in human glioma cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 2057–2066 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6156-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6156-x