Abstract
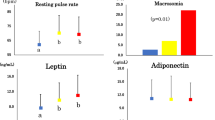
There is a rising trend in the prevalence of insulin resistance among obese, overweight children and adolescents. The serum insulin and its correlation with biochemical, clinical and anthropometric parameters were evaluated in 185 children and adolescents (59 control, 52 obese, 49 overweight, 25 congenital heart disease) of age group 10–17 years. The levels of serum insulin were measured by ELISA. Serum insulin levels were found to be significantly increased in children who were obese, overweight and had congenital heart disease, than controls. Serum insulin levels positively correlated with BMI, WHR, and serum C-peptide, serum leptin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Fasting glucose levels were found to be negatively correlated with serum insulin levels. HDL-cholesterol levels were non-significant among the study groups. We identified nine obese children (five girls and four boys) with the features of metabolic syndrome and 69% of obese and overweight children were identified with insulin resistance. Insulin resistance was strongly associated with metabolic syndrome and its components, especially with central obesity and hypertriglyceridemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castelli WP. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease: the Framingham study. Am J Med. 1984;76:4–12.
Despres JP, Lamarche B, Mauriege P, Cantin B, Dangenias GR, Moor Jani S, Lupin PJ. Hyperinsulinemia as an independent risk factor for ischemic heart disease. N Eng J Med. 1996;334(15):952–7.
Freedman DS, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. The relation of overweight to cardiovascular risk factors among children and adolescents; the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 1999;103:1175–82.
Berenson GS, Srinivasan SR, Bao W, Newman WP, Tracy RE, Wattigney WA. Association between multiple cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in children and young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1650–6.
Asato Y, Katsuren K, Oshiro T, Kikawa K, Shimabukuro T, Ohta T. Relationship between lipid abnormalities and insulin resistance in Japanese school children. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2781–6.
Graham TE, Yang Q, Bluher M, Hammarstedt A, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean obese and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2552–63.
Laakso M. How good a marker is insulin level for insulin resistance. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;137:959–65.
Martin BC, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Bergman RN, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR. Role of glucose and insulin resistance in development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: results of a 25-year follow-up study. Lancet. 1992;340:925–9.
Moreno LA, Pineda I, Rodriguez G, Fleta J, Giner A, Juste MG, Sarria A, Bueno M. Leptin and metabolic syndrome in obese and non obese children. Horm Metab Res. 2002;34:394–9.
Hamidi A, Fakhrzadeh H, Moayyeri A, Heshmat R, Ebrahimpour P, Larinjani B. Metabolic syndrome and leptin concentrations in obese children. Indian J Pediatr. 2006;73(7):593–6.
Wu D-M, Shen M-H, Chu N-F. Relationship between plasma leptin levels and lipid profiles among school children in Taiwan—The Taipei children heart study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2001;17:911–6.
Steinberger J, Moorehead C, Katch V, Rocchini PAlbert. Relationship between insulin resistance and abnormal lipid profile in obese adolescents. J Pediatr. 1995;126:690–5.
Keskin M, Selimkurtoglu M, Kendirci M, Atabek E, Yazici C. Homeostasis Model assessment is more reliable than the fasting glucose/insulin ratio and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index for assessing insulin resistance among obese children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2005;115:500–3.
Chu N-F, Chang J-B, Shieh S-M. Plasma leptin, fatty acids and tumor necrosis factor-receptor and insulin resistance in children. Obes Res. 2003;11:532–40.
Arslanian S, Suprasongsin C. Insulin sensitivity, lipids, body composition in childhood: is “syndromex” present? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:1058–62.
Caprio S, Bronson M, Sherwin RS, Rife F, Tamborlane WV. Co-existence of severe insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in pre-adolescent obese children. Diabetologia. 1996;39:1489–97.
Franks PW, Brage S, Luan J, Ekelund U, Rahman M, Farooqui IS, et al. Leptin predicts a worsening of the features of the metabolic syndrome independently of obesity. Obes Res. 2005;13:1476–84.
Jiang X, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Relation of obesity to insulin secretion and clearance in adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996;20:951–6.
Wabitsch M, Blum WF, Muche R, Braun M, Hube F, Rascher W, Heinze E, Teller W, et al. Contribution of androgens to the gender differences in leptin production in obese children and adolescents. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:808–13.
Lundell K-H, Sabel K-G, Eriksson B, Mellgren G. Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in children with cyanotic congenital heart disease. Acta Pediatr. 2008;86(10):1082–4.
Nagy TR, Gower BA, Trowbridge CA, Degenberg C, Shewchuk RM, Goran MI. Effects of gender, ethnicity, body composition and fat distribution on serum leptin concentrations in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:2148–52.
Misra A, Vikram NK, Arya S, Pandey RM, Dhingra V, Chatterjea A, et al. High prevalence of insulin resistance in post pubertal Asian Indian children is associated with adverse truncal body fat patterning, abdominal adiposity and excess body fat. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28:1217–26.
Falkner B, Hulman S, Kushner H. Insulin-stimulated glucose utilisation and borderline hypertension in young adult blacks. Hypertension. 1993;22:18–25.
Dubey S, Kabra M, Bajpai A, Pandey RM, Hasan M, Gautam RK, Menon PS. Serum leptin levels in obese Indian children: relation to clinical and biochemical parameters. Indian Pediatr. 2007;44:257–62.
Defronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance: a multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991;14:173–94.
IDF Press Conference. The IDF Consensus world wide definition of the metabolic syndrome. http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/IDF-Meta-syndrome_definition.pdf. Accessed 3 Feb 2006.
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Mohan V, Battacharyya PK, Viswanathan M. Decreased insulin sensitivity in offspring whose parents both have type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Med. 1990;7:331–4.
Mieyer P, Faustinelli S, Cowan PA. Identifying children at risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Spectr. 2005;18:213–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasa Nageswara Rao, G., Prema, G., Priya, G. et al. Comparison Between Serum Insulin Levels and Its Resistance With Biochemical, Clinical and Anthropometric Parameters in South Indian Children and Adolescents. Ind J Clin Biochem 26, 22–27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-010-0069-z