Abstract
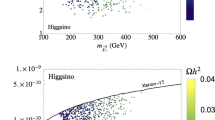
We investigate dark matter (DM) in the context of the minimal supersymmetric extension of the standard model (MSSM). We scan through the MSSM parameter space and search for solutions that (a) are consistent with the Higgs discovery and other collider searches; (b) satisfy the flavor constraints from B physics; (c) give a DM candidate with the correct thermal relic density; and (d) are allowed by the DM direct detection experiments. For the surviving models with our parameter scan, we find the following features: (1) The DM candidate is largely a Bino-like neutralino with non-zero but less than 20% Wino and Higgsino fractions; (2) The relic density requirement clearly pins down the solutions from the Z and Higgs resonances (Z, h, H, A funnels) and co-annihilations; (3) Future direct search experiments will likely fully cover the Z, h funnel regions, and H, A funnel regions as well except for the “blind spots”; (4) Future indirect search experiments will be more sensitive to the CP-odd Higgs exchange due to its s-wave nature; (5) The branching fraction for the SM-like Higgs decay to DM can be as high as 10%, while those from heavier Higgs decays to neutralinos and charginos can be as high as 20%. We show that collider searches provide valuable information complementary to what may be obtained from direct detections and astroparticle observations. In particular, the Z- and h-funnels with a predicted low LSP mass should be accessible at future colliders. Overall, the Higgs bosons may play an essential role as the portal to the dark sector.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Jungman, M. Kamionkowski and K. Griest, Supersymmetric dark matter, Phys. Rept. 267 (1996) 195 [hep-ph/9506380] [INSPIRE].
G. Bertone, D. Hooper and J. Silk, Particle dark matter: evidence, candidates and constraints, Phys. Rept. 405 (2005) 279 [hep-ph/0404175] [INSPIRE].
M. Drees and G. Gerbier, Mini-review of dark matter: 2012, arXiv:1204.2373 [INSPIRE].
DAMA, LIBRA collaboration, R. Bernabei et al., New results from DAMA/LIBRA, Eur. Phys. J. C 67 (2010) 39 [arXiv:1002.1028] [INSPIRE].
CoGeNT collaboration, C. Aalseth et al., Search for an annual modulation in a p-type point contact germanium dark matter detector, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (2011) 141301 [arXiv:1106.0650] [INSPIRE].
CRESST collaboration G. Angloher et al., Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II dark matter search, Eur. Phys. J. C 72 (2012) 1971 [arXiv:1109.0702] [INSPIRE].
CDMS collaboration, R. Agnese et al., Silicon detector dark matter results from the final exposure of CDMS II, Phys. Rev. Lett. (2013) [arXiv:1304.4279] [INSPIRE].
XENON10 collaboration, J. Angle et al., A search for light dark matter in XENON10 data, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (2011) 051301 [arXiv:1104.3088] [INSPIRE].
XENON100 collaboration, E. Aprile et al., Dark matter results from 225 live days of XENON100 data, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 (2012) 181301 [arXiv:1207.5988] [INSPIRE].
LUX collaboration, D. Akerib et al., The Large Underground Xenon (LUX) experiment, Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 704 (2013) 111 [arXiv:1211.3788] [INSPIRE].
XENON1T collaboration, E. Aprile, The XENON1T dark matter search experiment, arXiv:1206.6288 [INSPIRE].
TEXONO collaboration, H. Li et al., Limits on spin-independent couplings of WIMP dark matter with a p-type point-contact germanium detector, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 261301 [arXiv:1303.0925] [INSPIRE].
Fermi-LAT collaboration, M. Ackermann et al., Constraining dark matter models from a combined analysis of Milky Way satellites with the Fermi Large Area Telescope, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (2011) 241302 [arXiv:1108.3546] [INSPIRE].
AMS collaboration, First result from the alpha magnetic spectrometer on the international space station: Precision measurement of the positron fraction in primary cosmic rays of 0.5-350 GeV, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 141102.
