Abstract
Objectives
Endoscopy is a minimally invasive technique for the drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections. This study evaluated the clinical outcomes and predictors of treatment success in consecutive patients undergoing endoscopic transmural drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of patients who underwent endoscopic drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections over 7 years. Prior to drainage, an ERCP was attempted for stent placement in all patients with a pancreatic duct leak. Drainages were performed using conventional endoscopy or endoscopic ultrasound. Transmural stents and/or drainage catheters were deployed and endoscopic necrosectomy was undertaken when required. Data on clinical outcomes and complications were collected prospectively.
Results
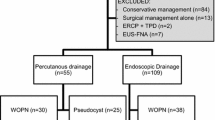
A total of 211 patients underwent drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections that was classified as pseudocyst in 45%, abscess in 28%, and necrosis in 27%. Mean diameter of the fluid collection was 100.6 mm, and 34.5% of patients had pancreatic duct stent placement. Median duration of follow-up was 356 days. Treatment success was 85.3% and was higher for pseudocyst and abscess compared to necrosis (93.5% vs. 63.2%, p < 0.0001). Complications were encountered in 17 patients (8.5%) and was higher for drainage of necrosis than pseudocyst or abscess (15.8% vs. 5.2%, p = 0.02). Treatment success was more likely for patients with pseudocyst or abscess than necrosis (adjusted OR = 7.6, 95% CI [2.9, 20.1], p < 0.0001) when adjusted for serum albumin and white cell count, type of endoscopic modality or accessory used, pancreatic duct stenting, luminal compression, size and location of fluid collection.
Conclusions
Endoscopic therapy is a highly effective technique for the management of patients with non-necrotic peripancreatic fluid collections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollen TL, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, van Leeuwen MS, Horvath KD, Freeny PC, Gooszen HG; Dutch Acute Pancreatitis Study Group. The Atlanta Classification of acute pancreatitis revisited. Brit J Surg 2008; 95: 6–21.
Hookey LC, Debroux S, Delhaye M, Arvanitakis M, Le Moine O, Devière J. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic-fluid collections in 116 patients: a comparison of etiologies, drainage techniques, and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63: 635–43.
Seewald S, Ang TL, Teng KCYK, Soehendra N. EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts, abscesses and infected necrosis. Digest Endosc 2009; 21 (Suppl. 1): S61-S65.
Smits ME, Rauws EAJ, Tytgat GNJ, Huibregtse K. The efficacy of endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 42: 202–7.
Sahel J, Bastid C, Pellat B, Schurgers P, Sarles H. Endoscopic cystoduodenostomy of cysts of chronic calcifying pancreatitis: a report of 20 cases. Pancreas 1987; 2: 447–53.
Cremer M, Deviere J, Engelholm L. Endoscopic management of cysts and pseudocysts in chronic pancreatitis: long-term follow-up after 7 years of experience. Gastrointest Endosc 1989; 35:1–9.
Ahn JY, Seo DW, Eum J Song TJ, Moon SH, Park do H, Lee SS, Lee SK, Kim MH. Single-step EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: analysis of technical feasibility, efficacy, and safety. Gut Liver 2010; 4: 524–529.
Lopes CV, Pesenti C, Bories E, Caillol F, Giovannini M. Endoscopic-ultrasound-guided endoscopic transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts and abscesses. Scand J Gastroentero 2007; 42: 524–529
Kruger M, Schneider AS, Manns MP, Meier PN. Endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocysts or abscesses after an EUS-guided 1-step procedure for initial access. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63: 409–16.
Antillon MR, Shah RJ, Stiegmann G, Chen YK. Single-step EUS-guided transmural drainage of simple and complicated pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63: 797–803.
Varadarajulu S, Tamhane A and Blakely J. Graded dilation technique for EUS-guided drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections: an assessment of outcomes and complications and technical proficiency (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68: 656–66.
Baron TH, Harewood GC, Morgan DE, Yates MR. Outcome differences after endoscopic drainage of pancreatic necrosis, acute pancreatic pseudocysts, and chronic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc 2002; 56: 7–17.
Weckman L, Kylänpää M-L, Puolakkainen P, Halttunen J. Endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc 2006; 20: 603–607.
Cahen D, Rauws E, Fockens P, Weverling G, Huibregtse K, Bruno M. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: Long-term outcome and procedural factors associated with safe and successful treatment. Endoscopy 2005; 37(10): 977–983.
Binmoeller KF, Seifert H, Walter A, Soehendra N. Transpapillary and transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 42: 219–24.
Sharma SS, Bhargawa N and Govil A. Endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocyst: A long-term follow-up. Endoscopy 2002; 34: 203–207.
Beckingham IJ, Krige JEJ, Bornman PC, Terblanche J. Long term outcome of endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94: 71–74.
Varadarajulu S, Trevino J, Wilcox CM, Sutton B, Christein JD. Randomized trial comparing EUS and surgery for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage. Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 71: AB 116.
Varadarajulu S, Lopes TL, Wilcox CM, Drelichman ER, Kilgore ML, Christein JD. EUS versus surgical cyst-gastrostomy for management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68:649–55.
Bradley EL III. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the international symposium on acute pancreatitis, Atlanta, GA, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg 1993; 128 (5): 586–90.
van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, Hofker HS, Boermeester MA, Dejong CH, van Goor H, Schaapherder AF, van Eijck CH, Bollen TL, van Ramshorst B, Nieuwenhuijs VB, Timmer R, Laméris JS, Kruyt PM, Manusama ER, van der Harst E, van der Schelling GP, Karsten T, Hesselink EJ, van Laarhoven CJ, Rosman C, Bosscha K, de Wit RJ, Houdijk AP, van Leeuwen MS, Buskens E, Gooszen HG; Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group. A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1491–1502.
Seifert H, Biermer M, Schmitt W, Jürgensen C, Will U, Gerlach R, Kreitmair C, Meining A, Wehrmann T, Rösch T. Transluminal endoscopic necrosectomy after acute pancreatitis: a multicentre study with long-term follow-up (the GEPARD Study). Gut 2009; 1260–1266.
Ross A, Gluck M, Irani S, Hauptmann E, Fotoohi M, Siegal J, Robinson D, Crane R, Kozarek R. Combined endoscopic and percutaneous drainage of organized pancreatic necrosis. Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 71: 79–84.
Adams DB, Harvey TS and Anderson MC. Percutaneous catheter drainage of infected pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections. Arch Surg 1990; 125: 1554–7.
Nealon WH, Bhutani M, Riall TS, Raju G, Ozkan O, Neilan R. A unifying concept: pancreatic ductal anatomy both predicts and determines the major complications resulting from pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg 2009; 208: 790–9.
Arvanitakis M, Delhaye M, Bali MA Matos C, De Maertelaer V, Le Moine O, Devière J. Pancreatic-fluid collections: a randomized controlled trial regarding stent removal after endoscopic transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 65: 609–19.
Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Tamhane A, Drelichman ER, Wilcox CM. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 68: 1102–11.
Varadarajulu S. EUS followed by endoscopic pancreatic pseudocyst drainage or all-in-one procedure: a review of basic techniques (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2009; 69 (2 Suppl): S176-81.
Varadarajulu S, Eloubeidi MA, Wilcox CM. The concept of bedside EUS. Gastrointest Endosc 2008; 67: 1180–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varadarajulu, S., Bang, J.Y., Phadnis, M.A. et al. Endoscopic Transmural Drainage of Peripancreatic Fluid Collections: Outcomes and Predictors of Treatment Success in 211 Consecutive Patients. J Gastrointest Surg 15, 2080–2088 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1621-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1621-8