Abstract
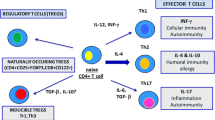
Different immune cell subsets have a relevant role in the pathogenesis of and tissue damage seen in autoimmune thyroid diseases (AITD), including T regulatory (Treg) lymphocytes and T helper (Th) 17 cells. There are several types of CD4+ Treg cells (Foxp3+, CD69+, Tr1), which are able to prevent the appearance of autoimmune diseases, down regulating the immune response and the inflammatory phenomenon. However, despite their presence in peripheral blood and thyroid tissue from patients with AITD, these cells are apparently unable to put down the autoimmune process. Moreover, many reports indicate the involvement of Th17 cells in chronic inflammatory diseases, including AITD. Nevertheless, it is now evident that these lymphocytes show a remarkable plasticity, giving rise to anti-inflammatory (including Treg lymphocytes) and pro-inflammatory cell subtypes. Nowadays, both Treg and Th17 cells must be considered as key elements in the pathogenesis of AITD as well as plausible potential targets for the next generation of therapeutic options of this condition.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Abs:
-
Antibodies
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibodies
- Tfh:
-
T follicular helper
- Treg:
-
T regulatory
- Th:
-
T helper
- AITD:
-
Autoimmune thyroid diseases
- IL-:
-
Interleukin
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- TG:
-
Thyroglobulin
- TPO:
-
Thyroperoxidase
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- GO:
-
Graves’ ophthalmopathy
References
A. Antonelli, S.M. Ferrari, A. Corrado, A. Di Domenicantonio, P. Fallahi, Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 14, 174–180 (2015)
S.A. Morshed, R. Latif, T.F. Davies, Delineating the autoimmune mechanisms in Graves’ disease. Immunol. Res. 54, 191–203 (2012)
H. Li, T. Wang, The autoimmunity in Graves’ disease. Front. Biosci. 18, 782–787 (2013)
Y. Wang, T.J. Smith, Current concepts in the molecular pathogenesis of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55, 1735–1748 (2014)
L. Bartalena, V. Fatourechi, Extrathyroidal manifestations of Graves’ disease: a 2014 update. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 37, 691–700 (2014)
L.A. Zúñiga, R. Jain, C. Haines, D.J. Cua, Th17 cell development: from the cradle to the grave. Immunol. Rev. 252, 78–88 (2013)
C.R. Grant, R. Liberla, G. Mieli-Vergani, D. Vergani, M.S. Longhi, Regulatory T-cells in autoinmune diseases: challenges, controversies and-yet-unanswered questions. Autoimmun. Rev. 14, 105–116 (2015)
A.L. Croxford, P. Kulig, B. Becher, IL-12 and IL-23 in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25, 415–421 (2014)
R.K. Gershon, K. Kondo, Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology 18, 723–737 (1970)
S. Hori, T. Takahashi, S. Sakaguchi, Control of autoimmunity by naturally arising regulatory CD4+ T cells. Adv. Immunol. 81, 331–371 (2003)
M. Miyara, Y. Ito, S. Sakaguchi, Treg-cell therapies for autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 10, 543–551 (2014)
S. Sakaguchi, D.A. Vignali, A.Y. Rudensky, R.E. Niec, H. Waldmann, The plasticity and stability of regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 461–467 (2013)
S. Sakaguchi, K. Wing, Y. Onishi, P. Prieto-Martin, T. Yamaguchi, Regulatory T cells: how do they suppress immune responses? Int. Immunol. 21, 1105–1111 (2009)
Y. Han, Q. Guo, M. Zhang, Z. Chen, X. Cao, CD69+ CD4+ CD25− T cells, a new subset of regulatory T cells, suppress T cell proliferation through membrane-bound TGF-β1. J. Immunol. 182, 111–120 (2009)
M. Vitales-Noyola, L. Doníz-Padilla, C. Álvarez-Quiroga, A. Monsiváis-Urenda, H. Portillo-Salazar, R. González-Amaro, Quantitative and functional analysis of CD69(+) NKG2D(+) T regulatory cells in healthy subjects. Hum. Immunol. 76, 511–518 (2015)
