Abstract
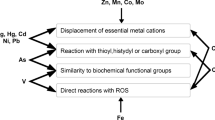
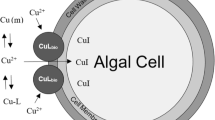
The bioaccumulation and toxicity of heavy metals were reviewed with special reference to microalgae, the key component of the food web in aquatic ecosystems. Heavy metals enter algal cells either by means of active transport or by endocytosis through chelating proteins and affect various physiological and biochemical processes of the algae. The toxicity primarily results from their binding to the sulphydryl groups in proteins or disrupting protein structure or displacing essential elements. Metals can break the oxidative balance of the algae, inducing antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX). The amount of oxidized proteins and lipids in the algal cells thus indicates the severity of the stress. Algal tolerance to heavy metal is highly dependent upon the defense response against the probable oxidative damages. Production of binding factors and proteins, exclusion of metals from cells by ion-selective transporters and excretion or compartmentalization have been suggested with regard to reducing heavy metal toxicity. However, a comprehensive description on the mechanisms underlining metal toxicity of microalgae and gaining tolerance is yet to be elaborated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhiya, J., X. H. Cai, R. T. Sayre, and S. Traina, 2002. Binding of aqueous cadmium by the lyophilized biomass of Chlamy domonas reinhardtii. Colloids Surf. A Physiochem. Eng. Aspects, 210: 1–11.
Alia, M. P., and J. Matysik, 2001. Effect of proline on the production of singlet oxygen. Amino. Acids., 21: 195–200.
Atri, N., and L. C. Rai, 2003. Differential responses of three cyanobacteria to UV-B and Cd. J. Microbiol. Biotech., 13: 544–551.
Avery, S. V., 2001. Metal toxicity in yeasts and the role of oxidative stress. Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 49: 111–142.
Bae, W., C. H. Wu, J. Kostal, A. Mulchandani, and W. Chen, 2003. Enhanced mercury biosorption by bacterial cells with surface-displayed MerR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69(6): 3176–3180.
Bajguz, A., 2000. Blockade of heavy metals accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris cells by 24-epibrassinolide. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 38: 797–801.
Bishop, P. L., 2002. Pollution Prevention: Fundamentals and Practice. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 768pp.
Cardozo, K. H. M., M. A. L. Oliveira, M. F. M. Tavares, P. Colepicolo, and E. Pinto, 2002. Daily oscillation of fatty acids and malondialdehyde in the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum. Biol. Rhythm Res., 33: 371–381.
Carr, H. P., F. A. Carino, M. S. Yang, and M. H. Wong, 1998. Characterization of cadmium-binding capacity of Chlorella Vulgaris. Bull. Envion. Cantam. Toxicol., 60: 433–440.
Cobbett, C., and P. Goldsbrough, 2002. Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 53: 159–182.
Conner, S. D., and S. L. Schimid, 2003. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature, 422: 37–44.
De Filippis, L. F., and C. K. Pallaghy, 1994. Heavy metals: sources and biological effects. In: Algae and Water Pollution. Rai, L. C., et al., eds., E. Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuch-handlung, Stuttgart, 31–37.
De Schamphelaere, K. A. C., F. M. Vasconncelos, D. G. Heijerick, F. M. G. Tack, K. Delbeke, H. E. Allen, et al., 2003. Development and field validation of a predictive copper toxicity model for the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 22: 2454–2465.
El-Enany, A. E., and A. A. Issa, 2000. Cyanobacteria as a biosorbent of heavy metals in sewage water. Environ. Toxicol. Phar., 8: 95–101.
El-Naggar, A. H., M. A. Osman, and E. A. El-Mohsenawy, 1999. Cobalt and lead toxicities on Calothrix fusca and Nostoc muscorum. J. Union Arab Boil. Cairo, 7: 421–441.
El-Sheekl, M. M., M. E. El-Naggar, M. E. H. Osman, and E. El-Mazaly, 2003. Effect of Cobalt on growth, pigments and the photosynthetic electron transport in Monoraphdium minutum and Nitzchia perminuta. Braz. J. Plant Physiol., 15(3): 159–166.
Fargasova, A., 1999. The green alga Scenedesmus quadricauda — a subject for the study of inhibitory effects of Cd, Cu, Zn, Pb and Fe. Biologia, 54: 393–398.
