Abstract
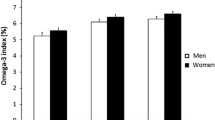
n−3 FA are beneficial for cardiovascular health, reducing platelet aggregation, TG levels, and the risk of sudden death from myocardial infarction. The percentage of EPA + DHA in red blood cells (RBC), also known as the Omega-3 Index, has recently been proposed as a risk marker for death from coronary heart disease (CHD). The purpose of this study was to begin to explore the factors that can influence RBC EPA + DHA. We collected information on the number of servings of tuna or nonfried fish consumed per month, as well as on age, gender, ethnicity, smoking status, the presence of diabetes, and body mass index (BMI) in 163 adults in Kansas City who were not taking fish oil supplements. The average RBC EPA + DHA in this population was 4.9±2.1%. On a multivariate analysis, four factors significantly and independently influenced the Omega-3 Index: fish servings, age, BMI, and diabetes. The Index increased by 0.24 units with each additional monthly serving of tuna or nonfried fish (P<0.0001), and by 0.5 units for each additional decade in age (P<0.0001). The Index was 1.13% units lower in subjects with diabetes (P=0.015) and decreased by 0.3% units with each 3-unit increase in BMI (P=0.001). Gender or smoking status had no effect, and the univariate relationship with ethnicity vanished after controlling for deathfrom CHD, further studies are warranted to delineate the nondietary factors that influence RBC EPA + DHA content.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- ANCOVA:
-
analysis of covariance
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CHD:
-
coronary heart disease
- RBC:
-
red blood cells
References
Kris-Etherton, P.M., Harris, W.S., and Appel, L.J. (2002) Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, n−3 Fatty Acids, and Cardiovascular Disease, Circulation 106, 2747–2757.
Knapp, H.R. (1997) Dietary Fatty Acids in Human Thrombosis and Hemostasis, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65 (Suppl.), 1687S-1698S.
Mori, T.A., Vandongen, R., Mahanian, F., and Douglas, A. (1992) Plasma Lipid Levels and Platelet and Neutrophil Function in Patients with Vascular Disease Following Fish Oil and Olive Oil Supplementation, Metabolism 41, 1059–1067.
Harris, W.S. (1997) n−3 Fatty Acids and Serum Lipoproteins: Human Studies, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65 (Suppl.), 1645S-1654S.
Christensen, J.H., Skou, H.A., Fog, L., Hansen, V.E., Vesterlund, T., Dyerberg, J., Toft, E., and Schmidt, E.B. (2001) Marine n−3 Fatty Acids, Wine Intake, and Heart Rate Variability in Patients Referred for Coronary Angiography, Circulation 103, 651–657.
Huikuri, H.V., Castellanos, A., and Myerberg, R.J. (2001) Sudden Death Due to Cardiac Arrhythmias, N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 1473–1482.
GISSI-Prevenzione Investigators (1999) Dietary Supplementation with n−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Vitamin E in 11,324 Patients with Myocardial Infarction: Results of the GISSI-Prevenzione Trial, Lancet 354, 447–455.
Harris, W.S., and von Schacky, C. (2004) RBC EPA + DHA: A New Risk Factor for Sudden Cardiac Death? Prev. Med. 39, 212–220.
Harris, W.S., Sands, S.A., Windsor, S.L., Ali, H.A., Stevens, T.L., Magalski, A., Porter, C.B., and Borkon, A.M. (2004) n−3 Fatty Acids in Cardiac Biopsies from Heart Transplant Patients: Correlation with Erythrocytes and Response to Supplementation, Circulation 110, 1645–1649.
Siscovick, D.S., Raghunathan, T.E., King, I., Weinmann, S., Wicklund, K.G., Albright, J., Bovbjerg, V., Arbogast, P., Smith, H., Kushi, L.H., et al. (1995) Dietary Intake and Cell Membrane Levels of Long-Chain n−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Risk of Primary Cardiac Arrest, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 274, 1363–1367.
Albert, C.M., Campos, H., Stampfer, M.J., Ridker, P.M., Manson, J.E., Willett, W.C., and Ma, J. (2002) Blood Levels of Long-Chain n−3 Fatty Acids and the Risk of Sudden Death, N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1113–1118.
Palozza, P., Sgarlata, E., Luberto, C., Piccioni, E., Anti, M., Marra, G., Armelao, F., Franceschelli, P., and Bartoli, G.M. (1996) n−3 Fatty Acids Induce Oxidative Modifications in Human Erythrocytes Depending on Dose and Duration of Dietary Supplementation, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 64, 297–304.
Lund, E.K., Harvey, L.J., Ladha, S., Clark, D.C., and Johnson, I.T. (1999) Effects of Dietary Fish Oil Supplementation on the Phospholipid Composition and Fluidity of Cell Membranes from Human Volunteers, Ann. Nutr. Metab. 43, 290–300.
Berlin, E., Bhathena, S.J., Judd, J.T., Nair, P.P., Peters, R.C., Bhagavan, H.N., Ballard-Barbash, R., and Taylor, P.R. (1992) Effects of n−3 Fatty Acid and Vitamin E Supplementation on Erythrocyte Membrane Fluidity, Tocopherols, Insulin Binding, and Lipid Composition in Adult Men, J. Nutr. Biochem. 3, 392–400.