M.G. Roncarolo, S. Gregori, R. Bacchetta, M. Battaglia, Tr1 cells and the counter-regulation of immunity: natural mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 380, 39–68 (2014)
M. Marazuela, M.A. García-López, N. Figueroa-Vega, H. de la Fuente, B. Alvarado-Sánchez, A. Monsiváis-Urenda, F. Sánchez-Madrid, R. González-Amaro, Regulatory T cells in human autoimmune thyroid disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 3639–3646 (2006)
P. Verginis, H.S. Li, G. Carayanniotis, Tolerogenic semimature dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune thyroiditis by activation of thyroglobulin-specific CD4+ CD25+ T cells. J. Immunol. 174, 7433–7439 (2005)
E. Gambineri, T.R. Torgerson, H.D. Ochs, Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked inheritance (IPEX), a syndrome of systemic autoimmunity caused by mutations of Foxp3, a critical regulator of T-cell homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 15, 430–435 (2003)
D.J. Kasprowicz, P.S. Smallwood, A.J. Tyznik, S.F. Ziegler, Scurfin (FoxP3) controls T-dependent immune responses in vivo through regulation of CD4+ T cell effector function. J. Immunol. 171, 1216–1223 (2003)
C. Mao, S. Wang, Y. Xiao, J. Xu, Q. Jiang, M. Jin, X. Jiang, H. Guo, G. Ning, Y. Zhang, Impairment of regulatory capacity of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells mediated by dendritic cell polarization and hyperthyroidism in Graves´ disease. J. Immunol. 186, 4734–4743 (2011)
M. Nakahara, Y. Nagayama, T. Ichikawa, L. Yu, G.S. Eisenbarth, N. Abiru, The effect of regulatory T-cell depletion on the spectrum of organ-specific autoimmune diseases in nonobese diabetic mice at different ages. Autoimmunity 44, 504–510 (2011)
D. Pan, Y.H. Shin, G. Gopalakrishnan, J. Hennessey, L.J. De Groot, Regulatory T cells in Graves’ disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 71, 587–593 (2009)
P. Verginis, H.S. Li, G. Carayanniotis, Tolerogenic semimature dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune thyroiditis by activation of thyroglobulin-specific CD4+ CD25+ T cells. J. Immunol. 174, 7433–7439 (2005)
A.B. Glick, A. Wodzinski, P. Fu, A.D. Levine, D.N. Wald, Impairment of regulatory T-cell function in autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid 23, 871–878 (2013)
A. Bossowski, M. Moniuszko, M. Dabrowska, B. Sawicka, M. Rusak, M. Jeznach, J. Wójtowicz, A. Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A. Bossowska, Lower proportions of CD4+ CD25high and CD4+ Foxp3+, but not CD4+ CD25+ CD127lowFoxp3+ T cell levels in children with autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmune 46, 222–230 (2013)
A. Rodríguez-Muñoz, M. Vitales-Noyola, A. Ramos-Levi, A. Serrano-Somavilla, R. González-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Levels of regulatory T cells CD69+ NKG2D+ IL-10+ are increased in patients with autoimmune thyroid disorders. Endocrine (2015). doi:10.1007/s12020-015-0662-2
R. Basu, R.D. Hatton, C.T. Weaver, The Th17 family: flexibility follows function. Immunol. Rev. 252, 89–203 (2013)
F. Annunziato, L. Cosmi, F. Liotta, E. Maggi, S. Romagnani, Human T helper type 1 dichotomy: origin, phenotype and biological activities. Immunology 144, 343–351 (2014)
Y.K. Lee, R. Mukasa, R.D. Hatton, C.T. Weaver, Developmental plasticity of Th17 and Treg cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 21, 274–280 (2009)
G. Beriou, C.M. Costantino, C.W. Ashley, L. Yang, V.K. Kuchroo, C. Baecher-Allan, D.A. Hafler, IL-17-producing human peripheral regulatory T cells retain suppressive function. Blood 113, 4240–4249 (2009)
H.J. Koenen, R.L. Smeets, P.M. Vink, E. van Rijssen, A.M. Boots, I. Joosten, Human CD25highFoxp3pos regulatory T cells differentiate into IL-17-producing cells. Blood 112, 2340–2352 (2008)
