Abstract
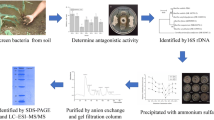
An antibacterial protein was isolated from the cultured mycelia ofCordyceps sinensis, and was designated asCordyceps sinensis Antibacterial Protein (CSAP). CSAP was single-chained, with an apparent molecular mass of 35×103 revealed by SDS-PAGE and a novel hydrophobic N-terminal sequence N-ALATQHGAP. The antimicrobial assays showed CSAP could inhibit the growth of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria but no significant inhibition against fungi or yeasts. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity of CSAP was not bactericidal but bacteriostatic. It was the first time that an antibacterial protein was described in theCordyceps species, which might involve in the chemical defense mechanism of the hosts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van der Goot F G, Lakey J, Pattus F,et al. Sectroscopic Study of the Activation and Oligomerization of the Channel-Forming Toxin Aerolysin: Identification of the Site of Proteolytic Activation [J].Biochemistry, 1992,31:8566–8570.
Antonio M R, Alvaro M P, Javier L,et al. Characterization of A Natural Larger form of the Antifungal Protein (AFP) fromAspergillus giganteus [J].Bioch Biophys Acta, 1997,1340:81–87.
Lam S K, Ng T B. First Simultaneous Isolation of a Ribosome Inactivating Protein and an Antifungal Protein from a Mushroom (Lyophyllum shimeji) together with Evidence for Synergism of their Antifungal Effects [J].Arch Biochem Biophys, 2001,393:271–280.
Bowles D J. Defense-Related Proteins in Higher Plants [J].Annu Rev Biochem, 1990,59:873–907.
Minn I, Kim H S, Kim S C. Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Pepsinogens in the Stomach of the Bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana [J].Biochi Biophys Acta, 1998,1407:31–39.
Lacadena J, Pozo A M, Gasset M,et al. Characterization of the Antifungal Protein Secreted by the MouldAspergillus gianteus [J].Arch Biochem Biophys, 1995,324:273–281.
Lee D G, Shin S Y, Maeng C Y,et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Antifungal Peptide fromAspergillus niger [J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1999,263:646–651.
Weiler F, Schmitt MJ, Zygocin A. Secreted Antifungal Toxin of the YeastZygosaccharomyces bailii, and Its Effect on. Sensitive Fungal Cells [J].FEMS Yeast Research, 2003,3:69–76.
Lam S K, Ng T B, Hypsin. A Nolvel Thermostable Ribosome Inactiving Protein with Antifungal and Antiproliferative Activities from Fruiting Bodies of the Edible MushroomHypsizingus marmoreus [J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001,285:1071–1075.
Zhu J S, Halpern G M, Jones K. The Scientific Rediscovery of an Ancient Chinese Herbal Medicine: Cordyceps sinensis: Part I [J].J Altern Complement Med, 1998,4(3):289–303.
SteinKraus D C, Whitfield J B. Chinese Caterpillar Fungus and World Record Runners [J].American Entomologist, 1994,40:235–236.
Zhu J S, Halpern G M, Jones K. The Scientific Rediscovery of an Ancient Chinese Herbal Medicine:Cordyceps sinensis: Part II [J].J Altern Complement Med, 1998,4(4):429–457.
Cunningham K G, Manson W, Spring F S,et al. Cordycepin, a Metabolic Product Isolated from Cultures ofCordyceps militaris (Linn.) Link [J].Nature, 1950,166:9–14.
Kredich N M, Guarino A J. Homocitrullyami-Noadenosine, a Nucleoside Isolated fromCordyceps militaris [J].J of Biological Chemistry, 1961,236:3300–3302.
Bok J W, Lermer L, Chilton J,et al. Antitumor Sterols from the Mycelia ofCordyceps sinensis [J].Phytochemistry, 1999,51:891–898.
Furuya T, Hirotani M, Matsuzawa M. N6 (2 hydroxyethyl) Adenosine, a Biologically Active Compound from Cultured Mycelia ofCordyceps andIsaria Species [J].Phytochemistry, 1983,22:2509–2510.
Laemmli U K, Favre M. Gel Electrophoresis of Protein [J].J of Molecular Biology, 1973,80:575–599.
Wang X, Bunkers G J, Walters M R,et al. Purification and Characterization of Three Antifungl Protein from Cheeseweed (Malva parvi flora) [J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2001,282:1224–1228.
Vijayakumar C, Wolf-Hall C E. Minimum Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Concentrations of Household Sanitizers forEscherichia coli Strains in Tryptic Soy Broth [J].Food Microbiology, 2002,19:383–388.
Wang H X, Ng T B, Ooi V E C. Studies on Purification of Lection from Fruiting Bodies of the Edible Shiitake MushroomLentinus edodes [J].In J Biochem Cell Biol, 1999,31:595–599.
Nilsen I W, ØverbØ K, Sandsdalen E,et al. Protein Purification and Gene Isolation of Chlamysin, a Cold-Activite Lysozyme-Like Enzyme with Antibacterial Activity [J].FEBS Letters, 1999,464:153–158.
Lear J D, Wasserman Z R, Degrado W F. Synthetic Amphiphilic Peptide Models for Protein Ion Channels [J].Science, 1988,240:1177–1181.
Ebran N, Julien S, Orange N,et al. Pore-Forming Properties and Antibacterial Activity of Proteins Extracted from Epidermal Mucus of Fish [J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 1999,122:181–189.
Melo V M M, Duarte A B G, Carvalho A F F U,et al. Punfication of a Novel Antibacterial and Haemagglutinating Protein from the Purple Gland of the Sea Hare,Aplysia dactylomela Rang, 1828 [J].Toxicon, 2000,38:1415–1427.
Hara S, Yamakawa M. Moricin, A Novel Type of Antibacterial Peptide Isolated from the SilkwormBombyx mori [J].J Biol Chem, 1995,270:29923–29927.
Hara S, Yamakawa M. A Novel Antibacterial Peptide Family Isolated from the SilkwormBombyx mori [J].Biochem J, 1995,310:651–656.
Wade D, Silberring J, Soliymani R,et al. Antibacterial Activities of Temporin Analogs [J].FEBS Letters, 2000,479: 6–9.
Mackintosh J A, Gooley A A, Karuso P H,et al. Agloverin-Like Antibacterial Protein is Synthesized in Helicoverpa Armigera Following Bacterial Challenge [J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 1998,22:387–399.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (39770200) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2004ABA228)
Biography: HU Zheng (1964-), Male, Associate professor, research direction: biochemistry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Maoqing, Y., Liqiu, X. et al. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein from the cultured mycelia ofCordyceps sinensis . Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 11, 709–714 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836695
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836695