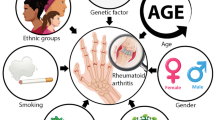
Abstract
Infections are believed to contribute to the maturation of the immune system from the innate to the adaptive phases and therefore may take part in the induction of autoimmune conditions. In the current study, we present an extensive analysis conducted on sera samples of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in order to seek evidence of previous or coexisting infectious processes using the Bio-Rad BioPlex immunoassay analyzer. We detected higher rates of serological evidence of infections with Epstein–Barr virus and cytomegalovirus viruses. Our findings may indicate a role of these viruses in the pathogenesis of RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedek TG (2006) The history of bacteriologic concepts of rheumatic fever and rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36:109–123
Shoenfeld Y, Blank M, bu-Shakra M, Amital H, Barzilai O, Berkun Y et al (2008) The mosaic of autoimmunity: prediction, autoantibodies, and therapy in autoimmune diseases—2008. Isr Med Assoc J 10:13–19
Shoenfeld Y, Zandman-Goddard G, Stojanovich L, Cutolo M, Amital H, Levy Y et al (2008) The mosaic of autoimmunity: hormonal and environmental factors involved in autoimmune diseases—2008. Isr Med Assoc J 10:8–12
Shoenfeld Y, Gilburd B, bu-Shakra M, Amital H, Barzilai O, Berkun Y et al (2008) The mosaic of autoimmunity: genetic factors involved in autoimmune diseases—2008. Isr Med Assoc J 10:3–7
Zifman E, Amital H, Gilburd B, Shoenfeld Y (2008) Antioxidants and smoking in autoimmune disease—opposing sides of the seesaw? Autoimmun Rev 8:165–169
Saag KG, Cerhan JR, Kolluri S, Ohashi K, Hunninghake GW, Schwartz DA (1997) Cigarette smoking and rheumatoid arthritis severity. Ann Rheum Dis 56:463–469
Karlson EW, Mandl LA, Hankinson SE, Grodstein F (2004) Do breast-feeding and other reproductive factors influence future risk of rheumatoid arthritis? Results from the Nurses' Health Study. Arthritis Rheum 50:3458–3467
Plot L, Amital H (2009) Infectious associations of Celiac disease. Autoimmun Rev 8:316–319
Doria A, Sarzi-Puttini P, Shoenfeld Y (2008) Infections, rheumatism and autoimmunity: the conflicting relationship between humans and their environment. Autoimmun Rev 8:1–4
Randone SB, Guiducci S, Cerinic MM (2008) Systemic sclerosis and infections. Autoimmun Rev 8:36–40
Doria A, Canova M, Tonon M, Zen M, Rampudda E, Bassi N et al (2008) Infections as triggers and complications of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 8:24–28
Tozzoli R, Barzilai O, Ram M, Villalta D, Bizzaro N, Sherer Y et al (2008) Infections and autoimmune thyroid diseases: parallel detection of antibodies against pathogens with proteomic technology. Autoimmun Rev 8:112–115
Ram M, Anaya JM, Barzilai O, Izhaky D, Porat Katz BS, Blank M et al (2008) The putative protective role of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection from autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun Rev 7:621–625
Barzilai O, Sherer Y, Ram M, Izhaky D, Anaya JM, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in autoimmune diseases: are they truly notorious? A preliminary report. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:567–577
Doria A, Arienti S, Rampudda M, Canova M, Tonon M, Sarzi-Puttini P (2008) Preventive strategies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 7:192–197
Doria A, Zampieri S, Sarzi-Puttini P (2008) Exploring the complex relationships between infections and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 8:89–91
Tanaka E, Singh G, Saito A, Syouji A, Yamada T, Urano W et al (2005) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of upper gastrointestinal ulcer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Mod Rheumatol 15:340–345
Ishikawa N, Fuchigami T, Matsumoto T, Kobayashi H, Sakai Y, Tabata H et al (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection in rheumatoid arthritis: effect of drugs on prevalence and correlation with gastroduodenal lesions. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:72–77
Zentilin P, Seriolo B, Dulbecco P, Caratto E, Iiritano E, Fasciolo D et al (2002) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori may reduce disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1291–1299
Aragona P, Magazzu G, Macchia G, Bartolone S, Di PG, Vitali C et al (1999) Presence of antibodies against Helicobacter pylori and its heat-shock protein 60 in the serum of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. J Rheumatol 26:1306–1311
Kalabay L, Fekete B, Czirjak L, Horvath L, Daha MR, Veres A et al (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection in connective tissue disorders is associated with high levels of antibodies to mycobacterial hsp65 but not to human hsp60. Helicobacter 7:250–256
Pockley AG (2002) Heat shock proteins, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 105:1012–1017
Tsoulfa G, Rook GA, Van-Embden JD, Young DB, Mehlert A, Isenberg DA et al (1989) Raised serum IgG and IgA antibodies to mycobacterial antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:118–123
Balandraud N, Roudier J, Roudier C (2004) Epstei–Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 3:362–367
Alspaugh MA, Henle G, Lennette ET, Henle W (1981) Elevated levels of antibodies to Epstein–Barr virus antigens in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 67:1134–1140
Tosato G, Steinberg AD, Blaese RM (1981) Defective EBV-specific suppressor T-cell function in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 305:1238–1243
Toussirot E, Auger I, Roudier C, Luka J, Wendling D, Tiberghien P et al (1999) HLA-DR polymorphism influences T-cell precursor frequencies to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gp110: implications for the association of HLA-DR antigens with rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens 54:146–152
Murayama T, Tsuchiya N, Jisaki F, Ozaki M, Sakamuro D, Hirai K et al (1994) Elevated cytokine levels in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis correlates with the presence of cytomegalovirus genome. Autoimmunity 17:333–337
Hooper M, Kallas EG, Coffin D, Campbell D, Evans TG, Looney RJ (1999) Cytomegalovirus seropositivity is associated with the expansion of CD4+. J Rheumatol 26:1452–1457
Tamm A, Ziegler T, Lautenschlager I, Nikkari S, Mottonen T, Luukkainen R et al (1993) Detection of cytomegalovirus DNA in cells from synovial fluid and peripheral blood of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 20:1489–1493
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. K. Meron and H. Amital equally contributed to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meron, M.K., Amital, H., Shepshelovich, D. et al. Infectious Aspects and the Etiopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 38, 287–291 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8158-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-009-8158-6