H.E.S.S. collaboration, A. Abramowski et al., Search for photon line-like signatures from dark matter annihilations with H.E.S.S., Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 041301 [arXiv:1301.1173] [INSPIRE].
MAGIC collaboration, J. Aleksic et al., Searches for dark matter annihilation signatures in the Segue 1 satellite galaxy with the MAGIC-I telescope, JCAP 06 (2011) 035 [arXiv:1103.0477] [INSPIRE].
Veritas collaboration, T. Arlen et al., Constraints on cosmic rays, magnetic fields and dark matter from gamma-ray observations of the Coma cluster of galaxies with VERITAS and Fermi, Astrophys. J. 757 (2012) 123 [arXiv:1208.0676] [INSPIRE].
Planck collaboration, P. Ade et al., Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters, arXiv:1303.5076 [INSPIRE].
WMAP collaboration, D. Larson et al., Seven-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: power spectra and WMAP-derived parameters, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 192 (2011) 16 [arXiv:1001.4635] [INSPIRE].
WMAP collaboration, G. Hinshaw et al., Nine-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: cosmological parameter results, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 208 (2013) 19 [arXiv:1212.5226] [INSPIRE].
S. Galli, F. Iocco, G. Bertone and A. Melchiorri, CMB constraints on dark matter models with large annihilation cross-section, Phys. Rev. D 80 (2009) 023505 [arXiv:0905.0003] [INSPIRE].
G. Hutsi, J. Chluba, A. Hektor and M. Raidal, WMAP7 and future CMB constraints on annihilating dark matter: implications on GeV-scale WIMPs, Astron. Astrophys. 535 (2011) A26 [arXiv:1103.2766] [INSPIRE].
S. Galli, F. Iocco, G. Bertone and A. Melchiorri, Updated CMB constraints on Dark Matter annihilation cross-sections, Phys. Rev. D 84 (2011) 027302 [arXiv:1106.1528] [INSPIRE].
A. Natarajan, A closer look at CMB constraints on WIMP dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 083517 [arXiv:1201.3939] [INSPIRE].
G. Giesen, J. Lesgourgues, B. Audren and Y. Ali-Haimoud, CMB photons shedding light on dark matter, JCAP 12 (2012) 008 [arXiv:1209.0247] [INSPIRE].
C. Evoli, S. Pandolfi and A. Ferrara, CMB constraints on light dark matter candidates, arXiv:1210.6845 [INSPIRE].
A. Geringer-Sameth and S.M. Koushiappas, Exclusion of canonical WIMPs by the joint analysis of Milky Way dwarfs with Fermi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (2011) 241303 [arXiv:1108.2914] [INSPIRE].
R. Cotta et al., Constraints on the pMSSM from LAT observations of dwarf spheroidal galaxies, JCAP 04 (2012) 016 [arXiv:1111.2604] [INSPIRE].
A. Fowlie, A. Kalinowski, M. Kazana, L. Roszkowski and Y.S. Tsai, Bayesian implications of current LHC and XENON100 search limits for the constrained MSSM, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 075012 [arXiv:1111.6098] [INSPIRE].
L. Roszkowski, E.M. Sessolo and Y.-L.S. Tsai, Bayesian implications of current LHC supersymmetry and dark matter detection searches for the constrained MSSM, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 095005 [arXiv:1202.1503] [INSPIRE].
Y.-L.S. Tsai, Q. Yuan and X. Huang, A generic method to constrain the dark matter model parameters from Fermi observations of dwarf spheroids, JCAP 03 (2013) 018 [arXiv:1212.3990] [INSPIRE].
J.L. Feng, K.T. Matchev and F. Wilczek, Neutralino dark matter in focus point supersymmetry, Phys. Lett. B 482 (2000) 388 [hep-ph/0004043] [INSPIRE].
J.D. Wells, PeV-scale supersymmetry, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 015013 [hep-ph/0411041] [INSPIRE].
