Abstract
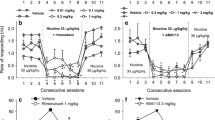
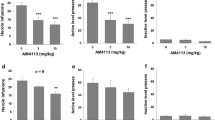
Several lines of preclinical evidence indicate the ability of the prototypic cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, rimonabant, to suppress various alcohol-related behaviors, including alcohol drinking and seeking behavior and alcohol self-administration in rats and mice. Together, these data—synthetically reviewed in the present paper—suggest (a) the involvement of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in the neural substrate controlling alcohol intake, alcohol reinforcement, and the motivational properties of alcohol and (b) that rimonabant may constitute a new and potentially effective medication for the treatment of alcohol dependence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mechoulam R, Parker, L (2003) Cannabis and alcohol—a close friendship. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:266–268
Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL (2005) Role of the endocannabinoid system in the development of tolerance to alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol 40:15–24
Colombo G, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2005) Endocannabinoid system and alcohol addiction: pharmacological studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:369–380
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Héauime M, Shire D, Calandra B, Congy C, Martinez S, Maruani J, Néliat G, Caput D, Ferrara P, Soubrié P, Breliére JC, Le Fur G (1994) SR 141716A, a potent and selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor. FEBS Lett 350:240–244
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Lumeng L, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2006) The alcohol-preferring P rat and animal models of excessive alcohol drinking. Addict Biol 11:270–288
Colombo G, Lobina C, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2006) Phenotypic characterization of genetically selected Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) and -non preferring (sNP) rats. Addict Biol 11:324–338
Serra S, Carai MAM, Brunetti G, Gómez R, Melis S, Vacca G, Colombo G, Gessa GL (2001) The cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR 141716 prevents acquisition of drinking behaviour in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 430:369–371
Bell RL, Rodd ZA, Sable HJK, McQueen VK, Davids MR, Murphy JM, Lumeng L, McBride WJ (2004) Cannabinoid CB1 antagonist reduces alcohol intake during acquisition, maintenance, and relapse in inbred alcohol preferring (IP) rats. Program No. 489.6. 2004 Abstract Viewer/It Planner. Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC
Arnone M, Maruanim J, Chaperon F, Thiébot ME, Poncelet M, Soubrié P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and alcohol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 132:104–106
Poncelet M, Maruani J, Calassi R, Soubrié P (2003) Overeating, alcohol and sucrose consumption decrease in CB1 receptor deleted mice. Neurosci Lett 343:216–218
Lallemand F, Soubrié PH, De Witte PH (2001) Effects of CB1 cannabinoid receptor blockade on ethanol preference after chronic ethanol administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1317–1323
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Congy C, Martinez S, Oustric D, Perio A, Poncelet M, Maruani J, Arnone M, Finance O, Soubrié P, Le Fur G (2004) SR147778 [5-(4-bromophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-ethyl-N-(1-piperidinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide], a new potent and selective antagonist of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor: biochemical and pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:905–914
Gessa GL, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Colombo G (2005) Suppressing effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR147778, on alcohol intake and motivational properties of alcohol in alcohol-preferring sP rats. Alcohol Alcohol 40:46–53
Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C (2003) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 84:698–704
Wang L, Liu J, Harvey-White J, Zimmer A, Kunos G (2003) Endocannabinoid signaling via cannabinoid receptor 1 is involved in ethanol preference and its age-dependent decline in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1393–1398
Naassila M, Pierrefiche O, Ledent C, Daoust M (2004) Decreased alcohol self-administration and increased alcohol sensitivity and withdrawal in CB1 receptor knockout mice. Neuropharmacology 46:243–253
Lallemand F, De Witte P (2005) Ethanol induces higher BEC in CB1 cannabinoid receptor knockout mice while decreasing ethanol preference. Alcohol Alcohol 40:54–62
Thanos PK, Dimitrakakis ES, Rice O, Gifford A, Volkow ND (2005) Ethanol self-administration and ethanol conditioned place preference are reduced in mice lacking cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Behav Brain Res 164:206–213
