Abstract
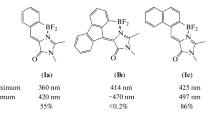
New analogues of green fluorescent protein (GFP) chromophore m GFP-C n (n = 1, 3, 5, 11) with alkyl chains of different lengths in the imidazolinone rings were synthesized and their crystal structures were determined. These GFP-like chromophores are all emissive in the solid state. And the solid-state emission quantum yields of increase by extending the lengths of alkyl chains, owing to the fact that the intermolecular pi-pi interactions are significantly weakened based on their crystal structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zimmer M. Green fluorescent protein (GFP): Applications, structure, and related photophysical behavior. Chem Rev, 2002, 102: 759–781
Chalfie M, Kain SR. Green fluorescent protein: Properties, applications, and protocols, 2nd ed. Wiley-Intersciences: NJ, 2005
Niwa H, Ionuye S, Horano T, Matsuno T, Kojima S, Kubota M, Ohashi M, Tsuji FI. Chemical nature of the light emitter of the Aequorea green fluorescent protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93: 13617–13622
Litvinenko KL, Webber NM, Meech SR. Internal conversion in the chromophore of the green fluorescent protein: Temperature dependence and isoviscosity analysis. J Phys Chem A, 2003, 107: 2616–2623
Weber W, Helms V, McCammon JA, Langhoff PW. Shedding light on the dark and weakly fluorescent states of green fluorescent proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96: 6177–6182
Liu RSH. Photoisomerization by hula-twist: A fundamental supramolecular photochemical reaction. Acc Chem Res, 2001, 34: 555–565
Mandal D, Tahara T, Meech SR. Excited-state dynamics in the green fluorescent protein chromophore. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108: 1102–1108
Stavrov SS, Solntsev KM, Tolbert LM, Huppert D. Probing the decay coordinate of the green fluorescent protein: Arrest of cis-trans isomerization by the protein significantly narrows the fluorescence spectra. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 1540–1546
Dong J, Abulwerdi F, Baldridge A, Kowalik J, Solntsev KM, Tolbert LM. Isomerization in fluorescent protein chromophores involves addition/elimination. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 14096–14098
Litvinenko KL, Webber NM, Meech SR. Internal conversion in the chromophore of the green fluorescent crotein: Temperature dependence and isoviscosity analysis. J Phys Chem A, 2003, 107: 2616–2623
Mandal D, Tahara T, Meech SR. Excited-state dynamics in the green fluorescent protein chromophore. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108: 1102–1108
Usman A, Mohammed OF, Nibbering ETJ, Dong J, Solntsev KM, Tolbert LM. Excited-state structure determination of the green fluores cent protein chromophore. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127: 11214–11215
Solntsev KM, Poizat O, Dong J, Rehault J, Lou Y, Burda C, Tolbert LM. Meta and para effects in the ultrafast excited-state dynamics of the green fluorescent protein chromophores. J Phys Chem B, 2008, 112: 2700–2711
Wu LX, Burgess K. Syntheses of highly fluorescent GFP-chromophore analogues. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 4089–4096
Baranov MS, Lukyanov KA, Borissova AO, Shamir J, Kosenkov D, Slipchenko LV, Tolbert LM, Yampolsky IV, Solntsev KM. Conformationally locked chromophores as models of excited-state proton transfer in fluorescent proteins. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134: 6025–6032
Baldridge A, Solntsev KM, Song C, Tanioka T, Kowalik J, Hardcastle K, Tolbert LM. Inhibition of twisting of a green fluorescent protein-like chromophore by metal complexation. Chem Commun, 2010, (46): 5686–5688
Li Y, Shi L, Qin LX, Qu LL, Jing C, Lan MB, James TD, Long YT. An off-on fluorescent probe for Zn2+ based on a GFP-inspired imidazolone derivative attached to a 1,10-phenanthroline moiety. Chem Commun, 2011, (47): 4361–4363
Naumov P, Kowalik J, Solntsev KM, Baldridge A, Moon JS, Kranz C, Tolbert LM. Topochemistry and photomechanical effects in crystals of green fluorescent protein-like chromophores: Effects of hydrogen bonding and crystal packing. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 5845–5857