N. Arkani-Hamed and S. Dimopoulos, Supersymmetric unification without low energy supersymmetry and signatures for fine-tuning at the LHC, JHEP 06 (2005) 073 [hep-th/0405159] [INSPIRE].
G. Giudice and A. Romanino, Split supersymmetry, Nucl. Phys. B 699 (2004) 65 [Erratum ibid. B 706 (2005) 65-89] [hep-ph/0406088] [INSPIRE].
G.F. Giudice, T. Han, K. Wang and L.-T. Wang, Nearly degenerate gauginos and dark matter at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010) 115011 [arXiv:1004.4902] [INSPIRE].
M. Farina et al., Implications of XENON100 and LHC results for dark matter models, Nucl. Phys. B 853 (2011) 607 [arXiv:1104.3572] [INSPIRE].
D. Albornoz Vasquez, G. Bélanger, R. Godbole and A. Pukhov, The Higgs boson in the MSSM in light of the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 115013 [arXiv:1112.2200] [INSPIRE].
M. Kadastik, K. Kannike, A. Racioppi and M. Raidal, Implications of the 125 GeV Higgs boson for scalar dark matter and for the CMSSM phenomenology, JHEP 05 (2012) 061 [arXiv:1112.3647] [INSPIRE].
A. Bottino, N. Fornengo and S. Scopel, Phenomenology of light neutralinos in view of recent results at the CERN Large Hadron Collider, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 095013 [arXiv:1112.5666] [INSPIRE].
J. Ellis and K.A. Olive, Revisiting the Higgs mass and dark matter in the CMSSM, Eur. Phys. J. C 72 (2012) 2005 [arXiv:1202.3262] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, V. Barger and A. Mustafayev, Neutralino dark matter in mSUGRA/CMSSM with a 125 GeV light Higgs scalar, JHEP 05 (2012) 091 [arXiv:1202.4038] [INSPIRE].
J.-J. Cao, Z.-X. Heng, J.M. Yang, Y.-M. Zhang and J.-Y. Zhu, A SM-like Higgs near 125 GeV in low energy SUSY: a comparative study for MSSM and NMSSM, JHEP 03 (2012) 086 [arXiv:1202.5821] [INSPIRE].
J.-J. Cao, Z. Heng, J.M. Yang and J. Zhu, Higgs decay to dark matter in low energy SUSY: is it detectable at the LHC?, JHEP 06 (2012) 145 [arXiv:1203.0694] [INSPIRE].
A. Choudhury and A. Datta, Many faces of low mass neutralino dark matter in the unconstrained MSSM, LHC data and new signals, JHEP 06 (2012) 006 [arXiv:1203.4106] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, V. Barger, P. Huang and X. Tata, Natural supersymmetry: LHC, dark matter and ILC searches, JHEP 05 (2012) 109 [arXiv:1203.5539] [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger, S. Biswas, C. Boehm and B. Mukhopadhyaya, Light neutralino dark matter in the MSSM and its implication for LHC searches for staus, JHEP 12 (2012) 076 [arXiv:1206.5404] [INSPIRE].
A. Arbey, M. Battaglia, A. Djouadi and F. Mahmoudi, The Higgs sector of the phenomenological MSSM in the light of the Higgs boson discovery, JHEP 09 (2012) 107 [arXiv:1207.1348] [INSPIRE].
J. Cao, Z. Heng, J.M. Yang and J. Zhu, Status of low energy SUSY models confronted with the LHC 125 GeV Higgs data, JHEP 10 (2012) 079 [arXiv:1207.3698] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, V. Barger, A. Lessa and X. Tata, Discovery potential for SUSY at a high luminosity upgrade of LHC14, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 117701 [arXiv:1207.4846] [INSPIRE].
R. Allahverdi, B. Dutta and K. Sinha, Non-thermal higgsino dark matter: cosmological motivations and implications for a 125 GeV Higgs, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 095016 [arXiv:1208.0115] [INSPIRE].
