Abstract
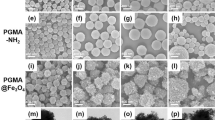
Micron-sized, monodisperse, superparamagnetic, luminescent composite poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) microspheres with functional amino-groups were successfully synthesized in this study. The process of preparation was as follows: preparation of monodisperse poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres by dispersion polymerization method; modification of poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres with ethylene diamine to form amino-groups; impregnation of iron ions (Fe2+ and Fe3+) inside the microspheres and subsequently precipitating them with ammonium hydroxide to form magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles within the polymer microspheres; infusion of CdSe/CdS core-shell quantum dots (QDs) into magnetic polymer microspheres. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to characterize surface morphology and size distribution of composite microspheres. The average size of microspheres was 1.42 μm with a size variation of 3.8%. The composite microspheres were bright enough and easily observed using a conventional fluorescence microscope. The composite microspheres were easily separated from solution by magnetic decantation using a permanent magnet. The new multifunctional composite microspheres are promising to be used in a variety of bioanalytical assays involving luminescence detection and magnetic separation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang D, He J, Rosenzweig N, et al. Superparamagnetic Fe2O3 beads-CdSe/ZnS quantum dots core-shell nanocomposite particles for cell separation. Nano Letters, 2004, 4: 409–413
Xie H, Zuo C, Liu Y, et al. Cell-targeting multifunctional nanospheres with both fluorescence and magnetism. Small, 2005, 1: 506–509
Gaponik N, Radtchenko I L, Sukhorukov G B, et al. Luminescent polymer microcapsules addressable by a magnetic field. Langmuir, 2004, 20: 1449–1452
Tan W B, Zhang Y. Multifunctional quantum-dot-based magnetic chiosan nanobeads. Adv Mater, 2005, 17: 2375–2380
Mulvaney S P, Mattoussi H, Whitman L J. Incorporating fluorescent dyes and quantum dots into magnetic microbeads for immunoassays. Biotechniques, 2004, 36: 602–609
Salgueiriño-Maceira V, Correa-Duarte M A, Spasova M, et al. Composite silica spheres with magnetic and luminescent. Adv Funct Mater, 2006, 16: 509–514
Hong X, Li J, Wang M, et al. Fabrication of magnetic luminescent nanocomposites by a layer-by-layer self-assembly approach. Chem Mater, 2004, 16: 4022–4027
Gu H, Zheng R, Zhang X, et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of bifunctional heterodimers of nanoparticles: A conjugate of quantum dot and magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126: 5664–5665
You X, He R, Gao F, et al. Hydrophilic high-luminescent magnetic nanocomposites. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18: 035701
Guo J, Yang W, Wang C, et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-coated luminescent-magnetic silica microspheres preparation, characterization, and biomedical applications. Chem Mater, 2006, 18: 5554–5562
Müller-Schulte D, Schmitz-Rode T, Borm P. Ultra-fast synthesis of magnetic and luminescent silica beads for versatile bioanalytical applications. J Magnet Magnet Mater, 2005, 293: 135–143
Selvan S T, Patra P K, Ang C Y, et al. Synthesis of silica-coated semiconductor and magnetic quantum dots and their use in the imaging of live cells. Angew Chem, 2007, 119: 2500–2504
Peng Z A, Peng X. Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor. J Am Chem Soc, 2001, 123: 183–184
Han M, Gao X, Su J Z, et al. Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules. Nat Biotechnol, 2001, 19: 631–635
Kalal J, Švec F, Maroušek V. Reacions of epoxide groups of glycidyl methacrylate copolymers. J Polym Sci: Polymer Symposia, 1974, 47: 155–166
Horák D. Magnetic polyglycidylmethacrylate microspheres by dispersion polymerization. J Polym Sci A: Polym Chem, 2001, 39: 3707–3715
Lee Y, Rho J, Jung B. Preparation of magnetic ion-exchange resins by the suspension polymerization of styrene with magnetite. J Appl Polym Sci, 2003, 89: 2058–2067
Liu X, Guan Y, Ma Z, et al. Surface modification and characterization of magnetic polymer nanospheres prepared by miniemulsion polymerization. Langmuir, 2004, 20: 10278–10282
Xie G, Zhang Q, Luo Z, et al. Preparation of magnetic P(St/BA/MAA) microspheres. Chin Polym Bull (in Chinese), 2002, 3: 314–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50373033)
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhang, Q., Zhang, B. et al. Preparation of monodisperse, superparamagnetic, luminescent, and multifunctional PGMA microspheres with amino-groups. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 1165–1170 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0512-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0512-6