Abstract
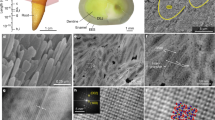
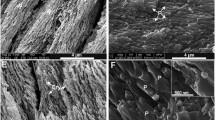
Crystal characteristics of tooth enamel and dentin were investigated using XRD, SEM, and EPMA methods. The results show that the mineral phase in enamel is HA and in dentin is HA and minor whitlockites. The dentin HA and the enamel HA have different crystallinity, the crystallinity of enamel HA is much higher than that of dentin HA. The average particle size of the enamel HA and dentin HA are 897 Å and 309 Å, respectively. The HA in enamel is regularly arranged, and in dentin the (irrangement of HA is different from the enamel HA in the same section. Both the enamel and the dentin are mainly consisted of Ca, P, O, and C, and the trace elements Mg, Sr, Al, Na, and K. The dentin contains more trace elements than the enamel. However, the incorporation of trace elements in both dentin and enamel are very limited. Other impurities such as F and Cl are less than their detection limit. The a and c values of enamel HA are 9.433 Å and 6.896 Å, and those of the dentin HA are 9.498 Å and 6.896 Å, respectively. The expansion in a value results from those the larger size of [CO3]2− group substituing for the smaller [OH]− group in the channel, and replacement of [OH]− by [CO3]2− dominates the change in cell parameter, taking into account of other trace elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Z LeGeros. Calcium Phosphates in Oral Biology and Medicine.Monographs in Oral Science. 1sted. Basel (Switzerland), Karger, 1991: 108–128
W Zhao, S Z Wang, H L Hong, Z Chen, M W Fan, and S F Yu. The Crystallographic Properties of the Mineral Phase of Enamel and Dentin in Normal Deciduous and Permanent Teeth.Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 2002, 37(3): 219–221 (in Chinese)
H Tsuda, J Ruben, and J Arends. Raman Spectra of Human Dentin Mineral.European Journal of Oral Science, 1996, 104: 123–131
P Houlle, J C Voegel, P Schultz, P Steuer, and F J G Cuisinier. High-resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: Structure and Growth Mechanisms of Human Dentin Crystals.Journal of Dental Research, 1997, 76(3): 895–904
Q Li, L P Zheng, Q G Wu, and Z Zheng. Study on the Structure of Human Enamel Hydroxylapatite.Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 1987, 22(4): 227–229(in Chinese)
O R Trautz, E Klein, E Fessenden. The Interpretation of the X-ray Diffractograms Obtained from Human Dental Enamel.Journal of Dental Research, 1953, 32: 420–425
P Wang, Z Pan, and L B Weng.Mineralogy. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987: 169(in Chinese)
Y Y Li and C Y Zheng. The Mineral Characteristics of Enamel.Chinese Journal of Stomatology, 1985, 20(4): 215–217(in Chinese)
L Schroeder and R M Frank. High-resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy of Adult Human Peritubular Dentine.Cell and Tissue Research, 1985, 242: 449–451
K S Lester and A Boyde. The Surface Morphology of Some Crystalline Components of Dentine. In: Symons NBB (ed)Dentine and Pulp: Their Structure and Reactions, London Livingstone, 1968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40172017).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanlie, H., Liyun, T. & Tao, J. The crystal characteristics of enamel and dentin by XRD method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 21, 9–12 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861458
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02861458