S. Mohanty, S. Rao and D. Roy, Predictions of a natural SUSY dark matter model for direct and indirect detection experiments, JHEP 11 (2012) 175 [arXiv:1208.0894] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, Radiative natural supersymmetry with mixed axion/higgsino cold dark matter, AIP Conf. Proc. 1534 (2012) 39 [arXiv:1210.7852] [INSPIRE].
J. Hisano, K. Ishiwata and N. Nagata, Direct search of dark matter in high-scale supersymmetry, Phys. Rev. D 87 (2013) 035020 [arXiv:1210.5985] [INSPIRE].
L.J. Hall, Y. Nomura and S. Shirai, Spread supersymmetry with wino LSP: gluino and dark matter signals, JHEP 01 (2013) 036 [arXiv:1210.2395] [INSPIRE].
W. Altmannshofer, M. Carena, N.R. Shah and F. Yu, Indirect Probes of the MSSM after the Higgs Discovery, JHEP 01 (2013) 160 [arXiv:1211.1976] [INSPIRE].
M.W. Cahill-Rowley, J.L. Hewett, A. Ismail and T.G. Rizzo, More energy, more searches, but the pMSSM lives on, Phys. Rev. D 88 (2013) 035002 [arXiv:1211.1981] [INSPIRE].
A. Arbey, M. Battaglia, A. Djouadi and F. Mahmoudi, An update on the constraints on the phenomenological MSSM from the new LHC Higgs results, Phys. Lett. B 720 (2013) 153 [arXiv:1211.4004] [INSPIRE].
C. Strege et al., Global fits of the CMSSM and NUHM including the LHC Higgs discovery and new XENON100 constraints, JCAP 04 (2013) 013 [arXiv:1212.2636] [INSPIRE].
K. Kowalska, L. Roszkowski and E.M. Sessolo, Two ultimate tests of constrained supersymmetry, JHEP 06 (2013) 078 [arXiv:1302.5956] [INSPIRE].
Heavy Flavor Averaging Group collaboration, Y. Amhis et al., Averages of B-hadron, C-hadron and τ-lepton properties as of early 2012, arXiv:1207.1158 [INSPIRE].
LHCb collaboration, First evidence for the decay \( B_s^0\to {\mu^{+}}{\mu^{-}} \), Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 021801 [arXiv:1211.2674] [INSPIRE].
M. Laine and Y. Schröder, Quark mass thresholds in QCD thermodynamics, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) 085009 [hep-ph/0603048] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, J. Hagelin, D.V. Nanopoulos, K.A. Olive and M. Srednicki, Supersymmetric relics from the Big Bang, Nucl. Phys. B 238 (1984) 453 [INSPIRE].
M.W. Goodman and E. Witten, Detectability of certain dark matter candidates, Phys. Rev. D 31 (1985) 3059 [INSPIRE].
K. Griest, Cross-sections, relic abundance and detection rates for neutralino dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 38 (1988) 2357 [Erratum ibid. D 39 (1989) 3802] [INSPIRE].
R. Barbieri and G. Giudice, Upper bounds on supersymmetric particle masses, Nucl. Phys. B 306 (1988) 63 [INSPIRE].
R. Kitano and Y. Nomura, Supersymmetry, naturalness and signatures at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) 095004 [hep-ph/0602096] [INSPIRE].
V. Barger, P. Langacker, H.-S. Lee and G. Shaughnessy, Higgs sector in extensions of the MSSM, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) 115010 [hep-ph/0603247] [INSPIRE].
M.W. Cahill-Rowley, J.L. Hewett, A. Ismail and T.G. Rizzo, The Higgs sector and fine-tuning in the pMSSM, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 075015 [arXiv:1206.5800] [INSPIRE].
J.L. Feng, Naturalness and the status of supersymmetry, arXiv:1302.6587 [INSPIRE].
