Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of moxibustion pretreatment on Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-Px), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Malondialchehyche (MDA) in gastric mucosa of rats with stress ulcer, and to investigate the mechanism of moxibustion pretreatment preventing the oxidized injury of gastric mucosa.
Methods
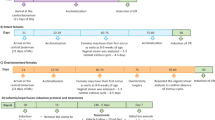
Forty-eight healthy SD rats were randomly allocated into 4 groups, namely control group, model group, acupoint moxibustion group, and non-acupoint moxibustion group. The ulcer model was developed by restraint and water immersion stress, Ulcer index (UI) was calculated with Guth method, and the contents of GSH-Px, and MDA and SOD activity in the gastric tissues were measured with chromatometry method.
Results
Compared those in the model group and nonacupoint moxibustion group, moxibustion at Zusanli (ST 36) could decrease the UI (P<0.01) and MDA (P<0.05) contents, and increase the activity of GSH-Px (P<0.01) and SOD (P<0.05).
Conclusion
Pretreatment of moxibustion at Zusanli (ST 36) could promote the recovery of gastric injury in rats induced by restraint and water immersion stress by enhancing the activity of GSH-Px and SOD, and lower MDA content.
摘要
目的
观察艾灸预处理对应激性溃疡大鼠胃黏膜谷胱甘肽过氧化酶(Glutathione Peroxidase, GSH-Px)、 超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase, SOD)的活性与丙二醛(Malondialchehyche, MDA)的影响, 探讨艾灸预处理抗胃黏膜氧化损伤的作用机制。
方法
将48 只健康SD 大鼠随机分为4 组, 即空白组、 模型组、 艾灸穴位组、 艾灸非穴点对照组。 束缚冷应激法制作应激性溃疡模型, 按Guth法计算胃黏膜损伤指数(Ulcer Index, UI), 比色法测定胃组织GSH-Px、 SOD的活性与MDA的含量。
结果
与模型组和艾灸非穴点对照组比较, 艾灸足三里等穴可使应激性溃疡大鼠胃黏膜损伤指数明显下降(P<0.01)、 GSH-Px 活性增强(P<0.01)、 SOD活性增强(P<0.05)、 MDA含量降低(P<0.05)。
结论
艾灸足三里等穴预处理可促进束缚水浸应激所造成大鼠胃黏膜损伤的修复, 可能是通过增加GSH-Px与SOD活性、 降低MDA含量 而达到其抗氧化损伤作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang XR, Peng N, Yi SX, Peng Y, Yan J. Moxibustion at Zusanli and Liangmen prevents gastric mucosa from oxidation injury through inducing high expression of heat shock protein 70. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 2006, 14(35): 3405–3408.
Wang TY, Zhu YQ, Yang ZX. Effect of oxygen free radical and apoptosis on stress ulcer in rats. Zhong Hua Xian Dai Nei Ke Xue Za Zhi, 2005, 2(6): 492–493.
Yi SX, Peng Y, Chang XR, Peng N, Yan J, Lin YP. Effect of moxibustion at Zusanli and Liangmen point on gastric mucosal cell apoptosis in rats with stress ulcer. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 2006, 14(33): 3163–3168.
Yi SX, Peng Y, Chang XR, Peng N, Yan J, Lin YP. Effects of moxibustion on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric mucosal cells and their relationship with heat shock protein expression in stress gastric ulcer rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2006, 31(5): 259–236.
Rokutan K. Role of heat shock proteins in gastric mucosal protection J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2000, 15(Suppl): D12–D19.
Guth PH, Aures D, Paulsen G. Topical aspirin plus HCl gastric lesions in the rat. Cytoprotective effect of prostaglandin, cimetidine, and probanthine. Gastroenterology, 1979, 76: 88–93.
Kwiecien S, Brzozowsri T, Konturek SJ. Effects of reactive oxygen species action on gastric mucosa in various models of mucosal injury. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2002, 53(1): 39–50.
Tang J. Observation of Serumal LPO content and activity of SOD and GSH-Px in patients with peptic ulcer. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 2000, 8(4): 487–488.
Li YD, Zhou YC, Wang XY. Research progress of acupuncture on peroxidation. Zhen Jiu Lin Chuang Za Zhi, 2004, 20(1): 47–48.
Li L, Gai QW, Yao L, Dou BY. Experimental study on the mechanism of electroacupuncture preventing acute gastric mucosal lesion in rats. Shang Hai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi, 2004, 23(12): 36–38.
Yi SX, Yu J, Chang XR, Peng Y, Wu HG, Yan J, Yang RD. Effect of moxibustion on expression of hsp70 and apoptosis-related factors in rats with acute gastric mucosal damage. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2010, 8(1): 5–11.
Du Y, Yi SX, Lin YP, Hong JB, Peng H, Huang Y, Chang XR, Wu HG. Effect of moxibustion on heat shock protein and related inflammatory cells in rats with acute gastric mucosal injury. Shang Hai Zhen Jiu Za Zhi, 2010, 29(5): 269–272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fund Items: National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2009CB522904); National Natural Science Foundation of China (30973802); Key Project of the Hu’nan Department of Education (08A048); Hu’nan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduates (CX2009B172)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Chang, X., Yan, J. et al. Effects of moxibustion pretreatment on GSH-Px, SOD and MDA in gastric mucosa of rats with stress ulcer. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 9, 17–20 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-011-0461-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-011-0461-0