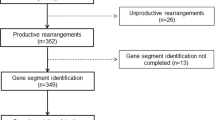
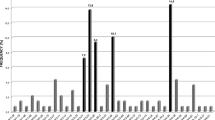
Abstract
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, originating from naïve B-cells. The blastoid MCL tumors often show complex cytogenetic aberrations. In this review, we summarized the data available on immunoglobulin heavy-chain (IgH) genes rearrangement for their importance in suggesting the MCL normal counterpart B-cell. Some new data suggesting an antigen selection process were also presented in this review.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jares P, Campo E. Advances in the understanding of mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2008; 142: 149–165.
Thelander EF, Rosenquist R. Molecular genetic characterization reveals new subsets of mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 1042–1049.
Swerdlow SH, Williams ME. From centrocytic to mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic and molecular review of 3 decades. Hum Pathol 2002; 33: 7–20.
Salaverria I, Zettl A, Beà S, et al. Specific secondary genetic alterations in mantle cell lymphoma provide prognostic information independent of the gene expressionbased proliferation signature. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1216–1222.
Sander S, Bullinger L, Leupolt E, et al. Genomic aberrations in mantle cell lymphoma detected by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization. Incidence and clinicopathological correlations. Haematologica 2008; 93: 680–687.
Argatoff LH, Connors JM, et al. Mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 80 cases. Blood 1997; 89: 2067–2078.
Bosch F, Lòpez-Guillermo A, Campo E, et al. Mantle cell lymphoma: presenting features, response to therapy, and prognostic factors. Cancer 1998; 82: 567–575.
Küppers R, Klein U, Hansmann ML, et al. Cellular origin of human B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1520–1529.
Vanasse GJ, Concannon P, Willerford DM. Regulated genomic instability and neoplasia in the lymphoid lineage. Blood 1999; 94: 3997–4010.
Delves PJ, Roitt IM. The immune system. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 37–49.
Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Papadaki T, et al. Somatic hypermutation patterns in germinal center B cell malignancies. Hematology 2003; 8: 319–328.
Fugmann SD, Lee AI, Shockett PE, et al. The RAG proteins and V (D) J recombination: complexes, ends, and transposition. Annu Rev Immunol 2000; 18: 495–527.
Gonzàlez D, van der Burg M, García-Sanz R, et al. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Blood 2007; 110: 3112–3121.
Kiyoi H, Naoe T. Immunoglobulin variable region structure and B-cell malignancies. Int J Hematol 2001; 73: 47–53.
Papavasiliou FN, Schatz DG. Somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes: merging mechanisms for genetic diversity. Cell 2002; 109: S35–44.
Rada C, Williams GT, Nilsen H, et al. Immunoglobulin isotype switching is inhibited and somatic hypermutation perturbed in UNG-deficient mice. Curr Biol 2002; 12: 1748–1755.
van Zelm MC, Szczepanski T, van der Burg M, et al. Replication history of B lymphocytes reveals homeostatic proliferation and extensive antigen-induced B cell expansion. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 645–655.
Bertoni F, Conconi A, Cogliatti SB, et al. Immunoglobulin heavy chain genes somatic hypermutations and chromosome 11q22-23 deletion in classic mantle cell lymphoma: a study of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research. Br J Haematol 2004; 124: 289–298.
Cogliatti SB, Bertoni F, Zimmermann DR, et al. IgV H mutations in blastoid mantle cell lymphoma characterize a subgroup with a tendency to more favourable clinical outcome. J Pathol 2005; 206: 320–327.
Bertoni F, Ponzoni M. The cellular origin of mantle cell lymphoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 39: 1747–1753.
Thorsélius M, Walsh S, et al. Eriksson I Somatic hypermutation and V(H) gene usage in mantle cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 2002; 68: 217–224.
Amato D, Oscier DG, Davis Z, et al. Cytogenetic aberrations and immunoglobulin VH gene mutations in clinically benign CD5-monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis. Am J Clin Pathol 2007; 128: 333–338.
Bertoni F, Rinaldi A, Zucca E, et al. Update on the molecular biology of mantle cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol 2006; 24: 22–27.
Swerdlow SH, Berger F, Isaacson PI, et al. Mantle cell lymphoma. In Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, & Vardiman JW (Eds.), World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (pp. 168–170) Lyon: IARC Press 2001.
Bertoni F, Zucca E, Cotter FE. Molecular basis of mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2004; 124: 130–140.
Welzel N, Le T, Marculescu R, et al. Templated nucleotide addition and immunoglobulin JH-gene utilization in t (11;14) junctions: implications for the mechanism of translocation and the origin of mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 1629–1636.
Dono M, Cerruti G, Zupo S. The CD5+ B-cell. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004; 36: 2105–2111.