N. Arkani-Hamed, A. Delgado and G. Giudice, The well-tempered neutralino, Nucl. Phys. B 741 (2006) 108 [hep-ph/0601041] [INSPIRE].
M. Perelstein and B. Shakya, Fine-tuning implications of direct dark matter searches in the MSSM, JHEP 10 (2011) 142 [arXiv:1107.5048] [INSPIRE].
P. Grothaus, M. Lindner and Y. Takanishi, Naturalness of neutralino dark matter, JHEP 07 (2013) 094 [arXiv:1207.4434] [INSPIRE].
C. Cheung, L.J. Hall, D. Pinner and J.T. Ruderman, Prospects and blind spots for neutralino dark matter, JHEP 05 (2013) 100 [arXiv:1211.4873] [INSPIRE].
CMS collaboration, Search for electroweak production of charginos and neutralinos using leptonic final states in pp collisions at \( \sqrt{s}=7 \) TeV, JHEP 11 (2012) 147 [arXiv:1209.6620] [INSPIRE].
T. Han, S. Padhi and S. Su, Electroweakinos in the light of the Higgs boson, arXiv:1309.5966 [INSPIRE].
A. Chatterjee, M. Drees and S. Kulkarni, Radiative corrections to the neutralino dark matter relic density — An effective coupling approach, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 105025 [arXiv:1209.2328] [INSPIRE].
S. Heinemeyer, W. Hollik and G. Weiglein, FeynHiggs: a program for the calculation of the masses of the neutral CP even Higgs bosons in the MSSM, Comput. Phys. Commun. 124 (2000) 76 [hep-ph/9812320] [INSPIRE].
P. Bechtle, O. Brein, S. Heinemeyer, G. Weiglein and K.E. Williams, HiggsBounds: confronting arbitrary Higgs sectors with exclusion bounds from LEP and the Tevatron, Comput. Phys. Commun. 181 (2010) 138 [arXiv:0811.4169] [INSPIRE].
CMS collaboration, Search for the standard model higgs boson produced in association with W or Z bosons, and decaying to bottom quarks for HCP 2012, CMS-PAS-HIG-12-044 (2012).
CMS collaboration, Higgs to tau tau (SM) (HCP), CMS-PAS-HIG-12-043 (2012).
CMS collaboration, Evidence for a particle decaying to W + W − in the fully leptonic final state in a standard model Higgs boson search in pp collisions at the LHC, CMS-PAS-HIG-12-042 (2012).
CMS collaboration, Updated results on the new boson discovered in the search for the standard model Higgs boson in the ZZ → 4 leptons channel in pp collisions at \( \sqrt{s}=7 \) and 8 TeV, CMS-PAS-HIG-12-041 (2012).
CMS collaboration, Combination of standard model Higgs boson searches and measurements of the properties of the new boson with a mass near 125 GeV, CMS-PAS-HIG-12-045 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, An update of combined measurements of the new Higgs-like boson with high mass resolution channels, ATLAS-CONF-2012-170 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Observation of an excess of events in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson in the H → ZZ(*) → 4l channel with the ATLAS detector, ATLAS-CONF-2012-169 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Observation and study of the Higgs boson candidate in the two photon decay channel with the ATLAS detector at the LHC, ATLAS-CONF-2012-168 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Study of the channel \( H\to {Z^{*}}Z\to {\ell^{+}}{\ell^{-}}q\overline{q} \) in the mass range 120-180 GeV with the ATLAS Detector at \( \sqrt{s}=7 \) TeV, ATLAS-CONF-2012-163 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Updated ATLAS results on the signal strength of the Higgs-like boson for decays into WW and heavy fermion final states, ATLAS-CONF-2012-162 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Search for the Standard Model Higgs boson in produced in association with a vector boson and decaying to bottom quarks with the ATLAS detector, ATLAS-CONF-2012-161 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Search for the standard model Higgs boson in H → ττ decays in proton-proton collisions with the ATLAS detector, ATLAS-CONF-2012-160 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Update of the H → WW (*) → eνμν analysis with 13 fb −1 of \( \sqrt{s}=8 \) TeV data collected with the ATLAS detector, ATLAS-CONF-2012-158 (2012).
