Abstract
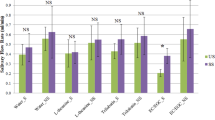
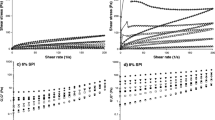
Thickness perception of starch-thickened products during eating has been linked to starch viscosity and salivary amylase activity. Calcium is an essential cofactor for α-amylase and there is anecdotal evidence that adding extra calcium affects amylase activity in processes like mashing of beer. The aims of this paper were to (1) investigate the role of salivary calcium on α-amylase activity and (2) to measure the effect of calcium concentration on apparent viscosity and thickness perception when interacting with salivary α-amylase in starch-based samples. α-Amylase activity in saliva samples from 28 people was assessed using a typical starch pasting cycle (up to 95 °C). The activity of the enzyme (as measured by the change in starch apparent viscosity) was maintained by the presence of calcium, probably by protecting the enzyme from heat denaturation. Enhancement of α-amylase activity by calcium at 37 °C was also observed although to a smaller extent. Sensory analysis showed a general trend of decreased thickness perception in the presence of calcium, but the result was only significant for one pair of samples, suggesting a limited impact of calcium enhanced enzyme activity on perceived thickness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alting AC, van de Fred V, Kanning MW, Burgering M, Mulleners L, Sein A, Buwalda P (2009) Improved creaminess of low-fat yoghurt: the impact of amylomaltase-treated starch domains. Food Hydrocolloids 23(3):980–987
Bertoft E, Andtfolk C, Kulp SE (1984) Effect of pH, temperature, and calcium-ions on barley malt alpha-amylase isoenzymes. J Inst Brew 90(5):298–302
Bush DS, Sticher L, Vanhuystee R, Wagner D, Jones RL (1989) The calcium requirement for stability and enzymatic-activity of 2 isoforms of barley aleurone alpha-amylase. J Biol Chem 264(32):19392–19398
Collado LS, Corke H (1999) Accurate estimation of sweetpotato amylase activity by flour viscosity analysis. J Agric Food Chem 47(3):832–835
Comrie AAD (1967) Brewing liquor—a review. J Inst Brew 73:335–341
de Wijk RA, Prinz JF, Engelen L, Weenen H (2004) The role of [alpha]-amylase in the perception of oral texture and flavour in custards. Physiol Behav 83(1):81–91
Edgar WM (1992) Saliva—its secretion, composition and functions. Br Dent J 172(8):305–312
Engelen L, Van Der Bilt A (2008) Oral physiology and texture perception of semisolids. J Texture Stud 39(1):83–113
Evans ID, Haisman DR, Elson EL, Pasternak C, McConnaughey WB (1986) The effect of salivary amylase on the viscosity behavior of gelatinized starch suspensions and the mechanical-properties of gelatinized starch granules. J Sci Food Agric 37(6):573–590
Ferry AL, Hort J, Mitchell JR, Lagarrigue S, Pamies B (2004) Effect of amylase activity on starch paste viscosity and its implications for flavor perception. J Texture Stud 35(5):511–524
Ferry ALS, Mitchell JR, Hort J, Hill SE, Taylor AJ, Lagarrigue S, Valles-Pamies B (2006) In-mouth amylase activity can reduce perception of saltiness in starch-thickened foods. J Agric Food Chem 54(23):8869–8873
Gonzalez CF, Farina JI, Figueroa LIC (2002) A critical assessment of a viscometric assay for measuring Saccharomycopsis fibuligera alpha-amylase activity on gelatinised cassava starch. Enzym Microb Technol 30(2):169–175
Harrison JGL, Stewart ED, Siebenberg J, Brenner MW (1963) Brewery liquor composition—present day views. J Inst Brew 69:323–331
Heinzerling CI, Smit G, Dransfield E (2008) Modelling oral conditions and thickness perception of a starch product. Int Dairy J 18(8):867–873