H.J. Bovenschen, P.C. van de Kerkhof, P.E. van Erp, R. Woestenenk, I. Joosten, H.J. Koenen, Foxp3+ regulatory T cells of psoriasis patients easily differentiate into IL-17A-producing cells and are found in lesional skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 131, 1853–1860 (2011)
S.A. McClymont, A.L. Putnam, M.R. Lee, J.H. Esensten, W. Liu, M.A. Hulme, U. Hoffmüller, U. Baron, S. Olek, J.A. Bluestone, T.M. Brusko, Plasticity of human regulatory T cells in healthy subjects and patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Immunol. 186, 3918–3926 (2011)
P. Pandiyan, J. Zhu, Origin and functions of pro-inflammatory cytokine producing Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Cytokine (2015). doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.07.005
R. Du, H. Zhao, F. Yan, H. Li, IL-17+ Foxp3+ T cells: an intermediate differentiation stage between Th17 cells and regulatory T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 96, 39–48 (2014)
L. Shi, M. Bi, R. Yang, J. Zhou, S. Zhao, C. Fan, Z. Shan, Y. Li, W. Teng, Defective expression of regulatory B cells in iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in non-obese diabetic H-2(h4) mice. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 37, 43–50 (2014)
T.R. Mosmann, H. Cherwinski, M.W. Bond, M.A. Giedlin, R.L. Coffman, Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokines activities and secreted proteins. J. Immunol. 136, 2348–2357 (1986)
N. Schmitt, H. Ueno, Regulation of human helper T cell subset differentiation by cytokines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 34, 130–136 (2015)
S. Aggarwal, N. Ghilardi, M.H. Xie, F.J. de Sauvage, A.L. Gurney, Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 1910–1914 (2003)
E. Rouvier, M.F. Luciani, M.G. Mattei, F. Denizot, P. Golstein, CTLA-8, cloned from an activated T cell, bearing AU-rich messenger RNA instability sequences, and homologous to a herpesvirus saimiri gene. J. Immunol. 150, 5445–5456 (1993)
Z. Yao, S.L. Painter, W.C. Fanslow, D. Ulrich, B.M. Macduff, M.K. Spriggs, R.J. Armitage, Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J. Immunol. 155, 5483–5486 (1995)
X. Song, H. Gao, Y. Qian, Th17 differentiation and their pro-inflammation function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 841, 99–151 (2014)
C.L. Langrish, Y. Chen, W.M. Blumenschein, J. Mattson, B. Basham, J.D. Sedgwick, T. McClanahan, R.A. Kastelein, D.J. Cua, IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 201, 233–240 (2005)
K. Ghoreschi, A. Laurence, X.P. Yang, C.M. Tato, M.J. McGeachy, J. Konkel, H.L. Ramos, L. Wei, T. Davidson, N. Bouladoux, J. Grainger, Q. Chen, Y. Kanno, W.T. Watford, H.W. Sun, G. Eberl, E. Schevach, Y. Belkaid, D.J. Cua, W. Chen, O´Shea, J.J.: Generation of pathogenic Th17 cells in the absence of TGF-β signaling. Nature 467, 967–971 (2010)
K. Ghoreschi, A. Laurence, X.P. Yang, K. Hirahara, J.J. O’Shea, T helper 17 cell heterogeneity and pathogenicity in autoinmune disease. Trends Immunol. 32, 395–401 (2011)
Y. Lee, A. Awasthi, N. Yosef, F.J. Quintana, S. Xiao, A. Peters, C. Wu, M. Kleinewietfeld, S. Kunder, D. Hafler, R.A. Sobel, A. Regev, V.K. Kuchroo, Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic Th17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 13, 991–999 (2012)
S.A. Basdeo, B. Moran, D. Cluxton, M. Canavan, J. McCormick, M. Connolly, C. Orr, K.H.G. Mills, D.J. Veale, U. Fearon, J.M. Fletcher, Polyfunctional, pathogenic CD161+ Th17 cells lineage cells are resistant to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in the context of autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 195, 528–540 (2015)
R. Ramesh, L. Kozhaya, K. McKevitt, I.M. Djuretic, T.J. Carlson, M.A. Quintero, J.L. McCauley, M.T. Abreu, D. Unutmaz, M.S. Sundrud, Pro-inflammatory human Th17 cells selectively express P-glycoprotein and are refractory to glucocorticoids. J. Exp. Med. 211, 89–114 (2014)