Racz I, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Toth ZE, Michel K, Palkovits M, Zimmer A (2003) A critical role for the cannabinoid CB1 receptors in alcohol dependence and stress-stimulated ethanol drinking. J Neurosci 23:2453–2458
Colombo G, Agabio R, Fà M, Guano L, Lobina C, Loche A, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998) Reduction of voluntary ethanol intake in ethanol-preferring sP rats by the cannabinoid antagonist SR 141716. Alcohol Alcohol 33:126–130
Di Marzo V, Matias I (2005) Endocannabinoid control of food intake and energy balance. Nat Neurosci 8:585–589
Gadde KM (2005) Endocannabinoid receptor antagonists and other emerging pharmacological strategies for weight reduction. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord 5:549–556
Carai MAM, Colombo G, Maccioni P, Gessa GL (2006) Efficacy of rimonabant and other cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists in reducing food intake and body weight: preclinical and clinical data. CNS Drug Rev 12:91–99
Kelaï S, Hanoun N, Aufrère G, Beaugé F, Hamon M, Lanfumey L (2006) Cannabinoid-serotonin interactions in alcohol-preferring vs. alcohol-avoiding mice. J Neurochem 99:308–320
Lallemand F, Soubrie P, De Witte P (2004) Effects of CB1 cannabinoid receptor blockade on ethanol preference after chronic alcohol administration combined with repeated re-exposures and withdrawals. Alcohol Alcohol 39, 486–492
Lallemand F, De Witte P (2006) SR147778, a CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, suppresses ethanol preference in chronically alcoholized Wistar rats. Alcohol 39125–134
Freedland CS, Sharpe AL, Samson HH, Porrino LJ (2001) Effects of SR 1417161A on alcohol and sucrose self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:277–282
Hansson AC, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Malinen H, Hyytiä P, Sanchez-Vera I, Rimondini R, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Kunos G, Sommer WH, Heilig M (2007) Genetic impairment of frontocortical endocannabinoid degradation and high alcohol preference. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:117–126
Rodd ZA, Bell RL, Pommer TJ, McQueen VK, Lumeng L, Murphy JM, McKinzie DL, McBride WL (2005) The CB1 antagonist SR141716 transiently reduces operant ethanol self-administration during relapse and maintenance, and inhibits alcohol seeking in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(Suppl):19A
Cippitelli A, Bilbao A, Hansson AC, del Arco I, Sommer W, Heilig M, Massi M, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Navarro M, Ciccocioppo R, de Fonseca FR (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonism reduces conditioned reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior in rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:2243–2251
Parsons LH (2005) Evidence for an endocannabinoid influence in the regulation of ethanol self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(Suppl):12A
Economidou D, Mattioli L, Cifani C, Perfumi M, Massi M, Cuomo V, Trabace L, Ciccocioppo R (2006) Effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716A on ethanol self-administration and ethanol-seeking behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:394–403
Pavon FJ, Bilbao A, Hernández-Folgado L, Cippitelli A, Jagerovic N, Abellán G, Rodríguez-Franco MA, Serrano A, Macias M, Gómez R, Navarro M, Goya P, and Rodríguez de Fonseca F (2006) Antiobesity effects of the novel in vivo neutral cannabinoid receptor antagonist 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-hexyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole—LH 21. Neuropharmacology 51:358–366
Ginsburg BC, Lamb RJ (2006) Cannabinoid effects on behaviors maintained by ethanol or food: a within-subjects comparison. Behav Pharmacol 17:249–257
Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL (2001) Cannabinoid receptor agonist-stimulated [35S]guanosine triphosphate gammaS binding in the brain of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. J Neurosci Res 64:429–436
Ortiz S, Oliva JM, Pérez-Rial S, Palomo T, Manzanares J (2004) Chronic ethanol consumption regulates cannabinoid CB1 receptor gene expression in selected regions of rat brain. Alcohol Alcohol 39:88–92
Gessa GL, Orrù A, Lai P, Maccioni P, Lecca R, Lobina C, Carai MAM, and Colombo G (2006) Lack of tolerance to the suppressing effect of rimonabant on chocolate intake in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185:248–254
Samson HH, Czachowski CL, Chappell A, Legg B (2003) Measuring the appetite strength of ethanol: use of an extinction trial procedure. Alcohol 31:77–86
Gallate JE, McGregor IS (1999) The motivation for beer in rats: effects of ritanserin, naloxone and SR 141716. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:302–308
Colombo G, Vacca G, Serra S, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2004) Suppressing effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716, on alcohol’s motivational properties in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 498:119–123