Fathi, A. A., F. T. Zaki, and A. A. Fathy, 2000. Bioaccumulation of some heavy metals and their influence on the metabolism of Scenedesmus bijuga and Anabaena spiroides. Egypt. J. Biotech., 7: 293–307.
Ferraz, A. I., T. Tavares, and J. A. Teixeira, 2004. Cr (III) removal and recovery from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Eng. J., 105: 11–20.
Franklin, N. M., M. S. Adams, J. L. Stauber, and R. P. Lim, 2001. Development of a rapid enzyme inhibition bioassay with marine and freshwater microalgae using flowcytometry. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 40: 469–480.
Franklin, N. M., J. L. Stauber, S. J. Markich, and R. P. Lim, 2000. pH-dependent toxicity of copper and uranium to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.). Aquat. Toxicol., 48: 275–289.
Gaur, J. P., and L. C. Rai, 2001. Heavy metal tolerance in algae. In: Algal Adaptation to Environmental Stresses: Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms. Rai L. C., and Gaur J. P., eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 363–388.
Gharieb, M. M., and G. M. Gadd, 2004. Role of glutathione in detoxification of metal (loid)s by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BioMetals, 17: 183–188.
Goyal, N., S. C. Jain, and U.C. Banerjee, 2003. Comparative studies on the microbial adsorption of heavy metals. Adv. Environ. Res., 7: 311–319.
Hassler, C. S., and K. J. Wilkinson, 2003. Failure of the biotic ligand and freeion activity models to explain zinc bioaccumulation by Chlorella kesslerii. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 22: 620–626.
Heng, L.Y., K. Jusoh, C. H. M. Ling, and M. Idris, 2004. Toxicity of single and combinations of lead and cadmium to the cyanobacteria Anabaena flos-aquae. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 72: 373–379.
Hu, S., K. W. K. Lau, and M. Wu, 2001. Cadmium sequestration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Sci., 161: 987–996.
Jordanova, A., A. Strezov, M. Ayranov, N. Petkov, and T. Stoilova, 1999. Heavy metal assessment in algae, sediments and water from the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Water Sci. Tech., 39: 207–212.
Kuroda, K., M. Ueda, S. Shibasaki, and A. Tanaka, 2002. Cell surface-engineered yeast with ability to bind, and self-aggregate in response to copper ion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech., 59: 259–264.
Lamaia, C., M. Kruatrachuea, P. Pokethitiyooka, E. S. Upathamb, and V. Soonthornsarathoola, 2005. Toxicity and accumulation of lead and cadmium in the filamentous green alga Cladophora fracta: A laboratory study. Sci. Asia, 31: 121–127.
Lasheen, M. R., 1990. Effect of cadmium, copper and chromium (VI) on the growth of nile algae. Water Air Soil Poll., 50: 19–30.
Leborans, G. F., and A. Novillo, 1996. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of cadmium in Olishodiscus luteus (Raphidophyceae). Water Res., 30: 57–62.
Liberton, M., R. Howard Berg, J. Heuser, R. Roth, and H. B. Pakrasi, 2006. Ultrastructure of the membrane systems in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Protoplasma, 227: 129–138.
Liu, R. X., H. X. Tang, and W. X. Lao, 2002. Advances in biosorption mechanism and equilibrium modeling for heavy metals on biomaterials. Prog. Chem., 14: 87–92 (in Chinese).
Ma, M., W. Zhu, Z. Wang, and G. J. Witkaamp, 2003. Accumulation, assimilation and growth inhibition of copper on freshwater alga (Scenedesmus subspicatus 86.81 SAG) in the presence of EDTA and fulvic acid. Aquat. Toxicol., 63: 221–228.
Macfarlane, G. R., and M. D. Burchett, 2001. Photosynthetic pigments and peroxidase activity as indicators of heavy metal stress in the greymangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 42: 233–240.
Mehta, S. K., and J. P. Gaur, 1999. Heavy-metal-induced proline accumulation and its role in ameliorating metal toxicity in Chlorella vulgaris. New Phytol., 143: 253–259.
Morlon, H., C. Fortin, C. Adam, and J. Garnier-Laplace, 2005. Cellular quotas and induced toxicity of selenite in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Radioprotection, 40: 101–106.