Tolbert LM, Baldridge A, Kowalik J, Solntsev KM. Collapse and recovery of green fluorescent protein chromophore emission through topological effects. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 171–181
Dong J, Solntsev KM, Tolbert LM. Activation and tuning of green fluorescent protein chromophore emission by alkyl substituent-mediated crystal packing. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 662–670
Huang GX, Zhang GX, Wu YS, Liao Q, Fu HB, Zhang DQ. Modification of GFP chromophore with large aromatic moieties: Photophysical study and solid-state emission. Asian J Org Chem, 2012, 1: 352–357
You YJ, He YK, Burrows PE, Forrest SR, Petasis NA, Thompson ME. Fluorophores related to the green fluorescent protein and their use in optoelectronic devices. Adv Mater, 2000, 12: 1678–1681
Liu Y, Tao XT, Wang FZ, Dang XN, Zou DC, Ren Y, Jiang MH. Aggregation-induced emissions of fluorenonearylamine derivatives: A new kind of materials for nondoped red organic light-emitting diodes. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112: 3975–3981
Hong Y, Lam JWY, Tang BZ. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem Commun, 2009, 4332–4353
Wang M, Zhang GX, Zhang DQ, Zhu DB, Tang BZ. Fluorescent bio/chemosensors based on silole and tetraphenylethene luminogens with aggregation-induced emission feature. J Mater Chem, 2010, 20: 1858–1867
Hong YH, Chen SJ, Leung CWT, Lam JWY, Liu JZ, Tseng NW, Kwok RTK, Yu Y, Wang ZK, Tang BZ. Fluorogenic Zn(II) and chromogenic Fe(II) sensors based on terpyridine-substituted tetraphenylethenes with aggregation-induced emission characteristics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2011, 3: 3411–3418
An BK, Kwon SK, Jung SD, Park SY. Enhanced emission and its switching in fluorescent organic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124, 14410–14415
An BK, Gierschner J, Park SY. -Conjugated cyanostilbene derivatives: a unique self-assembly motif for molecular nanostructures with enhanced emission and transport. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 544–554
Kumar NSS, Varghese S, Suresh CH, Rath NP, Das S. Correlation between solid-state photophysical properties and molecular packing in a series of indane-1,3-dione containing butadiene derivatives. J Phys Chem C, 2009, 113: 11927–11935
Varghese S, Das S. Role of molecular packing in determining solid-state optical properties of π-conjugated materials. J Phys Chem Lett, 2011, 2: 863–873
Zhang ZY, Xu B, Su JH, Shen LP, Xie YS, Tian H. Color-tunable solid-state emission of 2,2′-biindenyl-based fluorophores. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2011, 50: 11654–11657
Shi CX, Guo ZQ, Yan YL, Zhu SQ, Xie YS, Zhao YS, Zhu WH, Tian H. Self-assembly solid-state enhanced red emission of quinolinemalononitrile: Optical waveguides and stimuli response. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, 5: 192–198
Wang H, Yue BL, Xie ZQ, Gao BR, Xu YX, Liu LL, Sun HB, Ma Y G. Controlled transition dipole alignment of energy donor and energy acceptor molecules in doped organic crystals, and the effect on intermolecular Förster energy transfer. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2013, 15: 3527–3534
Gu XG, Yao JJ, Zhang GX, Yan YL, Zhang C, Peng Q, Liao Q, Wu YS, Xu ZZ, Zhao YS, Fu HB, Zhang DQ. Polymorphism-dependent emission for di(p-methoxylphenyl)dibenzofulvene and analogues: optical waveguide/amplified spontaneous emission behaviors. Adv Funct Mater, 2012, 22: 4862–4872
Zyryanov GV, Rudkevich DM. Encapsulated reagents for nitrosation. Org Lett, 2003, 5: 1253–1256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X., Huang, G., Li, K. et al. Tuning the solid-state emission of the analogous GFP chromophore by varying alkyl chains in the imidazolinone ring. Sci. China Chem. 56, 1197–1203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4913-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4913-x