Abstract
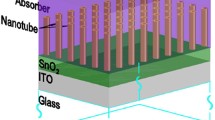
Vertically aligned periodic arrays of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are used to create topographically enhanced light-trapping photovoltaic cells. The CNTs form the back contact of the device and serve as a scaffold to support the photoactive heterojunction. Molecular beam epitaxy is used to deposit CdTe and CdS as the p/n-type materials and ion-assisted deposition is used to deposit a conformal coating of indium-tin oxide as the transparent top contact. X-ray diffraction data shows (111) texture of the CdTe. Photocurrent produced “per cm2 of footprint” for the CNT-based device is 63 times that of a commercially available planar single crystal silicon device.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kim and D. Kim, “Influence of CdS Heat Treatment on the Microstructure of CdS and the Performance of CdS/CdTe Solar Cells,” Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 67(1–4) (2001), pp. 297–304.
J. Lee, “Comparison of CdS Films Deposited by Different Techniques: Effects on CdTe Solar Cell,” Applied Surface Science, 252(5) (2005), pp. 1398–1403.
J. Terrazas et al., “Ordered Polycrystalline Thin Films for High Performance CdTe/CdS Solar Cells,” Thin Solid Films, 490(2) (2005), pp. 146–153.
L. Worschech et al., “Cadmium Vacancy Related Defects in MBE Grown CdTe,” Journal of Crystal Growth, 161(1–4) (1996), pp. 134–138.
D. Niles and H. Hochst, “ZnTe. A Potential Interlayer to Form Low Resistance Back Contacts in CdS/CdTe Solar Cells,” Journal of Applied Physics, 73(12) (1993), pp. 8381–8385.
U. Jahn et al., “Doping and Intermixing in CdS/CdTe Solar Cells Fabricated under Different Conditions,” Journal of Applied Physics, 90(5) (2001), pp. 2553–2558.
P. Boieriu et al., “Wurtzite CdS on CdTe Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy,” Journal of Electronic Materials, 29(6) (2000), p. 718.
M. Aslan et al., “Sulfur Diffusion in Polycrystalline Thin-Film CdTe Solar Cells,” Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings (Warrendale, PA: MRS, 1997), pp. 203–208.
J. Lee, “Photovoltaic Effect in Ideal Carbon Nanotube Diodes,” Applied Physics Letters, 87 (2005), pp. 73101–73103.
E. Katz, “Fullerenes for Photovoltaics,” Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, vol. 3, ed. Hari Singh Nalwa (Valencia, CA: American Scientific Publishers, 2004), pp. 661–683.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camacho, R.E., Morgan, A.R., Flores, M.C. et al. Carbon nanotube arrays for photovoltaic applications. JOM 59, 39–42 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0037-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0037-0