B. Allanach et al., SUSY Les Houches accord 2, Comput. Phys. Commun. 180 (2009) 8 [arXiv:0801.0045] [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger, F. Boudjema, A. Pukhov and A. Semenov, MicrOMEGAs 2.0: a program to calculate the relic density of dark matter in a generic model, Comput. Phys. Commun. 176 (2007) 367 [hep-ph/0607059] [INSPIRE].
ATLAS collaboration, Measurements of the properties of the Higgs-like boson in the two photon decay channel with the ATLAS detector using 25 fb−1 of proton-proton collision data, ATLAS-CONF-2013-012 (2013).
CMS collabroation, Updated measurements of the Higgs boson at 125 GeV in the two photon decay channel, CMS-PAS-HIG-13-001 (2013).
R. Barbieri and G. Giudice, b → sγ decay and supersymmetry, Phys. Lett. B 309 (1993) 86 [hep-ph/9303270] [INSPIRE].
M. Misiak et al., Estimate of \( B\left( {\overline{B}\to {X_s}\gamma } \right) \) at \( O\left( {\alpha_s^2} \right) \), Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 (2007) 022002 [hep-ph/0609232] [INSPIRE].
T. Becher and M. Neubert, Analysis of \( Br\left( {\overline{B}\to X\left( {s\gamma } \right)} \right) \) at NNLO with a cut on photon energy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98 (2007) 022003 [hep-ph/0610067] [INSPIRE].
M. Benzke, S.J. Lee, M. Neubert and G. Paz, Factorization at subleading power and irreducible uncertainties in \( \overline{B}\to {X_s}\gamma \) decay, JHEP 08 (2010) 099 [arXiv:1003.5012] [INSPIRE].
K. Babu and C.F. Kolda, Higgs mediated B 0 → μ + μ − in minimal supersymmetry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 (2000) 228 [hep-ph/9909476] [INSPIRE].
A.J. Buras, J. Girrbach, D. Guadagnoli and G. Isidori, On the standard model prediction for \( BR\left( {{B_{s,d }}\to {\mu^{+}}{\mu^{-}}} \right) \), Eur. Phys. J. C 72 (2012) 2172 [arXiv:1208.0934] [INSPIRE].
K. De Bruyn et al., Branching ratio measurements of B s decays, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 014027 [arXiv:1204.1735] [INSPIRE].
K. De Bruyn et al., Probing new physics via the \( B_s^0\to {\mu^{+}}{\mu^{-}} \) effective lifetime, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 (2012) 041801 [arXiv:1204.1737] [INSPIRE].
Super-Kamiokande collaboration, S. Desai et al., Search for dark matter WIMPs using upward through-going muons in Super-Kamiokande, Phys. Rev. D 70 (2004) 083523 [Erratum ibid. D 70 (2004) 109901] [hep-ex/0404025] [INSPIRE].
IceCube collaboration, M. Aartsen et al., Search for dark matter annihilations in the Sun with the 79-string IceCube detector, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 131302 [arXiv:1212.4097] [INSPIRE].
N.D. Christensen, T. Han and S. Su, MSSM Higgs bosons at The LHC, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 115018 [arXiv:1203.3207] [INSPIRE].
M. Carena, S. Heinemeyer, O. Stal, C. Wagner and G. Weiglein, MSSM Higgs boson searches at the LHC: benchmark scenarios after the discovery of a Higgs-like particle, Eur. Phys. J. C 73 (2013) 2552 [arXiv:1302.7033] [INSPIRE].
T. Han, T. Li, S. Su and L.-T. Wang, Non-decoupling MSSM Higgs sector and light superpartners, arXiv:1306.3229 [INSPIRE].
