Summary
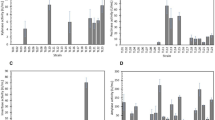
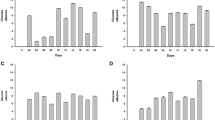
Microorganisms which produce strong raw-starch degrading enzymes were isolated from soil using a medium containing a unique carbon source, “α-amylase resistant starch (α-RS)”, which is insoluble in water and hardly digested with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens α-amylase. Among the isolates, three strains showing high activities were characterized. Two of them, K-27 (fungus) and K-28 (yeast), produced α-amylase and glucoamylase, and the final product from starch was only glucose. The third strain, K-2, was a bacterium and produced α-amylase, which produced glucose and malto-oligosaccharides from starch. The enzyme preparation of these strains degraded raw corn starch rapidly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishigami H, Hashimoto H, Kainuma K (1985) Determination of optimum culture conditions for the Chalara enzyme production. J Jpn Soc Starch 32:189–196
Hizukuri S, Tabata S, Nikuni Z (1970) Studies on starch phosphate. Part 1. Estimation of glucose 6-phosphate residues in starch and the presence of other bound phosphate(s). Staerke 22:338–343
Hizukuri S, Takeda Y, Yasuda M, Suzuki A (1981) Multibranched nature of amylose and the action of debranching enzymes. Carbohydr Res 94:205–213
Kainuma K, French D (1969) Action of pancreatic amylase on starch oligosaccharides containing single glucose side chains. FEBS Lett 5:257–261
Kilburne DM, Taylor PM (1969) Effect of sulfhydryl reagents on glucose determination by the glucose oxidase method. Anal Biochem 27:555–558
Koehler LH (1952) Differentiation of carbohydrates by anthrone reaction rate and color intensity. Anal Chem 24:1576–1579
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Okuda J, Miwa I, Maeda K, Tokui K (1977) Rapid and sensitive, colorimetric determination of the anomers of d-glucose with d-glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and mutarotase. Carbohydr Res 58:267–270
Robyt J, French D (1963) Action pattern and specificity of an amylase from Bacillus subtilis. Arch Biochem Biophys 100:451–467
Smith JS, Lineback DR (1976) Hydrolysis of native wheat and corn starch granules by glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus niveus. Staerke 29:243–249
Somogyi M (1952) Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem 195:19–23
Taniguchi H, Odashima F, Igarashi M, Maruyama Y, Nakamura M (1982) Characterization of a potato starch digesting bacterium and its production of amylase. Agric Biol Chem 46:2107–2115
Ueda S (1980) Raw starch digestion by mold glucoamylases and debranching enzymes in: Marshall JJ (ed) Mechanisms of Saccharide Polymerization and Depolymerization. Academic Press, New York, pp 55–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergmann, F.W., Abe, Ji. & Hizukuri, S. Selection of microorganisms which produce raw-starch degrading enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 443–446 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451610
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451610