Abstract
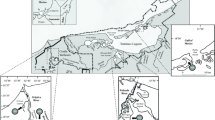
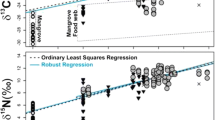
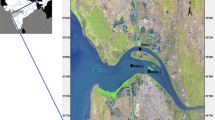
Alterations of hydrology are known to trigger changes in coastal ecosystems, such as the composition and abundances of local flora and fauna. It is less well known how these alterations lead to changes in nutrient and energy transfers in these systems. We used comparisons of stable isotope signatures (δ 13C, δ 15N, and δ 34S) in the tissues of conspecific plants and animals collected on each side of the Mobile Bay Causeway to determine the extent to which the causeway may have altered energy and nutrient exchange between the Mobile–Tensaw Delta and upper Mobile Bay. While the δ 13C signatures of most plants and animals varied irrespective of their location relative with causeway location, their δ 15N and δ 34S signatures were almost always more enriched south of the causeway, indicating significant alterations of trophic linkages within this estuarine food web. Dual isotope plots and mixing model analyses indicated that while terrestrial and floating plants were trophically important to consumers north of the causeway, submerged aquatic vegetation was more important to consumers south of the causeway. Although limited in spatial and temporal scale, our results preliminarily show that there are noteworthy differences in stable isotope signatures most likely due to the Mobile Bay Causeway altering energy and nutrient transference.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baya, E.E., L.S. Yokel, C.A. Pinyerd, III, E.C. Blancher, S.S. Sklenar, and W.C. Isphording. 1998. Preliminary Characterization of Water Quality of the Mobile Bay National Estuary Program (MBNEP) Study Area. Mobile Bay National Estuary Program, Fairhope, AL. http://www.mobilebaynep.com/site/news_pubs/research.htm. Accessed 06 March 2008.
Ben-David, M., and D. Schell. 2001. Mixing models in analyses of diet using multiple stable isotopes: a response. Oecologia 127: 180–184. doi:10.1007/s004420000570.
Benson, E.M., J.M. O’Neil, and W.C. Dennison. 2008. Using aquatic macorphyte Vallisneria americana as a nutrient bioindicator. Hydrobologia 596: 187–196. doi:10.1007/s10750–007–9095–0.
Beshears, W.W.J. 1982. Mobile Delta vegetative survey. Alabama Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. 31 pages.
Boon, P.I. and Bunn, S.E. 1994. Variations in the stable isotope composition of aquatic plants and their implications for food web analysis. Aquatic Botany 48: 99–108.
Borom, J. 1979. Submerged grassbed communities in Mobile Bay, Alabama. In Symposium on the natural resources of Mobile Estuary, Alabama, eds. H.J. Loyacano, and J. Smith, 123–132. Mobile, Alabama: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Mobile District.
Chanton, J., and F. Lewis. 2002. Examination of coupling between primary and secondary production in a river-dominated estuary: Apalachicola Bay, Florida, USA. Limnology and Oceanography 473: 683–697.
Cloern, J.E., E.A. Canuel, and D. Harris. 2002. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of aquatic and terrestrial plants of the San Francisco Bay estuarine system. Limonology and Oceanography 473: 713–729.
Coffin, R., and L. Cifuentes. 1999. Stable isotope analysis of carbon cycling in the Perdido Estuary, Florida. Estuaries 22: 917–926. doi:10.2307/1353071.
Cole, M.L., I. Valieila, K.D. Kroeger, G.L. Tomasky, J. Cebrian, C. Wigand, R.A. McKinney, S.P. Grady, and M.H.C. da Silva. 2004. Assessment of a δ 15N isotopic method to indicate anthropogenic euthrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Journal of Environmental Quality 33: 124–132.
Costanzo, S.D., M.J. O’Donohue, W.C. Dennison, M.R. Longeragan, and M. Thomas. 2001. A new approach for detecting and mapping sewage impacts. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42: 149–156. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00125-9.
Crossley, M.N., Dennison, W.C., Williams, R.R. and A.H. Wearing. 2002. The interaction of water flow and nutrients on aquatic plant growth. Hydrobiologia 489: 63–70.
Dale, N.G. 1974. Bacteria in intertidal sediments: factors related to their distribution. Limnology and Oceanography 193: 509–518.
Day, J.W., C.A.S. Hall, M.W. Kemp, and A. Yanez-Aranciba. 1989. Estuarine ecology. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Darnell, R.M. 1958. Food habits of fishes and large invertebrates of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, an estuarine community. Publ Inst Mar Sci Univ Tex 5: 353–416.
Darnell, R.M. 1961. Trophic spectrum of an estuarine community, based on studies of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana. Ecology 423: 553–568. doi:10.2307/1932242.
Deegan, L., and R. Garritt. 1997. Evidence for spatial variability in estuarine food webs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 147: 31–47. doi:10.3354/meps147031.
