Abstract
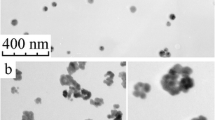
We report a morphology-correlated surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) from molecules on the surface of individual clusters of gold nanoparticles of two types and compare the signal from clusters of two, three, four, and five nanoparticles with the signal from single particles. Cluster geometry and particle morphology are determined from transmission electron microscopy for both clusters of 78- to 133-nm nanospheres and clusters of ~250-nm-etched cylindrical particles with crevices and sharp edges, formed in templates. Scattering from molecules on etched cylinders, but not spheres, is sufficiently strong to allow spectra to be collected from single particles illuminated at 632.8 nm. SERS intensities from clusters of cylinders are found to scale linearly with particle number, whereas, for nanospheres, the scaling is non-linear. The linear scaling of SERS from cylinders is a reflection of the high enhancement provided by the sharp features of the individual particles; whereas, the non-linear scaling of SERS from clusters of spheres is found to be consistent with the near-field enhancement from inter-particle coupling simulated for clusters of spheres arranged in representative-observed geometries.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleischm M, Hendra PJ, McQuilla AJ (1974) Raman-spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem Phys Lett 26(2):163–166
Jeanmaire DL, Vanduyne RP (1977) Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry 1. Heterocyclic, aromatic and aliphatic-amines adsorbed on anodized silver electrode. J Electroanal Chem 84(1):1–20
Moskovits M (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a brief retrospective. J Raman Spectrosc 36(6–7):485–496
Vo-Dinh T (1998) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy using metallic nanostructures. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 17(8–9):557–582
Gunnarsson L et al (2001) Interparticle coupling effects in nanofabricated substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Appl Phys Lett 78(6):802–804
Dick LA et al (2002) Metal film over nanosphere (MFON) electrodes for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): improvements in surface nanostructure stability and suppression of irreversible loss. J Phys Chem B 106(4):853–860
Lin HH et al (2004) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from silver-plated porous silicon. J Phys Chem B 108(31):11654–11659
Futamata M, Maruyama Y, Ishikawa M (2002) Microscopic morphology and SERS activity of Ag colloidal particles. Elsevier, New York
Kneipp K et al (2002) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering and biophysics. J Phys Condens Matter 14(18):R597–R624
Schwartzberg AM et al (2004) Unique gold nanoparticle aggregates as a highly active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate. J Phys Chem B 108(50):19191–19197
Futamata M, Maruyama Y, Ishikawa M (2005) Critical importance of the junction in touching Ag particles for single molecule sensitivity in SERS. J Mol Struct 735:75–84
Imura K et al (2006) Visualization of localized intense optical fields in single gold-nanoparticle assemblies and ultrasensitive Raman active sites. Nano Lett 6(10):2173–2176
Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Kneipp J (2006) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering in local optical fields of silver and gold nanoaggregatess—from single-molecule Raman spectroscopy to ultrasensitive probing in live cells. Acc Chem Res 39(7):443–450
Svedberg F et al (2006) Creating hot nanoparticle pairs for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy through optical manipulation. Nano Lett 6(12):2639–2641
Sztainbuch IW (2006) The effects of Au aggregate morphology on surface-enhanced Raman scattering enhancement. J Chem Phys 125(12):12
Zhao LL, Jensen L, Schatz GC (2006) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of pyrazine at the junction between two Ag-20 nanoclusters. Nano Lett 6(6):1229–1234
Talley CE et al (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from individual Au nanoparticles and nanoparticle dimer substrates. Nano Lett 5(8):1569–1574
McLellan JM et al (2007) The SERS activity of a supported ag nanocube strongly depends on its orientation relative to laser polarization. Nano Lett 7(4):1013–1017
Wiley BJ et al (2007) Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanobars and nanorice. Nano Lett 7(4):1032–1036
Xu HX et al (2000) Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Physical Review E 62(3):4318–4324
Hao E, Schatz GC (2004) Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J Chem Phys 120(1):357–366
Kneipp K, Moskovits M, Kneipp H (2006) Surface-enhanced raman scattering: physics and applications. Springer, Berlin; New York
Markel VA et al (2004) Electromagnetic density of states and absorption of radiation by aggregates of nanospheres with multipole interactions. Physical Review B 70(5):19
Kerker M, Wang DS, Chew H (1980) Surface enhanced Raman-scattering (SERS) by molecules adsorbed at spherical particles. Appl Opt 19(24):4159–4174
Shalaev VM, Sarychev AK (1998) Nonlinear optics of random metal-dielectric films. Physical Review B 57(20):13265–13288
Tsai DP et al (1994) Photon scannning tunneling microscopy images of optical excitations of fractal metal colloid clusters. Phys Rev Lett 72(26):4149–4152
Mulvaney SP et al (2003) Glass-coated, analyte-tagged nanoparticles: a new tagging system based on detection with surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 19(11):4784–4790
Reiss BD et al (2002) Electrochemical synthesis and optical readout of striped metal rods with submicron features. J Electroanal Chem 522(1):95–103
Krug JT et al (1999) Efficient Raman enhancement and intermittent light emission observed in single gold nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 121(39):9208–9214
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of noble metals. Physical Review B 6(12):4370–4379
Jain PK, Huang WY, El-Sayed MA (2007) On the universal scaling behavior of the distance decay of plasmon coupling in metal nanoparticle pairs: a plasmon ruler equation. Nano Lett 7(7):2080–2088
Ross BM, Lee LP (2009) Comparison of near- and far-field measures for plasmon resonance of metallic nanoparticles. Opt Lett 34(7):896–898
Shegai T et al (2008) Managing light polarization via plasmon-molecule interactions within an asymmetric metal nanoparticle trimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(43):16448–16453
Acknowledgment
A.A.L. acknowledges support of the NSF through grant DMR-0706397; DRS and S.N. acknowledge support of the ASAF/AFRL through grant FA9550-05-C-0098.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mock, J.J., Norton, S.M., Chen, SY. et al. Electromagnetic Enhancement Effect Caused by Aggregation on SERS-Active Gold Nanoparticles. Plasmonics 6, 113–124 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9176-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9176-1