A. Arbey, M. Battaglia and F. Mahmoudi, Light neutralino dark matter in the pMSSM: implications of LEP, LHC and dark matter searches on SUSY particle spectra, Eur. Phys. J. C 72 (2012) 2169 [arXiv:1205.2557] [INSPIRE].
C. Boehm, P.S.B. Dev, A. Mazumdar and E. Pukartas, Naturalness of light neutralino dark matter in pMSSM after LHC, XENON100 and Planck data, JHEP 06 (2013) 113 [arXiv:1303.5386] [INSPIRE].
A. Arbey, M. Battaglia and F. Mahmoudi, Supersymmetry with light dark matter confronting the recent CDMS and LHC results, arXiv:1308.2153 [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger et al., LHC constraints on light neutralino dark matter in the MSSM, arXiv:1308.3735 [INSPIRE].
K. Hagiwara, S. Mukhopadhyay and J. Nakamura, 10 GeV neutralino dark matter and light stau in the MSSM, arXiv:1308.6738 [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, K.A. Olive and C. Savage, Hadronic uncertainties in the elastic scattering of supersymmetric dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 77 (2008) 065026 [arXiv:0801.3656] [INSPIRE].
E. Accomando, R.L. Arnowitt, B. Dutta and Y. Santoso, Neutralino proton cross-sections in supergravity models, Nucl. Phys. B 585 (2000) 124 [hep-ph/0001019] [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger, F. Boudjema, A. Cottrant, R. Godbole and A. Semenov, The MSSM invisible Higgs in the light of dark matter and g − 2, Phys. Lett. B 519 (2001) 93 [hep-ph/0106275] [INSPIRE].
J. Edsjo and P. Gondolo, Neutralino relic density including coannihilations, Phys. Rev. D 56 (1997) 1879 [hep-ph/9704361] [INSPIRE].
J. Edsjo, M. Schelke, P. Ullio and P. Gondolo, Accurate relic densities with neutralino, chargino and sfermion coannihilations in mSUGRA, JCAP 04 (2003) 001 [hep-ph/0301106] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, T. Falk and K.A. Olive, Neutralino-Stau coannihilation and the cosmological upper limit on the mass of the lightest supersymmetric particle, Phys. Lett. B 444 (1998) 367 [hep-ph/9810360] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, T. Falk, K.A. Olive and M. Srednicki, Calculations of neutralino-stau coannihilation channels and the cosmologically relevant region of MSSM parameter space, Astropart. Phys. 13 (2000) 181 [Erratum ibid. 15 (2001) 413-414] [hep-ph/9905481] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, K.A. Olive and Y. Santoso, Calculations of neutralino stop coannihilation in the CMSSM, Astropart. Phys. 18 (2003) 395 [hep-ph/0112113] [INSPIRE].
M. Carena, A. Freitas and C. Wagner, Light stop searches at the LHC in events with one hard photon or jet and missing energy, JHEP 10 (2008) 109 [arXiv:0808.2298] [INSPIRE].
A. Rajaraman, W. Shepherd, T.M. Tait and A.M. Wijangco, LHC bounds on interactions of dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 84 (2011) 095013 [arXiv:1108.1196] [INSPIRE].
P.J. Fox, R. Harnik, J. Kopp and Y. Tsai, Missing energy signatures of dark matter at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 85 (2012) 056011 [arXiv:1109.4398] [INSPIRE].
A. Delgado, G.F. Giudice, G. Isidori, M. Pierini and A. Strumia, The light stop window, Eur. Phys. J. C 73 (2013) 2370 [arXiv:1212.6847] [INSPIRE].
T. Lin, E.W. Kolb and L.-T. Wang, Probing dark matter couplings to top and bottom at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 88 (2013) 063510 [arXiv:1303.6638] [INSPIRE].
H. An, L.-T. Wang and H. Zhang, Dark matter with t-channel mediator: a simple step beyond contact interaction, arXiv:1308.0592 [INSPIRE].