T. Feng, A.T. Cao, C.T. Weaver, C.O. Elson, Y. Cong, Interleukin-12 converts Foxp3+ regulatory T cells to interferon-γ-producing Foxp3+ T cells that inhibit colitis. Gastroenterology 140, 2031–2043 (2011)
M.A. Kluger, M.C. Meyer, A. Nosko, B. Goerke, M. Luig, C. Wegscheid, G. Tiegs, R.A. Stahl, U. Panzer, O.M. Steinmetz, RORγt+ Foxp3+ cells are an independent bifunctional regulatory T cell lineage and mediate crescentic GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. (2015). doi:10.1681/ASN.2014090880
K. Eyerich, S. Eyerich, Th22 cells in allergic disease. Allergo. J. Int. 24, 1–7 (2015)
I. Horie, N. Abiru, Y. Nagayama, G. Kuriya, O. Saitoh, T. Ichikawa, Y. Iwakura, K. Eguchi, T helper type 17 immune response plays an indispensable role for development of iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in nonobese diabetic-H2h4 mice. Endocrinology 150, 5135–5142 (2009)
F. Hayashi, M. Watanabe, T. Nanba, N. Inoue, T. Akamizu, Y. Iwatani, Association of the -31C/T functional polymorphism in the interleukine-1β gene with the intractability of Graves’ disease and the proportion of T helper type 17 cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 158, 281–286 (2009)
T. Nanba, M. Watanabe, N. Inoue, Y. Iwatani, Increases of the Th1/Th2 cell ratio in severe Hashimoto’s disease and in the proportion of Th17 cells in intractable Graves’ disease. Thyroid 19, 495–501 (2009)
N. Figueroa-Vega, M.A. Pérez, I. Benedicto, F. Sánchez-Madrid, R. González-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Increased circulating pro-inflammatory cytokine and Th17 lymphocytes in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 953–962 (2010)
Q. Qin, P. Liu, L. Liu, R. Wang, N. Yan, J. Yang, X. Wang, M. Pandey, J. Zhang, The increased but non-predominant expression of Th17- and Th1-specific cytokines in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis but not in Graves´ disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 45, 1202–1208 (2012)
D. Peng, B. Xu, Y. Wang, H. Guo, Y. Jiang, A high frequency of circulating Th22 and Th17 cells in patients with new onset Graves’ disease. PloS One 8, e68446 (2013)
D. Li, W. Cai, R. Gu, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, K. Tang, P. Xu, F. Katirai, W. Shi, L. Wang, T. Huang, B. Huang, Th17 plays a role in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in patients. Clin. Immunol. 149, 411–420 (2013)
B. Kristensen, L. Hegedüs, H.O. Madsen, T.J. Smith, C.H. Nielsen, Altered balance between self-reactive T helper (Th)17 cells and Th10 cells and between full-length forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3) and FoxP3 splice variants in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 180, 58–69 (2015)
H. Guo, D. Peng, Y. Wang, B.C. Xu, J.S. Ni, W. Meng, Y.F. Jiang, A higher frequency of circulating IL-22+ CD4+ T cells in chinese patients with newly diagnosed Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. PloS One 9, e84545 (2014)
H. Xue, X. Yu, L. Ma, S. Song, Y. Li, L. Zhang, T. Yang, H. Liu, The possible role of CD4+ CD25highFoxp3+/CD4+ IL-17A+ cell imbalance in the autoimmunity of patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Endocrine (2015). doi:10.1007/s12020-015-0569-y
S. Wang, S.E. Baidoo, Y. Liu, C. Zhu, J. Tian, J. Ma, J. Tong, J. Chen, X. Tang, H. Xu, L. Lu, T cell-derived leptin contributes to increased frequency oh T helper type 17 cells in female patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 171, 63–68 (2012)
Y. Liu, X. Tang, J. Tian, C. Zhu, H. Peng, K. Rui, Y. Wang, C. Mao, J. Ma, L. Lu, H. Xu, S. Wang, Th17/Treg cells imbalance and GITRL profile in patients with Hashimoto´s thyroiditis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 21674–21686 (2014)