Francois, C.A., Connor, S.L., Bolewicz, L.C., and Connor, W.E. (2003) Supplementing Lactating Women with Flaxseed Oil Does Not Increase Docosahexaenoic Acid in Their Milk, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 77, 226–233.
Mills, D.E., Murthy, M., and Galey, W.R. (1995) Dietary Fatty Acids, Membrane Transport, and Oxidative Sensitivity in Human Erythrocytes, Lipids 30, 657–663.
Kamada, T., Yamashita, T., Baba, Y., Kai, M., Setoyama, S., Chuman, Y., and Otsuji, S. (1986) Dietary Sardine Oil Increases Erythrocyte Membrane Fluidity in Diabetic Patients, Diabetes 35, 604–611.
Flaten, H., Hostmark, A.T., Kierulf, P., Lystad, E., Trygg, K., Bjerkedal, T., and Osland, A. (1990) Fish-Oil Concentrate: Effects on Variables Related to Cardiovascular Disease, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 300–306.
Mozaffarian, D., Lemaitre, R.N., Kuller, L.H., Burke, G.L., Tracy, R.P., and Siscovick, D.S. (2003) Cardiac Benefits of Fish Consumption May Depend on the Type of Fish Meal Consumed: The Cardiovascular Health Study, Circulation 107, 1372–1377.
Gudbjarnason, S. (1989) Dynamics of n−3 and n−6 Fatty Acids in Phospholipids of Heart Muscle, J. Intern. Med. 225 (Suppl. 1), 117–128.
Dewailly, E., Blanchet, C., Gingras, S., Lemieux, S., Sauve, L., Bergeron, J., and Holub, B.J. (2001) Relations Between n−3 Fatty Acids Status and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Among Quebecers, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 74, 603–611.
Dewailly, E., Blanchet, C., Lemieux, S., Sauve, L., Gingras, S., Ayotte, P., and Holub, B.J. (2001) n−3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Among the Inuit of Nunavik, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 74, 464–473.
Dewailly, E., Blanchet, C., Gingras, S., Lemieux, S., and Holub, B.J. (2002) Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and n−3 Fatty Acid Status in the Adult Population of James Bay Cree, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 76, 85–92.
Cazzola, R., Rondanelli, M., Russo-Volpe, S., Ferrari, E., and Cestaro, B. (2004) Decreased Membrane Fluidity and Altered Susceptibility to Peroxidation and Lipid Composition in Overweight and Obese Female Erythrocytes, J. Lipid Res. 45, 1846–1851.
Burdge, G.C., and Wootton, S.A. (2002) Conversion of α-Linolenic Acid to Eicosapentaenoic, Docosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids in Young Women, Br. J. Nutr. 88, 411–420.
Kuriki, K., Nagaya, T., Tokudome, Y., Imaeda, N., Fujiwara, N., Sato, J., Goto, C., Ikeda, M., Maki, S., Tajima, K., and Tokudrme, S. (2003) Plasma Concentrations of (n−3) Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids Are Good Biomarkers of Relative Dietary Fatty Acid Intakes: A Cross-Sectional Study, J. Nutr. 133, 3643–3650.
Hibbeln, J.R., Makino, K.K., Martin, C.E., Dickerson, F., Boronow, J., and Fenton, W.S. (2003) Smoking, Gender, and Dietary Influences on Erythrocyte Essential Fatty Acid Composition Among Patients with Schizophrenia or Schizoaffective Disorder, Biol. Psychiatry 53, 431–441.
Giltay, E.J., Gooren, L.J., Toorians, A.W., Katan, M.B., and Zock, P.L. (2004) Docosahexaenoic Acid Concentrations Are Higher in Women Than in Men Because of Estrogenic Effects, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 80, 1167–1174.
Simon, J.A., Fong, J., Bernert, J.T., Jr., and Browner, W.S. (1996) Relation of Smoking and Alcohol Consumption to Serum Fatty Acids, Am. J. Epidemiol. 144, 325–334.
Seigneur, M., Freyburger, G., Gin, H., Claverie, M., Lardeau, D., Lacape, G., LeMoigne, F., Crockett, R., and Boisseau, M.R. (1994) Serum Fatty Acid Profiles in Type I and Type II Diabetes: Metabolic Alterations of Fatty Acids of the Main Serum Lipids, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 23, 169–177.
Pelikanova, T., Kohout, M., Valek, J., Base, J., and Stefka, Z. (1991) Fatty Acid Composition of Serum Lipids and Erythrocyte Membranes in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) Diabetic Men, Metabolism 40, 175–180.
Clore, J.N., Allred, J., White, D., Li, J., and Stillman, J. (2002) The Role of Plasma Fatty Acid Composition in Endogenous Glucose Production in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolism 51, 1471–1477.
Brenner, R.R. (2003) Hormonal Modulation of Δ6 and Δ5 Desaturases: Case of Diabetes, Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 68, 151–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sands, S.A., Reid, K.J., Windsor, S.L. et al. The impact of age, body mass index, and fish intake on the EPA and DHA content of human erythrocytes. Lipids 40, 343–347 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-006-1392-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-006-1392-2