Eggleston, D.B. 1990. Foraging behavior of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, on juvenile oysters, Crassostrea virginica: Effects of prey density and size. Bulletin of Marine Science 46: 62–82.
Etzold, D.J., and J.Y. Christmas, eds. 1979. A Mississippi marine fin fish management plan. Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Consortium MASCP-78-046. 36 p.
Fahy, E., R. Goodwillie, J. Rochford, and D. Kelly. 1975. Eutrophication of a partially enclosed estuarine mudflat. Marine Pollution Bulletin 6: 29–31. doi:10.1016/0025–326X(75)90233–7.
Finlay, J.C., M.E. Power, and G. Cabana. 1999. Effects of water velocity on algal carbon isotope ratios: implications for river food webs studies. Limnology and Oceanography 445: 1198–1203.
Fry, B. 1988. Food web structure on Georges Bank from stable C, N and S isotopic compositions. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 1182–1190.
Fry, B. 2002. Conservative mixing of stable isotopes across estuarine salinity gradients: a conceptual framework for monitoring watershed influences on downstream fisheries production. Estuaries 25 (2): 264–271.
Fry, B., and E.B. Sherr. 1984. δ 13C Measurement as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contributions in Marine Science 27: 13–47.
Gosselink, J.B. 1984. The ecology of delta marshes of coastal Louisiana: a community profile. FWS/OBS-84/09. Washington, DC: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Biological Services: 134 p.
Harrington, R.W. Jr., and E.S. Harrington. 1961. Food selection among fishes invading a high subtropical salt marsh: From onset of flooding through the progress of a mosquito brood. Ecology 42: 646–666. doi:10.2307/1933496.
Hoffman, J.C., and D.A. Bronk. 2006. Interannual variation in stable carbon and nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry of the Mattaponi River, Virginia. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 2319–2332.
Kaushal, S.S., W.M. Lewis, and J.H. McCutchan. 2006. Land use change and nitrogen enrichment of a rocky mountain watershed. Ecological Applications 16: 299–312. doi:10.1890/05-0134.
Kline, T.C., J.J. Goering, O.A. Mathisen, and P.L. Parker. 1989. Recycling elements transported upstream by runs of Pacific Salmon. 1. δ 15N and δ 13C evidence in Sashin Creek southeastern Alaska. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 47: 136–144. doi:10.1139/f90-014.
Kwak, T., and J. Zedler. 1997. Food web analysis of southern California coastal wetlands using multiple stable isotopes. Oecologia 110: 262–277. doi:10.1007/s004420050159.
Lehrter, J., J.R. Pennock, and G.B. McManus. 1999. Microzooplankton Grazing and Nitrogen Excretion across a Surface Estuarine-Coastal Interface. Estuaries 22: 113–125. doi:10.2307/1352932.
MacAvoy, S.E., S.A. Macko, and G.C. Garman. 2001. Isotopic turnover in aquatic predators: quantifying the exploitation of migratory prey. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58: 923–932. doi:10.1139/cjfas-58-5-923.
McAlice, B., and G. Jaeger Jr. 1983. Circulation changes in the Sheepscot River Estuary, Maine, following removal of a causeway. Estuaries 6: 190–199. doi:10.2307/1351511.
McClelland, J.W., and I. Valiela. 1998. Linking nitrogen in estuarine produces to land-derived sources. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 577–585.
McClelland, J.W., I. Valiela, and R.H. Michener. 1997. Nitrogen-stable isotope signatures in estuarine food webs: A record of increasing urbanization in coastal watersheds. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 930–937.
MacLeod, N.A., and D.R. Barton. 1998. Effects of light intensity, water velocity, and species composition on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios in periphyton. Canadian Journal of Fish and Aquatic Science 558: 1919–1925. doi:10.1139/cjfas-55-8-1919.
McCutchan, J.H. Jr., W.M. Lewis Jr., C. Kendall, and C.C. McGrath. 2003. Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102: 378–390. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.12098.x.
Michener, R.H., and D.M. Schell. 1994. Stable isotope ratios as tracers in marine aquatic food webs. In Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science, eds. K. Lajtha, and R.H. Michener, 138–157. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Moeri, O., L. da Sternberg, L.P. Rodicio, and P.J. Walsh. 2003. Direct effects of ambient ammonia on the nitrogen isotope ratios of fish tissues. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 282: 61–66. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00446-X.
Nealson, K.H. 1997. Sediment bacteria: who’s there, what are they doing, and what’s new? Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 25: 403–434. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.25.1.403.
Odum, W.E., and E.J. Heald. 1972. Trophic analyses of estuarine mangrove community. Bulletin of Marine Science 22: 671–738.
Peterson, B.J., and B. Fry. 1987. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annul Review of Ecology and Systematics 18: 293–320. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.18.110187.001453.
Peterson, B.J., and R.W. Howarth. 1987. Sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen isotopes used to trace organic matter flow in the salt-marsh estuaries of Sapelo Island, Georgia. Limnology and Oceanography 32: 1195–1213.