Hummel M, Tamaru J, Kalvelage B, et al. Mantle cell (previously centrocytic) lymphomas express VH genes with no or very little somatic mutations like the physiologic cells of the follicle mantle. Blood 1994; 84: 403–407.
Du MQ, Diss TC, Xu CF, et al. Ongoing immunoglobulin gene mutations in mantle cell lymphomas. Br J Haematol 1997;96: 124–131.
Pittaluga S, Tierens A, Pinyol M, et al. Blastic variant of mantle cell lymphoma shows a heterogenous pattern of somatic mutations of the rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain variable genes. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 1301–1306.
Hashimoto Y, Nakamura N, Kuze T, et al. Multiple lymphomatous polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract is a heterogenous group that includes mantle cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma: analysis of somatic mutation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene variable region. Hum Pathol 1999; 30: 581–587.
Làszló T, Nagy M, Kelényi G, et al. Immunoglobulin V(H) gene mutational analysis suggests that blastic variant of mantle cell lymphoma derives from different stages of B-cell maturation. Leuk Res 2000; 24: 27–31.
Camacho FI, Algara P, Rodríguez A, et al. Molecular heterogeneity in MCL defined by the use of specific VH genes and the frequency of somatic mutations. Blood 2003; 101: 4042–4046.
Kienle D, Kröber A, Katzenberger T, et al. VH mutation status and VDJ rearrangement structure in mantle cell lymphoma: correlation with genomic aberrations, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Blood 2003; 102: 3003–3009.
Orchard J, Garand R, Davis Z, et al. A subset of t (11;14) lymphoma with mantle cell features displays mutated IgVH genes and includes patients with good prognosis, nonnodal disease. Blood 2003; 101: 4975–4981.
Walsh SH, Thorsélius M, Johnson A, et al. Mutated VH genes and preferential VH3-21 use define new subsets of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2003; 101: 4047–4054.
Lai R, Lefresne SV, Franko B, et al. Immunoglobulin VH somatic hypermutation in mantle cell lymphoma: mutated genotype correlates with better clinical outcome. Mod Pathol 2006; 19: 1498–1505.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Thorsélius M, Kröber A, Murray F, et al. Strikingly homologous immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and poor outcome in VH3-21-using chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients independent of geographic origin and mutational status. Blood 2006; 107: 2889–2894.
Bomben R, Dal Bo M, Capello D, et al. Comprehensive characterization of IGHV3-21-expressing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an Italian multicenter study. Blood 2007; 109: 2989–2998.
Carreras J, Villamor N, Colomo L, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of ZAP-70 expression in B-cell lymphoid neoplasms. J Pathol 2005; 205: 507–513.
Murray F, Darzentas N, Hadzidimitriou A, et al. Stereotyped patterns of somatic hypermutation in subsets of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implications for the role of antigen selection in leukemogenesis. Blood 2008; 111: 1524–1533.
Fält S, Merup M, Tobin G, Distinctive gene expression pattern in VH3-21 utilizing B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 681–689.
Muñoz L, Lasa A, Carricondo MT, et al. Carricondo MT Comparative analysis of ZAP-70 expression and Ig VH mutational status in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2007; 72: 96–102.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Johnson A, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemias utilizing the VH3-21 gene display highly restricted Vlambda2-14 gene use and homologous CDR3s: implicating recognition of a common antigen epitope. Blood 2003; 101: 4952–4957.
Ghiotto F, Fais F, Valetto A, et al. Remarkably similar antigen receptors among a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 1008–1016.
Messmer BT, Albesiano E, Efremov DG, et al. Multiple distinct sets of stereotyped antigen receptors indicate a role for antigen in promoting chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 519–525.
Tobin G, Thunberg U, Karlsson K, Subsets with restricted immunoglobulin gene rearrangement features indicate a role for antigen selection in the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 2879–2885.
Widhopf GF 2nd, Rassenti LZ, Toy TL, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells of more than 1% of patients express virtually identical immunoglobulins. Blood 2004; 104: 2499–2504.
Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Moreno C, et al. Over 20% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia carry stereotyped receptors: Pathogenetic implications and clinical correlations. Blood 2007; 109: 259–270.
Ghia EM, Jain S, Widhopf GF 2nd, et al. Use of IGHV3-21 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with high-risk disease and reflects antigen-driven, post-germinal center leukemogenic selection. Blood 2008; 111: 5101–5108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Hl., Wang, Hq., Hao, Xs. et al. Biased immunoglobulin genes rearrangement in mantle cell lymphoma: Hints to identify the normal B-cell counterpart. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Res. 8, 65–70 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11805-011-0561-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11805-011-0561-0