S. Leskela, A. Serrano, H. de la Fuente, A. Rodríguez-Muñoz, A. Ramos-Levi, M. Sampedro-Núñez, F. Sánchez-Madrid, R. González-Amaro, M. Marazuela, Graves’ disease is associated with defective expression of the immune regulatory molecule galectin-9 in antigen-presenting dendritic cells. PLoS One 16, e0123938 (2015)
J.R. Li, F.Y. Hong, J.Y. Zeng, G.L. Huang, Functional interleukin-17 receptor A are present in the thyroid gland in intractable Graves’ disease. Cell. Immunol. 281, 85–90 (2013)
R.H. Song, Z.Y. Yu, Q. Qin, X. Wang, F.S. Muhali, L.F. Shi, W.J. Jiang, L. Xiao, D.F. Li, J.A. Zhang, Different levels of circulating Th22 cell and its related molecules in Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 7, 4024–4031 (2014)
X. Bai, J. Sun, W. Wang, Z. Shan, H. Zheng, Y. Zhao, M. Gong, W. Teng, Increased differentiation of Th22 cells in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr. J. 61, 1181–1190 (2014)
R.M. Ruggeri, P. Minciullo, S. Saitta, S. Giovanazzo, R. Certo, A. Campennì, F. Trimarchi, S. Gangemi, S. Benvenga, Serum interleukin-22 (IL-22) is increased in the early stage of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis compared to non-autoimmune thyroid disease and healthy controls. Hormones 13, 338–344 (2014)
R.M. Ruggeri, S. Saitta, M. Cristani, S. Giovanazzo, V. Tigano, F. Trimarchi, S. Benvenga, S. Gangemi, Serum interleukin-23 (IL-23) is increased in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis. Endocr. J. 61, 359–363 (2014)
L. Guan, X. Wang, S. Meng, L. Shi, W. Jiang, L. Xiao, X. Shi, J. Xu, J. Zhang, Increased IL-21/IL-22R expression and its proinflammatory effects in autoimmune thyroid disease. Cytokine 72, 160–165 (2015)
S.J. Shan, R.S. Douglas, The pathophysiology of thyroid eye disease. J. Neuroophthalmol. 34, 177–185 (2014)
H. Wei, M. Guan, Y. Qin, C. Xie, X. Fu, F. Gao, Y. Xue, Circulating levels of miR-146a and IL-17 are significantly correlated with the clinical activity of Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Endocr. J. 61, 1087–1089 (2014)
S.E. Kim, J.S. Yoon, K.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, Increased serum interleukin-17 in Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 250, 1521–1526 (2012)
A.K. Huber, E.M. Jacobson, K. Jazdzewski, E.S. Concepcion, Y. Tomer, Interleukin (IL)-23 receptor is a major susceptibility gene for Graves’ ophthalmopathy: the IL-23/T-helper 17 axis extends to thyroid autoimmunity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1077–1081 (2008)
L. Zheng, P. Ye, C. Liu, The role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in the pathogenesis of Graves’ disease. Endocr. J. 60, 591–597 (2013)
F. Rajaii, A.N. McCoy, T.J. Smith, Cytokines are both villains and potential therapeutic targets in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: From bench to bedside. Expert. Rev. Ophthalmol. 9, 227–234 (2014)
D. Cao, R. van Vollenhoven, L. Klareskog, C. Trollmo, V. Malmstrom, CD25brightCD4+ regulatory T cells are enriched in inflamed joints of patients with chronic rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 6, R335–R346 (2004)
M.R. Ehrenstein, J.G. Evans, A. Singh, S. Moore, G. Warnes, D.A. Isenberg, C. Mauri, Compromised function of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by anti-TNFalpha therapy. J. Exp. Med. 200, 277–285 (2004)
J. Haas, A. Hug, A. Viehover, B. Fritzsching, C.S. Falk, A. Filser, T. Vetter, L. Milkova, M. Korporal, B. Fritz, B. Storch-Hagenlocher, P.H. Krammer, E. Suri-Payer, B. Wildemann, Reduced suppressive effect of CD4+ CD25 high regulatory T cells on the T cell immune response against myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 3343–3352 (2005)
U. Feger, C. Luther, S. Poeschel, A. Melms, E. Tolosa, H. Wiendl, Increased frequency of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in the cerebrospinal fluid but not in the blood of multiple sclerosis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 147, 412–418 (2007)