Okamoto, O. K., C. S. Asano, E. Aidar, and P. Colepicolo, 1996. Effects of cadmium on growth and superoxide dismutase activity of the marine microalga Tetraselmis gracilis. J. Phycol., 32: 74–79.
Pawlik-Skowrońska, B., 2002. Correlations between toxic Pb effects and production and production of Pb-induced thiol peptides in the microalga Stichococcus bacillaris. Environ. Pollut., 119: 119–127.
Pawlik-Skowrońska, B., and T. Skowroński, 2001. Freshwater algae. In: Metals in the Environment: Analysis by Biodiversity. Prasad M. N. V., ed., Marcel Dekker, New York, 59–94.
Pinto, E., T. C. S. Sigaud-Kutner, M. A. S. Leitaõ, O. K. Okamoto, and D. Morse, 2003. Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress in algae. J. Phycol., 39:1008–1018.
Rai, P. K., N. Mallick, and L. C. Rai, 1993. Physiological and biochemical studies on an acid-tolerant Chlorella vulgaris under copper stress. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 39: 529–540.
Rangsayatorn, N., E. S. Upatham, M. Kruatrachue, P. Pokethitiyook, and G.R. Lanza, 2002. Phytoremediation potential of Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis: Biosorption and toxicity studies of cadmium. Environ. Pollut., 119: 45–53.
Sies, H., 1999. Glutathione and its role in cellular functions. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 27: 916–921.
Siripornadulsil, S., S. Traina, S. D. Verma, and R. T. Sayre, 2002. Molecular mechanisms of proline-mediated tolerance to toxic heavy metals in transgenic microalgae. The Plant Cell, 14: 2837–2847.
Stauber, J. L., and C. M. Davies, 2000. Use and limitations of microbial bioassays for assessing copper bioavailability in the aquatic environment. Environ. Rev., 8: 255–301.
Stauber, J. L., and T. M. Florence, 1990. Mechanism of toxicity of zinc to the marine diatom Nitzschia closterium. Mar. Biol., 105: 519–524.
Tripathi, B. N., A. Singh, and J. P. Gaur, 2000. Impact of heavy metal pollution on algal assemblages. Envsciences, 9: 1–7.
Tripathi, B. N., and J. P. Gaur, 2006. Physiological behavior of Scenedesmus sp. during exposure to elevated levels of Cu and Zn and after withdrawal of metal stress. Protoplasma, 229: 1–9.
Van Ho, A., D. M. Ward, and J. Kaplan, 2002. Transition metal transport in yeast. Ann. Rev. Microbiol., 56: 237–261.
Verma, D. P. S., 1999. Osmotic stress tolerance in plants: Role of praline and sulfur metabolisms. In: Molecular Responses to Cold, Drought, Heat and Salt Stress in Higher Plants. Shinozaki K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., eds., R. G. Landers Company, Texas, 153–168.
Vijver, M. G., C. A. M. V. Gestel, R. P. Lanno, N. M. Van Straalen, and W. J. G. M. Peijnenburg, 2004. Internal metal sequestration and its ecotoxicological relevance: a review. Environ. Sci. Technol., 38: 4705–4712.
Wang, J. L., 2005. Microbial cell-surface display and the application in bioremediation of contaminated environment. Chin. Biotechnol., 25: 112–117 (in Chinese).
Wang, J., and C. Chen, 2006. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotech. Adv., 24: 427–451.
Wang, J. L., 2002. Microbial Immobilization Techniques and Water Pollution Control. Science Press, Beijing, 326pp (in Chinese).
Wilde, K. L., J. L. Stauber, S. J. Markich, N. M. Franklin, and P. L. Brown, 2006. The effect of pH on the uptake and toxicity of copper and zinc in a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.) Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 51: 174–185.
Wong, S. L., L. Nakamoto, and J. F. Wainwright, 1994. Identification of toxic metals in affected algal cells in assays of wastewaters. J. Appl. Phycol., 6: 405–414.
Zalups, R. K., and S. Ahmad, 2003. Molecular handling of cadmium in transporting epithelia. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 186: 163–188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arunakumara, K.K.I.U., Zhang, X. Heavy metal bioaccumulation and toxicity with special reference to microalgae. J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 60–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0060-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0060-y