Anton RF (2001) Pharmacological approaches to the management of alcoholism. J Clin Psychiatry 62(Suppl):11–17
Lê A, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to alcohol in rats. Pharmacol Ther 94:137–156
Spanagel R (2005) How to measure relapse in animals. In: Spanagel R, Mann K (eds) Drugs for relapse prevention of alcoholism. Birkäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 13–21
Lê AD, Funk D, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Fletcher PJ, Shaham Y (2006) Effects of dexfenfluramine and 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:82–92
Bienkowski P, Koros E, Kostowski W, Bogucka-Bonikowska A (2000) Reinstatement of ethanol seeking in rats: behavioral analysis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:123–128
Bienkowski P, Kostowski W, Koros E (1999) Ethanol-reinforced behaviour in the rat: effects of naltrexone. Eur J Pharmacol 374:321–327
Hölter SM, Spanagel R (1999) Effects of opiate antagonist treatment on the alcohol deprivation effect in long-term ethanol-experienced rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 145:360–369
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–7861
Bäckström P, Hyytiä P (2004) Ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists modulate cue-induced reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:558–565
Heilig M, Egli M (2006) Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 111:855–876
Serra S, Brunetti G, Pani M, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2002) Blockade by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716, of alcohol deprivation effect in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 443:95–97
Fattore L, Spano MS, Deiana S, Melis V, Cossu G, Fadda P, Fratta W (2007) An endocannabinoid mechanism in relapse to drug seeking: a review of animal studies and clinical perspectives. Brain Res Rev 53:1–16
Corchero J, Manzanares J, Fuentes JA (2004) Cannabinoid/opioid crosstalk in the central nervous system. Crit Rev Neurobiol 16:159–172
Cota D, Tschop MH, Horvath TL, Levine AS (2006) Cannabinoids, opioids and eating behavior: the molecular face of hedonism? Brain Res Rev 51:85–107
Manzanares J, Ortiz S, Oliva JM, Perez-Rial S, Palomo T (2005) Interactions between cannabinoid and opioid receptor systems in the mediation of ethanol effects. Alcohol Alcohol 40:25–34
Colombo G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Gómez R, Melis S, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2002) Stimulation of voluntary ethanol intake by cannabinoid receptor agonists in ethanol-preferring sP rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159:181–187
Gallate JE, Saharov T, Mallet PE, McGregor IS (1999) Increased motivation for beer in rats following administration of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 370:233–240
Vacca G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2002) Boosting effect of morphine on alcohol drinking is suppressed not only by naloxone but also by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR 141716. Eur J Pharmacol 445:55–59
Carai MAM, Lobina C, Gessa GL, Colombo G (2005) Cannabinoid receptor antagonists: a perspective. In: Spanagel R, Mann K (eds) Drugs for relapse prevention of alcoholism. Birkäuser Verlag, Basel, pp 181–187
Gallate JE, Mallet PE, McGregor IS (2004) Combined low dose treatment with opioid and cannabinoid receptor antagonists synergistically reduces the motivation to consume alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 173:210–216
Weiss F, Porrino LJ (2002) Behavioral neurobiology of alcohol addiction: recent advances and challenges. J Neurosci 22:3332–3337
Lupica CR, Riegel AC (2005) Endocannabinoid release from midbrain dopamine neurons: a potential substrate for cannabinoid receptor antagonist treatment of addiction. Neuropharmacology 48:1105–1116
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29:225–232
Cohen C, Perrault G, Voltz C, Steinberg R, Soubrié P (2002) SR 141716, a central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor antagonist, blocks the motivational and dopamine-releasing effects of nicotine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:51–463
Perra S, Pillolla G, Melis M, Muntoni AL, Gessa GL, Pistis M (2005) Involvement of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the effects of alcohol in the mesolimbic reward circuit: electrophysiological evidence in vivo. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:368–377
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Marco Pistis for helpful discussions and Ms. Anne Farmer for language editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombo, G., Orrù, A., Lai, P. et al. The Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonist, Rimonabant, as a Promising Pharmacotherapy for Alcohol Dependence: Preclinical Evidence. Mol Neurobiol 36, 102–112 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0017-y