Summary
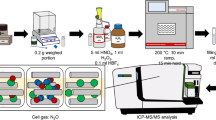
The application of slurry nebulization/inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to trace elemental analysis of biological samples has been investigated. Three standard samples of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) were dispersed in 1% aqueous Triton X-100 solution by grinding with a planetary micronizing mill. The resulting slurries were nebulized into an ICP without any additional treatments. The 1% (m/v) slurry of the NIST bovine liver showed no significant influence on cone blockage and signal suppression/enhancement. Detection limit, precision and accuracy were discussed for the determination of 24 elements of interest in bovine liver, rice flour and pine needles. Detection limits ranged from 0.0001 μg g−1 for U to 0.52 μg g−1 for Zn at the effective integrating time of 10 s. For high mass elements, low blank values were obtained, yielding excellent limits (<0.01 μg g−1). Acceptable accuracy and precision were obtained for most of the elements in the NIST bovine liver and rice flour, even for the volatile elements, such as As, Se and Br. However, relatively poor accuracy was obtained for the analysis of pine needles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray AL (1985) Analyst 110:551–556
Darke SA, Long SE, Pickford CJ, Tyson JF (1990) Fresenius J Anal Chem 337:284–289
Mochizuki T, Sakashita A, Iwata H, Kagaya T, Shimamura T, Blair P (1988) Anal Sci 4:403–409
Jiang SJ, Houk RS (1986) Anal Chem 58:1739–1743
Jiang SJ, Houk RS (1987) Spectrochim Acta 42B:93–100
Williams JG, Gray AL, Norman P, Ebdon L (1987) J Anal At Spectrom 2:469–472
Ebdon L, Foulkes ME, Parry HGM, Tye CT (1988) J Anal At Spectrom 3:753–761
Dean JR, Ebdon L, Massey R (1987) J Anal At Spectrom 2:369–374
Mochizuki T, Sakashita A, Iwata H, Ishibashi Y, Gunji N (1989) Anal Sci 5:311–317
Munro S, Ebdon L, McWeeny DJ (1986) J Anal At Spectrom 1:211–219
Fuller CW, Hutton RC, Preston B (1981) Analyst 106:913–920
Halicz L, Brenner IB (1987) Spectrochim Acta 42B:207–217
Ebdon L, Wilkinson R (1987) J Anal At Spectrom 2:39–44
Sparkes S, Ebdon L (1986) Anal Proc 23:410–412
Hutton RC (1986) J Anal At Spectrom 1:259–263
Hausler D (1987) Spectrochim Acta 42B:63–73
Veillon C (1986) Anal Chem 58:851A-866A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, T., Sakashita, A., Iwata, H. et al. Application of slurry nebulization to trace elemental analysis of some biological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 339, 889–894 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321672
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321672