P. Salucci, F. Nesti, G. Gentile and C. Martins, The dark matter density at the Sun’s location, Astron. Astrophys. 523 (2010) A83 [arXiv:1003.3101] [INSPIRE].
M. Srednicki and R. Watkins, Coherent couplings of neutralinos to nuclei from squark mixing, Phys. Lett. B 225 (1989) 140 [INSPIRE].
G. Gelmini, P. Gondolo and E. Roulet, Neutralino dark matter searches, Nucl. Phys. B 351 (1991) 623 [INSPIRE].
M. Drees and M. M. Nojiri, Neutralino relic density in minimal n = 1 supergravity, Phys. Rev. D 47 (1993) 376 [hep-ph/9207234] [INSPIRE].
M. Drees and M.M. Nojiri, New contributions to coherent neutralino-nucleus scattering, Phys. Rev. D 47 (1993) 4226 [hep-ph/9210272] [INSPIRE].
M. Drees and M. Nojiri, Neutralino-nucleon scattering revisited, Phys. Rev. D 48 (1993) 3483 [hep-ph/9307208] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, A. Ferstl and K.A. Olive, Reevaluation of the elastic scattering of supersymmetric dark matter, Phys. Lett. B 481 (2000) 304 [hep-ph/0001005] [INSPIRE].
CMS collaboration, Search for direct top squark pair production in events with a single isolated lepton, jets and missing transverse energy at \( \sqrt{s}=8 \) TeV, CMS-PAS-SUS-12-023 (2012).
ATLAS collaboration, Multi-channel search for squarks and gluinos in \( \sqrt{s}=7 \) TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector, Eur. Phys. J. C 73 (2013) 2362 [arXiv:1212.6149] [INSPIRE].
Y.G. Kim, T. Nihei, L. Roszkowski and R. Ruiz de Austri, Upper and lower limits on neutralino WIMP mass and spin independent scattering cross-section and impact of new (g − 2) μ measurement, JHEP 12 (2002) 034 [hep-ph/0208069] [INSPIRE].
V. Barger, W.-Y. Keung and G. Shaughnessy, Spin dependence of dark matter scattering, Phys. Rev. D 78 (2008) 056007 [arXiv:0806.1962] [INSPIRE].
H. Davoudiasl, T. Han and H.E. Logan, Discovering an invisibly decaying Higgs at hadron colliders, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 115007 [hep-ph/0412269] [INSPIRE].
Y. Bai, P. Draper and J. Shelton, Measuring the invisible Higgs width at the 7 and 8 TeV LHC, JHEP 07 (2012) 192 [arXiv:1112.4496] [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger, B. Dumont, U. Ellwanger, J. Gunion and S. Kraml, Status of invisible Higgs decays, Phys. Lett. B 723 (2013) 340 [arXiv:1302.5694] [INSPIRE].
A. Blondel et al., Report of the ICFA beam dynamics workshop ’accelerators for a Higgs factory: linear vs. circular’ (HF2012), arXiv:1302.3318 [INSPIRE].
E. Arganda, J.L. Diaz-Cruz and A. Szynkman, Decays of H 0 /A 0 in supersymmetric scenarios with heavy sfermions, Eur. Phys. J. C 73 (2013) 2384 [arXiv:1211.0163] [INSPIRE].
B. Dutta et al., Top squark searches using dilepton invariant mass distributions and bino-higgsino dark matter at the LHC, Phys. Rev. D 87 (2013) 095007 [arXiv:1302.3231] [INSPIRE].
G. Steigman, B. Dasgupta and J.F. Beacom, Precise relic WIMP abundance and its impact on searches for dark matter annihilation, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 023506 [arXiv:1204.3622] [INSPIRE].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1303.3040
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, T., Liu, Z. & Natarajan, A. Dark matter and Higgs bosons in the MSSM. J. High Energ. Phys. 2013, 8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP11(2013)008
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP11(2013)008