Peterson, B.J., R.W. Howarth, and R.H. Garritt. 1985. Multiple stable isotopes used to trace the flow of organic matter in estuarine food webs. Science 227: 1361–1363. doi:10.1126/science.227.4692.1361.
Phillips, D. 2001. Mixing models in analyses of diet using multiple stable isotopes: a critique. Oecologia 127: 166–170. doi:10.1007/s004420000571.
Phillips, D., and J. Gregg. 2001. Uncertainty in source partitioning using stable isotopes. Oecologia 127: 171–179. doi:10.1007/s004420000578.
Phillips, D., and J. Gregg. 2003. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too many sources. Oecologia 136: 261–269. doi:10.1007/s00442-003-1218-3.
Post, D.M. 2002. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 833: 703–718.
Sheridan, P. 1978. Food habits of the bay anchovy in Apalachicola Bay, Florida. Northeast Gulf Science 2: 125–132.
Schoeninger, M.J., and M.J. DeNiro. 1984. Nitrogen and carbon isotopic composition of bone collagen form marine and terrestrial animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48: 625–639. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(84)90091-7.
Steffy, L.Y., and S.S. Kilham. 2004. Elevated δ 15N in stream biota in areas with septic tank systems in an urban watershed. Ecological Applications 14: 637–641. doi:10.1890/03-5148.
Sullivan, M.J., and C.A. Moncreiff. 1990. Edaphic algae are an important component of salt marsh food-webs: evidence from multiple stable isotope analyses. Marine Ecology Progress Series 62: 149–159. doi:10.3354/meps062149.
Trudeau, V., and J.B. Rasmussen. 2003. The effect of water velocity on stable carbon and nitrogen isotope signatures of periphyton. Limnology and Oceanography 486: 2194–2199.
Tucker, J., N. Sheats, A.E. Giblin, C.S. Hopkinson, and J.P. Montoya. 1999. Using stable isotopes to trace sewage-derived material through Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay. Marine Environmental Research 48: 353–375. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00069-0.
Udy, J.W., and W.C. Dennison. 1997. Physiological responses of seagrasses used to identify anthropogenic nutrient inputs. Marine and Freshwater Resources 48: 605–614. doi:10.1071/MF97001.
US Army Corps of Engineers. 2001. Upper Mobile Bay ecosystem restoration project proposed modification of US Highway 90 (Causeway). Mobile, AL, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Mobile District: 42 p. and appendices.
Vanderklift, M.A., and S. Ponsard. 2003. Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ 15N enrichment: a meta-analysis. Oecologia 136: 169–182. doi:10.1007/s00442-003-1270-z.
Valentine, J.F. and S. Sklenar. 2006. Mobile–Tensaw Delta Hydrological Modifications Impact Study. A final report. Mobile Bay Keepers and Mobile Bay National Estuary Program. 176 pages. http://www.mobilebaynep.com/site/news_pubs/research.htm. Accessed 06 March 2008.
Valentine, J.F., S. Sklenar, and M. Goecker. 2004. Mobile–Tensaw Delta Hydrological Modifications Impact Study. Final Report to the Mobile Bay National Estuary Program. 139 pages.
Wallace, R.K. 1994. Mobile Bay and Alabama Coastal Waters Fact Sheet. Mississippi Alabama Publication 94-0 17, Circular ANR-919. Alabama Cooperative Extension Service, Auburn, AL. http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR-0919/. Accessed 06 March 2008.
Wayland, M., and K.A. Hobson. 2001. Stable carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur isotope ratios in riparian food webs on rivers receiving sewage and pulp-mill effluents. Canadian Journal of Zoology 79: 5–15. doi:10.1139/cjz-79-1-5.
Wood, A.K.H., Z. Ahmad, N.A.M. Shazili, R. Yaakob, and R. Carpenter. 1997. Geochemistry of sediments in Johor Strait between Malaysia and Singapore. Continental Shelf Research 17: 1207–1228. doi:10.1016/S0278-4343(97)00011-3.
Xie, Y., S. An, and B. Wu. 2005. Resource allocation in submerged plant Vallisneria natans related to sediment type, rather than water-column nutrients. Freshwater Biology 50: 391–402. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01327.x.
Yamamoto, N., and G. Lopez. 1985. Bacterial abundance in relation to surface area and organic content of marine sediments. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 903: 209–220. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(85)90167-4.
Zimmerman, R., R. Gibson, and J. Harrington. 1979. Herbivory and detritivory among gammaridean amphipods from a Florida seagrass community. Marine Biology 54: 41–47. doi:10.1007/BF00387050.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to A. Gunter for all his help in the field. This project was funded by Mobile Bay National Estuary Program Mini-Grant Program and the Alabama Center for Estuarine Studies (ACES). Thank you to anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goecker, M.E., Valentine, J.F., Sklenar, S.A. et al. Influence from Hydrological Modification on Energy and Nutrient Transference in a Deltaic Food Web. Estuaries and Coasts 32, 173–187 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-008-9105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-008-9105-0