Abstract
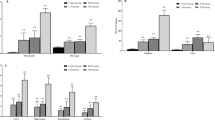
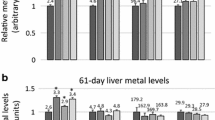
Effects of low level lead (Pb) exposure on the time-dependent organ-tissue distribution of zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and calcium (Ca) were investigated in the neonatal rat. Pups were exposed to Pb acetate (50 mg/kg) via intragastric intubation at 3-d intervals from day 6 postpartum to day 18. This level of Pb exposure had no significant effect on body weight. Exposure to Pb resulted in an alteration of the normal, time-dependent organ distribution of the essential elements and significantly lower concentrations of Zn were found in brain, liver, kidney, and femur of Pb-treated animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. L. Needleman, L. E. Gunnoe, A. Levition, R. Reed, H. Peresie, C. Mahev, and P. Barrett,N. Engl. J. Med. 300, 689 (1979).
B. De La Burde, and M. S. Choate,J. Pediatr. 87, 638 (1975).
O. David,Environ, Health Perspect. 7, 17 (1974).
R. Baloh, R. Strum, B. Green, and G. Gleser,Arch. Neural. 32, 326 (1975).
D. Brown,Toxicol. Appl, Pharmacol. 32, 628 (1975).
K. M. Jason and C. K. Kellogg,Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 15, 641 (1981).
R. Kishi, T. Ikeda, H. Miyake, E. Uchino, T. Tsuzki, and K. Inoue,Arch. Environ. Health. 38, 25 (1983).
G. D. Miller, T. F. Massaro, R. W. Granlund, and E. J. Massaro,J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 11, 121 (1983).
I. A. Michaelson and M. W. Sauerhoff,Life Sci. 13, 417 (1973).
T. F. Massaro and P. Widmayer,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 864 (1981).
T. F. Massaro, M. Mohs, and G. Fosmire,Physiol. Behav. 25, 117 (1982).
G. D. Miller, C. C, Reddy, T. F. Massaro, and E. J. Massaro,The Toxicologist 2, 81 (1982).
M. S. Clegg, C. L. Keen, B. Lönnerdal, and L. S. Hurley,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 3, 107 (1981).
F. J. Fernandez,Clin. Chem. 21, 558 (1975).
J. J. Helwig and K. A. Council (ed.), SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, 1979.
W. W. Daniel,Applied Nonparametric Statistics, Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston, MA, 1978.
S. R. Overman, L. Zimmer, and D. E. Woolley,Neurotoxicol. 2, 725 (1981).
G. H. Hirsch,Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 25, 84 (1973).
S. Overman,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 41, 459 (1977).
B. P. Fine, B. S. Jortner, A. Ty, D. Cause, and S. M. Lyon,Environ. Res. 19, 215 (1979).
B. Fowler, C. Kimmel, J. Woods, E. McConell, and L. Grant,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmcaol. 56, 59 (1980).
R. A. Goyer,Curr. Top. Pathol. 55, 147 (1971).
D. D. Choie and G. W. Richter, inLead Toxicity, R. L. Singhal and J. A. Thomas, eds., 1980, pp. 187–212.
D. D. Choie, W. Goetz, and L. B. Young,Beitr. Pathol. 155, 197 (1975).
P. Mistry, G. W. Lucier, and B. A. Fowler,Fed. Proc. 41 (3), 527 (1982).
C. L. Keen and L. S. Hurley,Mech. Ageing Dev. 13, 161 (1980).
J. A. Blair, I. P. L. Coleman, and M. E. Hilburn,J. Physiol. 286, 343 (1979).
K. R. Mahaffey, inLead Toxicity, R. L. Singhal and J. A. Thomas, eds., 1980, pp. 425–460.
I. A. Michaelson, inLead Toxicity, R. L. Singhal and J. A. Thomas, eds., 1980, pp. 301–365.
C. L. Keen, B. Löonnerdal, M. Clegg, and L. S. Hurley,J. Nutr. 111, 226 (1981).
A. J. Vander, D. L. Taylor, K. Kalitis, D. R. Mouw, and W. Victery,Am. J. Physiol. 233, F532 (1977).
W. Victery, D. Thomas, P. Schoeps, and A. J. Vander,Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 4, 211 (1982).
R. J. Kavlock and J. A. Gray,Biol. Neonate 41, 279 (1982).
D. A. Cory-Slechta and T. Thompson,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 47, 157 (1979).
L. D. Grant, C. A. Kimmel, G. L. West, C. M. Martinez-Varges, and J. L. Howard,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 56, 42 (1980).
E. D. Levin and R. E. Bowman,Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 5, 391 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, G.D., Massaro, T.F., Koperek, E. et al. Low-level lead exposure and the time-dependent organ-tissue distribution of essential elements in the neonatal rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 6, 519–530 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987205
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987205