Abstract
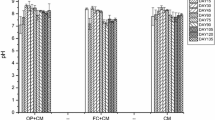
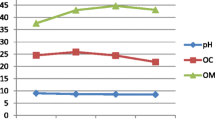
Comparative study was performed to evaluate the vermicomposting efficiency of two earthworm species Eisenia fetida, Eudrilus eugenia from the garden wastes, vegetable market wastes. Three different experimental works were conducted. For each experiment three plastic vermibins were used. Experiment (1) mentioned for control without earthworms. Experiment (2) bedded with Eudrilus eugenia, Experiment (3) comprised of bedding with Eisenia fetida. Pre composting was allowed for 10 days after that Eudrilus eugenia, Eisenia fetida were added in respective vermibins. The multiplication of earthworms in terms of number was calculated at the end of vermicomposting. The N, P, K value of the manure in each vermibin was estimated before and after the completion of the experiment. High N, P, K value was obtained in Experiment (2) and Experiment (3) compared to control. Among the solid wastes, the vegetable wastes were degraded quickly by Eudrilus eugenia and also it has the best quality of manure. Eudrilus eugenia was found to be efficient for quick degradation of both garden wastes and vegetable wastes. After manure production, field trials were conducted using different fertilizers to assess the manure quality in the growth and yield of tomato plants. Six types of experimental trial pots were prepared where one was kept as control and five others were treated with different category of fertilizers. The treatment pots (P3) showed better growth parameters (leaf numbers, stem diameter, plant height) than the rest of the trial.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.J. Adi, Z.M. Noor, Waste recycling: utilisation of coffee grounds and kitchen waste in vermicomposting. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 1027–1030 (2008)
S. Kumar, J.K. Bhattacharyya, A.N. Vaidya, T. Chakrabarti, S. Devotta, Assessment of the status of municipal solid waste management in metro cities, state capitals, class I cities and class II towns in India. Waste Manag 29, 883–895 (2009)
A. Chauhan, S. Kumar, A.P. Singh, M. Gupta, Vermicomposting of vegetable wastes with cowdung using three earthworm species Eisenia foetida, Eudrilus eugeniae and Perionyx excavatus. Nat Sci 8(1), 33–43 (2010)
D. Sharma, J.K. Katnoria, A. Pal Vig, Chemical changes of spinach waste during composting and vermicomposting. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10(16), 3124–3127 (2011)
A. Amsath, K. Muthukumaravel, M. Sukumaran, Vermicomposting of vegetable wastes using cowdung. E-J. Chem. 5(4), 810–813 (2008)
M.H. Fulekar, D.C. Jadia, Vermicomposting of vegetable waste: a bio-physicochemical process based on hydro operating bioreactor. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 7(20), 3723–3730 (2008)
Elvira, Vermicomposting of sludge’s from paper mill and dairy industries with Eisenia andrei. A pilot scale study. Bioresour. Technol. 63, 205–211 (1998)
E. Bentize, Isolation by isoelectric focusing of humic urease complex from earthworm Eisenia foetida processed sewage sludge. Biol. Fertil. Soils 31, 489–493 (2000)
V. Reddy, S. Patnaik, Nutrient status of vermicompost of urban green waste processed by three earthworm species. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. (2010). doi:10.1155/2010/967526
C.A. Edwards, Biology and Ecology of Earthworms, (1997), pp. 56–58
R.M. Atiyeh, J. Dominguez, S. Subler, C.A. Edwards, Changes in biochemical properties of cow manure during processing by earthworms (Eisenia andrei, Bouché) and the effects on seedling growth. Pedobiologica 44, 709–724 (2000)
V.K. Garg, R. Gupta, Solid waste management by vermitechnology. J. Sci. 654–667 (2005)
A.S. Kalamdhad, Y.K. Singh, M. Ali, M. Khwairakpam, A.A. Kazmi, Rotary drum composting of vegetable wastes and tree leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 100(24), 6442–6450 (2009)
R. Kumar, D. Verma, B.L. Singh, U. Kumar, Composting of sugar cane waste by products through treatment with microorganisms and subsequent vermicomposting. Bioresour. Technol. 101(17), 6707–6711 (2010)
S. Suthar, S. Singh, Vermicomposting of domestic waste by using two epigeic earthworms. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 5(1), 99–106 (2008)
R.B. Thompson, R. Nogales, Nitrogen and carbon mineralization in soil of vermicomposted and unprocessed dry olive cake produced from two stage centrifugation for olive oil extraction. J Environ Sci Health 34(5), 917–928 (1999)
U. Tomati, A. Grappeili, E. Gaili, The hormone like effect of earthworm casts on plant growth. Biol. Fertil. Soils 5, 288–294 (1988)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, S.M. Biodegradation of Garden Waste, Market Waste Using Eisenia fetida and Eudrilus eugenia and Assessment of Manure Quality on Tomato. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 95, 75–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-014-0077-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-014-0077-8