Abstract
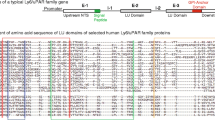
The murine tumor rejection antigen gp96 (TRA1, mapped to mouse chromosome 10) is a member of the heat shock protein family. Using a fragment of the murine gp96 cDNA as a probe, three gp96-related human genes have been isolated and structurally characterized. They have been mapped to human chromosomes 1 (p22), 12 (q24.2 → q24.3), and 15 (q25 → q26) by Southern blot hybridization and in situ hybridization of gene-specific probes. Only one of the genes, designatedTRA1 (human chromosome 12) is a coding gene; the other genes (TRA1P1 andTRAP2) appear to be independently derived, processed pseudogenes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Lindquist, S., and Craig, E.A. (1988).Annu. Rev. Genet. 22631–677.
Jaattela, M., Wissing, D., Bauer, P.A., and Li, G.C. (1992).EMBO J. 113507–3512.
Srivastava, P.K., DeLeo, A.B., and Old, L.J. (1986).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 833407–3411.
Ullrich, S.J., Robinson, E.A., Law, L.W., Wilingham, M., and Appella, E. (1986).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 833121–3125.
Srivastava, P.K., and Maki, R.G. (1991).Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 165109–123.
Moore, S.K., Kozak, C.A., Robinson, E.A., Ullrich, S.J., and Appella, E. (1989).Gene 5629–40.
Hickey, E., Brandon, S.E., Sadis, S., Smale, G., and Weber, L.A. (1989).Mol. Cell Biol. 92615–2626.
Rebbe, N.F., Hickman, W.S., Ley, T.J., Stafford, D.W., and Hickman, S. (1989).J. Biol. Chem. 26415006–15011.
Mazzarella, R.A., and Green, M. (1987).J. Biol. Chem. 2628875–8883.
Kulomaa, M.S., Weigel, N.L., Kleinsek, D.A., Beattie, W.G., Conneely, O.M., March, C., Zarucki-Schulz, T., Schrader, W.T., and O'Malley, B.W. (1986).Biochemistry 256244–6251.
Sorger, P.K., and Pelham, H.R.B. (1987).J. Mol. Biol. 194341–344.
Srivastava, P.K., Chen, Y.-T., and Old, L.J. (1987).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 843807–3811.
Maki, R.G., Old, L.J., and Srivastava, P.K. (1990).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 875658–5662.
Chang, S.C., Erwin, A.E., and Lee, A.S. (1989).Mol. Cell Biol. 92153–2162.
Srivastava, P.K., Kozak, C.A., and Old, L.J. (1988).Immunogenetics 28205–207.
Srivastava, P.K., and Old, L.J. (1989).Cancer Res. 491341–1343.
Moore, S.K., Rijli, F., and Appella, E. (1990).DNA Cell Biol. 9387–400.
Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.A., Smith, J.G., and Struhl, K. (eds.) (1987).Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (John Wiley & Sons, New York).
Feinberg, A.P., and Vogelstein, B. (1983).Anal. Biochem. 1326–13.
Shows, T.B., Brown, J.A., Haley, L.L., Byers, M.G., Eddy, R.L., Cooper, E.S., and Goggin, A.P. (1978).Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2199–104.
Shows, T., Eddy, R., Haley, L., Byers, M., Henry, M., Fujita, T., Matsui, H., and Taniguchi, T. (1984).Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 10315–318.
Shows, T.B., Sakaguchi, A.Y., and Naylor, S.L. (1982).Adv. Hum. Genet. 12341–452.
Shows, T.B. (1983).Isozymes: Curr. Top. Biol. Med. Res. 10323–339.
Zabel, B.U., Naylor, S.L., Sakaguchi, A.Y., Bell, G.I., and Shows, T.B. (1983).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 806932–6936.
Fan, Y.-S., Davis, L.M., and Shows, T.B. (1990).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 876223–6227.
Sanger, F., Coulson, A.R., Hong, G.F., Hill, D.F., and Peterson, G.B.J. (1982).DNA. Mol. Biol. 162729–773.
Tabor, S., and Richardson, C.C. (1987).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 844767–4771.
Mizusawa, S., Nishimura, S., and Seela, F. (1986).Nucleic Acids Res. 141319–1324.
Innis, M.A., Myambo, K.B., Gelfand, D.H., and Brow, M.A.D. (1988).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 859436–9440.
Searle, A.G., Peters, J., Lyon, M.F., Hall, J.G., Evans, E.P., Edwards, J.H., and Buckle, V.J. (1989).Ann. Hum. Genet. 5389–140.
Karin, M., and Richards, R.I. (1982).Nature 299797–802.
Wilde, C.D., Crowther, C.E., Cripe, T.P., Lee, M.G.-S., and Cowan, N.J. (1982).Nature 29783–84.
Rose, M.D., Misra, L.M., and Vogel, J.P. (1989).Cell 571211–1221.
Normington, K.K., Kohno, K., Kozustumi, Y., Gething, M.-J., and Sambrook, J.F. (1989).Cell 571223–1236.
Tachibana, C., and Stevens, T.H. (1992).Mol. Cell Biol. 124601–4611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maki, R.G., Eddy, R.L., Byers, M. et al. Mapping of the genes for human endoplasmic reticular heat shock protein gp96/grp94. Somat Cell Mol Genet 19, 73–81 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01233956
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01233956