Hsiu J, Fischer H, Stein EA (1964) Alpha-amylases as calcium-metalloenzymes. II. Calcium and the catalytic activity. Biochemistry 3(1):61–66
Kivela J, Parkkila S, Metteri J, Parkkila AK, Toivanen A, Rajaniemi H (1997) Salivary carbonic anhydrase VI concentration and its relation to basic characteristics of saliva in young men. Acta Physiol Scand 161(2):221–225
Kumari A, Rosenkranz T, Kayastha AM, Fitter J (2010) The effect of calcium binding on the unfolding barrier: a kinetic study on homologous alpha-amylases. Biophys Chem 151(1–2):54–60
Larsen MJ, Jensen AF, Madsen DM, Pearce EIF (1999) Individual variations of pH, buffer capacity, and concentrations of calcium and phosphate in unstimulated whole saliva. Arch Oral Biol 44(2):111–117
Lin J, Lin YS, Kuo ST, Jiang CM, Wu MC (2009) Purification of alpha-amylase from human saliva by superparamagnetic particles. J Sci Food Agric 89(4):574–578
Machius M, Declerck N, Huber R, Wiegand G (1998) Activation of Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase through a disorder ->order transition of the substrate-binding site mediated by a calcium-sodium-calcium metal triad. Structure 6(3):281–292
Mandel AL, des Gachons CP, Plank KL, Alarcon S, Breslin PAS (2010) Individual differences in AMY1 gene copy number, salivary alpha-amylase levels, and the perception of oral starch. PLoS One 5(10)
Muralikrishna G, Nirmala M (2005) Cereal alpha-amylases—an overview. Carbohydr Polym 60(2):163–173
Nazmi AR, Reinisch T, Hinz HJ (2008) Calorimetric studies on renaturation by CaCl2 addition of metal-free alpha-amylase from Bacillus licheniformis (BLA). J Therm Anal Calorim 91(1):141–149
Nielsen AD, Fuglsang CC, Westh P (2003) Effect of calcium ions on the irreversible denaturation of a recombinant Bacillus halmapalus alpha-amylase: a calorimetric investigation. Biochem J 373(2):337–343
O’Mahony M (1986) Sensory evaluation of food, statistical methods and procedures. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York
Salvolini E, Mazzanti L, Martarelli D, Di Giorgio R, Fratto G, Curatola G (1999) Changes in the composition of human unstimulated whole saliva with age. Aging Clin Exp Res 11(2):119–122
Schipper RG, Silletti E, Vingerhoeds MH (2007) Saliva as research material: biochemical, physicochemical and practical aspects. Arch Oral Biol 52(12):1114–1135
Sewon L, Laine M, Karjalainen S, Doroguinskaia A, Lehtonen-Veromaa M (2004) Salivary calcium reflects skeletal bone density of heavy smokers. Arch Oral Biol 49(5):355–358
Suvd D, Fujimoto Z, Takase K, Matsumura M, Mizuno H (2001) Crystal structure of Bacillus stearothermaphilus alpha-amylase: possible factors determining the thermostability. J Biochem 129(3):461–468
Tietz M, Buettner A, Conde-Petit B (2008) Changes in structure and aroma release from starch-aroma systems upon alpha-amylase addition. Eur Food Res Technol 227(5):1439–1446
Vallee BL, Stein EA, Sumerwell WN, Fischer EH (1959) Metal content of alpha-amylases of various origins. J Biol Chem 234(11):2901–2905
Woolnough JW, Bird AR, Monro JA, Brennan CS (2010) The effect of a brief salivary alpha-amylase exposure during chewing on subsequent in vitro starch digestion curve profiles. Int J Mol Sci 11(8):2780–2790
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, C., Fichtel, S.L. & Taylor, A.J. Impact of Calcium on Salivary α-Amylase Activity, Starch Paste Apparent Viscosity, and Thickness Perception. Chem. Percept. 4, 116–122 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12078-011-9091-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12078-011-9091-7