Abstract
Self-stimulation behavior was studied in untreated rats and rats injected with apomorphine with electrodes implanted in the nucleus accumbens, the lateral hypothalamus, the catecholaminergic cell-groups A9–A10 and the locus coeruleus.
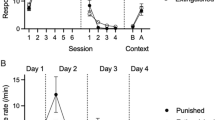
Apomorphine (0.2 mg/kg s. c.) consistently facilitated self-stimulation in a number of rats but inhibited this behavior in others.
This individual variation could be observed in all four groups of rats but was further analysed in the rats with an electrode in the A9–A10 area. The effect of the drug was highly reproducible for individual animals.
Extinction after reduction of the rewarding current to zero could not be demonstrated as long as the drug was active.
These results substantiate the hypothesis that apomorphine is able to replace the reinforcing action of intracranial rewarding stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Butcher, S. G., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Ungerstedt, U.: Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 11, 303–314 (1970)
Andén, N.-E., Rubenson, A., Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T.: Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 627–629 (1967)
Atrens, D. M.: Reinforcing and emotional consequences of electrical self-stimulation of the subcortical limbic forebrain. Physiol. Behav. 5, 1461–1471 (1970)
Butcher, L. L.: Effects of apomorphine on free-operant avoidance behavior in the rat. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 163–166 (1968)
Carlsson, S. G.: Effects of apomorphine on exploration. Physiol. Behav. 9, 127–129 (1972)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J., Olley, J. E.: The substantia nigra and stereotyped behavior. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 95–106 (1972)
Crow, T. J.: Enhancement by cocaine of intracranial self-stimulation in the rat. Life Sci. (part 1) 9, 375–381 (1970)
Crow, T. J.: A map of rat mesencephalon for electrical self-stimulation. Brain Res. 36, 265–273 (1972)
Crow, T. J., Spear, P. J., Arbuthnott, G. W.: Intracranial self-stimulation with electrodes in the region of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 36, 275–287 (1972)
Dresse, A.: Influence de 15 neuroleptique (butyrophénones et phenothiazines) sur les variations de la teneur du cerveau en noradrenaline et l'activité du rat dans le test d'autostimulation. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 159, 353–365 (1966)
Ellinwood, E. H., Jr.: “Accidental conditioning” with chronic methamphetamine intoxication. Implications for a theory of drug habituation. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 21, 131–138 (1971)
Ernst, A. M.: Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphetamine on gnawing compulsion in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 316–323 (1967)
Fog, R.: Stereotyped and non-stereotyped behavior in rats induced by various stimulant drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 14, 299–304 (1969)
Fog, R.: Behavioral effects in rats of morphine and amphetamine and a combination of the two drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 16, 305–312 (1970)
Haley, T. J., Flesher, A. M., Komesu, N.: Influence of reserpine, tetrabenazine and iproniazid on self-stimulation by rats. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 171, 198–205 (1968)
König, J. F. R., Klippel, R. A.: The rat brain. Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Comp. 1963
Liebman, J. M., Butcher, L. L.: Effects on self-stimulation behavior of drugs influencing dopaminergic neurotransmission mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 305–313 (1973)
Nymark, M.: Apomorphine provoked stereotypy in the dog. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 26, 361–368 (1972)
Oliveira, L. de, Graeff, F. G.: Comparison between the effects of apomorphine and amphetamine on operant behavior. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 159–165 (1972)
Olds, J., Travis, R. P.: Effects of chlorpromazine, meprobamate, pentobarbital and morphine on self-stimulation. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 128, 397–404 (1960)
Pellegrino, L. J., Cushman, A. J.: A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. New York: Meredith Publ. Comp. 1967
Phillips, A. G., Fibiger, H. G.: Dopaminergic and noradrenergic substrates of positive reinforcement: differential effects of d- and l-amphetamine. Science 179, 575–577 (1973)
Poschel, B. P. H., Ninteman, F. W.: Excitatory (antidepressant?) effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the reward system of the brain. Life Sci. 3, 903–910 (1964)
Poschel, B. P. H., Ninteman, F. W.: Hypothalamic self-stimulation; its suppression by blockade of norepinephrine biosynthesis and reinstatement by methamphetamine. Life Sci. 5, 11–16 (1966)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Stereotyped activities produced by amphetamine in several animal species and man. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 11, 300–310 (1967)
Randrup, A., Munkvad, I.: Biochemical, anatomical and psychological investigations of stereotyped behavior induced by amphetamines. In: Amphetamines and related compounds. Proceedings of the Mario Negri institute for pharmacological research, Milan, Italy. E. Costa and S. Garattini, Eds., pp. 695–713. New York: Raven Press 1970
Roll, S. K.: Intracranial self-stimulation and wakefulness: effect of manipulating ambient brain catecholamines. Science 168, 1370–1372 (1970)
Rolls, E. T.: Contrasting effects of hypothalamic and nucleus accumbens septi self-stimulation on brain stem single unit activity and cortical arousal. Brain Res. 31, 275–285 (1971)
Rossum, J. M. van: The significance of dopaminergic receptor blockade for the mechanism of action of neuroleptic drugs. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 160, 492–494 (1966)
Rotrosen, J., Wallach, M. B., Angrist, B., Gershon, S.: Antagonism of apomorphine-induced stereotypy and emesis in dogs by thioridazine, haloperidol and pimozide. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 26, 185–194 (1972)
Skinner, B. F.: “Superstition” in the pigeon. J. exp. Psychol. 38, 168–172 (1948)
Stein, L.: Self-stimulation of the brain and the central stimulant action of amphetamine. Fed. Proc. 23, 836–850 (1964)
Stein, L.: Chemistry of reward and punishment. In: Psychopharmacology. A review of progress 1957–1967 (Public health service publication no. 1836). D. H. Efron, J. O. Cole, J. Levine, and J. B. Wittenborn, Eds., pp. 105–123. Washington: Government Printing Office 1968
Wauquier, A., Niemegeers, C. J. B.: Intracranial self-stimulation in rats as a function of various stimulus parameters III. Influence of apomorphine on medial forebrain bundle stimulation with monopolar electrodes. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 30, 163–172 (1973)
Wise, C. D., Stein, L.: Facilitation of brain self-stimulation by central administration of norepinephrine. Science 163, 299–301 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broekkamp, C.L.E., van Rossum, J.M. Effects of apomorphine on self-stimulation behavior. Psychopharmacologia 34, 71–80 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421222
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421222