Abstract
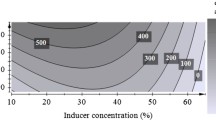
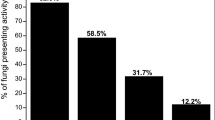
Colletotrichum lindemuthianum isolated from soybean in Saudi Arabia produced polygalacturonase, pectin methylesterase, pectin trans-eliminase and carboxymethylcellulasein vitro. Polygalacturonase showed maximaum activity at 30 to 35°C and pH 4.0 to 5.0. The absorption maximum for pectin trans-eliminase reaction products was at approximately 548 nm. The polygalacturonase and pectin trans-eliminase activities increased with culture age. The degradation of carboxymethylcellulose was also demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A.J. 1978 Extracellular enzymes produced byColletotrichum lindemuthianum andHelminthosporium maydis during growth on isolated bean and corn cell walls.Phytopathology 68, 1585–1589.
Bahkali, A.H. 1987 Degradation of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cell walls by extracellular pectolytic enzymes produced byVerticillium alboatrum andVerticillium dahliae.Journal of Tropical Plant Diseases 5, 165–172.
Bahkali, A.H. 1989 Specificities of pectolytic enzymes produced byVerticillium tricorpus.Transactions of Mycological Society of Japan 30, 161–167.
Barkai, R.G. 1974 Production of cellulase and polygalacturonase bySclerotinia minor.Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 54, 297–302.
Barker, K.R. & Walker, J.C. 1962 Relationship of pectolytic and cellulolytic enzymes production by strains ofPellicularia filamentosa to their pathogenicity.Phytopathology 52, 1119–1125.
Barnett, H.L. & Hunter, B.B. 1972Illustrated Genera of Imperfect Fungi. Minnesota: Burgess Publishing Company. 200 pp.
Hall, J.A. & Wood, R.K.S. 1973 The killing of plant cells by pectolytic enzymes. InFungal Pathogenicity and the Plant's Response, ed. Byrde, R.J.W. and Cutting, C.V., pp. 19–31. New York: Academic Press.
Kelman, A. & Cowling, E.B. 1965 Cellulase ofPseudomonas solanacearum in relation to pathogenesis.Phytopathology 55, 148–155.
Mount, M.S. & Bateman, D.F. 1970 Induction of electrolyte loss, tissue maceration and cellular death of potato tissue by an endopolygalacturonate trans-eliminase.Phytopathology 60, 924–934.
Mussell, H.W. & Strand, L.L. 1976 Pectic enzymes: involvement in pathogenesis and possible relevance to tolerance and specificity. InCell Wall Biochemistry Related to Specificity in Host-Plant Pathogen Interactions, ed. Solheim, B. and Raa, J., pp. 31–70. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget.
Natour, R. M. 1970 A survey of plant diseases in Saudi Arabia.Beitrage zur Tropischen und Subtropischen Landwirtschaft und Tropenveterium Medizin I, 65–70.
Nelson, N. 1944 A photometric adaptation of Somogyi method for the determination of glucose.Journal of Biological Chemistry 153, 375–380.
Starr, M.P. & Moran, F. 1962 Eliminating split of pectic substances by phytopathogenic soft rot bacteria.Science 135, 920–921.
Talboys, P.W. & Busch, L.V. 1970 Pectin enzymes produced byVerticillium species.Transactions of British Mycological Society 55, 367–381.
Tiffany, L.H. & Gilman, J.C.1954 Species ofColletotrichum from legumes.Mycologia 46, 52–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahkali, A.H. In vitro production of pectolytic and cellulolytic enzymes byColletotrichum lindemuthianum isolated from soybean grown in Saudi Arabia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8, 55–59 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01200685
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01200685