J. Maul, C. Loddenkemper, P. Mundt, E. Berg, T. Giese, A. Stallmach, M. Zeitz, R. Duchmann, Peripheral and intestinal regulatory CD4+ CD25(high) T cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 128, 1868–1878 (2005)
H. Sugiyama, R. Gyulai, E. Toichi, E. Garaczi, S. Shimada, S.R. Stevens, T.S. McCormick, K.D. Cooper, Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J. Immunol. 174, 164–173 (2005)
H.J. Bovenschen, P.C. van de Kerkhof, P.E. van Erp, R. Woestenenk, I. Joosten, H.J. Koenen, Foxp3+ regulatory T cells of psoriasis patients easily differentiate into IL-17Aproducing cells and are found in lesional skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 131, 1853–1860 (2011)
T.M. Brusko, C.H. Wasserfall, M.J. Clare-Salzler, D.A. Schatz, M.A. Atkinson, Functional defects and the influence of age on the frequency of CD4+ CD25+ T-cells in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 54, 1407–1414 (2005)
J.M. Lawson, J. Tremble, C. Dayan, H. Beyan, R.D. Leslie, M. Peakman, T.I. Tree, Increased resistance to CD4+ CD25hi regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 154, 353–359 (2008)
B. Alvarado-Sánchez, B. Hernández-Castro, D. Portales-Pérez, L. Baranda, E. Layseca-Espinosa, C. Abud-Mendoza, A.C. Cubillas-Tejeda, R. González-Amaro, Regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 27, 110–118 (2006)
J.C. Crispin, A. Martínez, J. Alcocer-Varela, Quantification of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 21, 273–276 (2003)
A. Alunno, M. Manetti, S. Caterbi, L. Ibba-Manneschi, O. Bistoni, E. Bartoloni, V. Valentini, R. Terenzi, R. Gerli, Altered immunoregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of regulatory T cells and proinflammatory th17 cells and therapeutic implications. Mediat. Inflamm. (2015). doi:10.1155/2015/751793
S. Alvermann, C. Hennig, O. Stüve, H. Wiendl, M. Stangel, Immunophenotyping of cerebrospinal fluid cells in multiple sclerosis: in search of biomarkers. JAMA Neurol. 71, 905–912 (2014)
J.S. Tzartos, M.A. Friese, M.J. Craner, J. Palace, J. Newcombe, M.M. Esiri, L. Fugger, Interleukin-17 production in central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 172, 146–155 (2008)
C.S. Catana, I. Berindan Neagoe, V. Cozma, C. Magdas, F. Tabaran, D.L. Dumitrascu, Contribution of the IL-17/IL-23 axis to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 21, 5823–5830 (2015)
J.L. Harden, J.G. Krueger, A.M. Bowcock, The immunogenetics of psoriasis: a comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.008
L. Reinert-Hartwall, J. Honkanen, H.M. Salo, J.K. Nieminen, K. Luopajärvi, T. Härkönen, R. Veijola, O. Simell, J. Ilonen, A. Peet, V. Tillmann, M. Knip, O. Vaarala, DIABIMMUNE Study Group, Th1/Th17 plasticity is a marker of advanced β cell autoimmunity and impaired glucose tolerance in humans. J. Immunol. 194, 68–75 (2015)
M.S. Maddur, P. Miossec, S.V. Kaveri, J. Bayry, Th17 cells: biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and therapeutic strategies. Am. J. Pathol. 181, 8–18 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the following grants: 95395 from the Fondo de Cooperación Internacional en Ciencia y Tecnología (FONCICYT-European Union, México, to R.G.-A.); PI13-01414 and PIE-0041 BIOIMID from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria—Instituto de Salud Carlos III (to M.M.), and S2011/BMD-2328 TIRONET from the Comunidad de Madrid (to M.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Amaro, R., Marazuela, M. T regulatory (Treg) and T helper 17 (Th17) lymphocytes in thyroid autoimmunity. Endocrine 52, 30–38 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0759-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0759-7